
最新刊期
卷 30 , 期 12 , 2025
- “在文物领域,人工智能技术正推动着文物防护、保护、研究、管理与传播方式的变革,为文物行业应用发展与未来提供新方向。”
 摘要:Cultural relics embody the brilliance of civilization, preserve historical heritage, and uphold the national spirit, serving as vivid manifestations of the confidence and depth of Chinese cultural identity. These artifacts are not merely historical remnants; they are living testaments to a nation’s cultural consciousness and aesthetic achievements. In the Chinese context, such artifacts encompass a wide array of forms——ceramics, bronzes, calligraphy, painting, architecture, and intangible heritage such as folk music and traditional theater——which jointly form a rich, continuous narrative of human development and collective memory. Through their material and symbolic importance, these cultural elements reflect and reinforce a shared sense of belonging and historical continuity. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI), now empowering a broad spectrum of industries and becoming deeply integrated into everyday life, the field of cultural heritage is undergoing a fundamental transformation. This transformation is not only technical but also conceptual, redefining how we understand, protect, and interact with our cultural legacy. AI no longer functions solely as a tool for automation or computation; it now plays a central role in knowledge production, decision-making, and creative processes. These capacities are driving a paradigm shift in cultural heritage work——from reactive, static models to proactive, adaptive systems powered by data and learning. The cultural heritage sector, historically reliant on manual preservation, scholarly interpretation, and traditional dissemination methods, is currently being transformed by advanced algorithms, machine learning models, and intelligent data processing frameworks. The profound capabilities of AI——in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), data mining, semantic segmentation, and 3D reconstruction——are increasingly being leveraged to support the digitization, restoration, analysis, management, and public engagement of cultural heritage. These developments, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, are poised to reshape the entire lifecycle of cultural relics—from their initial discovery and documentation to their long-term preservation and dynamic presentation to the public. The key challenge that currently arises—and forms the central concern of this paper—is the effective, responsible, and innovative application of AI within the cultural heritage field. While the potential of AI is undeniable, its implementation must be carefully aligned with the values, sensitivities, and interdisciplinary nature of cultural preservation. In particular, the complex materiality, symbolic importance, and contextual uniqueness of cultural relics demand AI approaches that are interpretable, ethical, and inclusive of human expertise. Ethical considerations, such as bias in training data, the risks of over-reliance on automated interpretations, and the protection of indigenous knowledge systems, must be at the forefront of AI deployment in cultural domains. This paper explores five critical dimensions of AI applications in the cultural heritage sector: prevention, preservation, research, management, and utilization. The five aspects collectively form a holistic framework for understanding how AI technologies can support the sustained vitality and accessibility of cultural resources. In terms of prevention, AI can play a crucial role in developing early warning systems to identify environmental changes and potential threats to cultural relics. By integrating sensor networks with AI-driven monitoring tools, institutions can proactively detect fluctuations in humidity, temperature, light exposure, and other environmental factors that may contribute to material deterioration. Additionally, predictive models based on historical data can be employed to forecast risks and guide strategic conservation efforts. For instance, machine learning algorithms have been employed in several European museums to predict mold outbreaks in organic cultural relics based on microclimatic data, enabling timely interventions. In terms of preservation, AI contributes to digital restoration, 3D reconstruction, and non-invasive diagnostics. For example, deep learning models can help reconstruct missing parts of fragmented murals or manuscripts by learning visual patterns from intact sections. Additionally, hyperspectral imaging combined with AI analysis can uncover faded texts or underdrawings that are invisible to the human eye. These technologies not only extend the physical lifespan of cultural relics but also introduce innovative approaches to virtual preservation. Some institutions are already using AI in the reconstruction of historical architecture through photogrammetry and simulation of ancient environments for educational use. In the domain of research, AI notably enhances the capabilities of scholars to extract knowledge from vast, heterogeneous datasets. Natural language processing facilitates the digitization and analysis of ancient texts, while computer vision supports the classification of cultural relics based on style, origin, and function. Semantic knowledge graphs and AI-assisted databases promote cross-referencing across disciplines and collections, fostering highly integrated and interdisciplinary research outcomes. These tools are proving essential in digital humanities projects that aim to map large cultural corpora or trace stylistic influences across time and geography. The management of cultural heritage institutions and resources also benefits substantially from AI. Intelligent information systems can optimize inventory tracking, automate metadata tagging, and streamline exhibition logistics. Recommendation systems can be tailored to guide curatorial decisions and enhance user interaction. AI can also help balance conservation needs with public access by dynamically regulating visitor flow in sensitive exhibition areas. Moreover, the integration of blockchain with AI for provenance tracking is emerging as a promising area, enhancing the security and transparency of cultural relic records. In terms of utilization, AI is reshaping how cultural heritage is accessed and experienced—particularly in education, tourism, and public engagement. Virtual museums, intelligent chatbots, augmented reality (AR), and personalized content delivery are making cultural experiences highly interactive and accessible. AI-generated reconstructions and immersive simulations allow audiences to engage with history in immersive ways, expanding the reach of cultural heritage to new demographics and global audiences. Platforms such as Google Arts & Culture, along with various national museum initiatives, are increasingly leveraging AI for context-aware storytelling and multilingual access, making culture more inclusive and dynamic. Beyond practical applications, this paper also examines how traditional research methodologies are evolving in response to AI integration. The paper highlights the epistemological shifts occur as cultural interpretation moves from purely human-centered approaches to hybrid models that combine human expertise with computational inference. While AI presents powerful tools, it also raises critical questions about authenticity, authorship, and cultural sovereignty——especially when applied across diverse cultural contexts and communities. The co-construction of meaning between human curators and intelligent systems may enrich interpretations, but it also demands careful calibration of roles and responsibilities. Overall, the integration of AI into the field of cultural heritage presents an unprecedented opportunity and a profound responsibility. As we navigate this new landscape, balancing technological innovation and cultural sensitivity is essential, ensuring that AI serves as a tool for cultural empowerment, rather than erasure. This paper ultimately offers insights into the current landscape and future trajectory of AI in cultural heritage, advocating for collaborative, interdisciplinary efforts to harness the potential of AI while honoring the depth, diversity, and dignity of the world’s cultural legacies.关键词:cultural heritage;artificial intelligence (AI);deep learning;museums;cultural relic preservation305|524|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:Cultural relics embody the brilliance of civilization, preserve historical heritage, and uphold the national spirit, serving as vivid manifestations of the confidence and depth of Chinese cultural identity. These artifacts are not merely historical remnants; they are living testaments to a nation’s cultural consciousness and aesthetic achievements. In the Chinese context, such artifacts encompass a wide array of forms——ceramics, bronzes, calligraphy, painting, architecture, and intangible heritage such as folk music and traditional theater——which jointly form a rich, continuous narrative of human development and collective memory. Through their material and symbolic importance, these cultural elements reflect and reinforce a shared sense of belonging and historical continuity. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI), now empowering a broad spectrum of industries and becoming deeply integrated into everyday life, the field of cultural heritage is undergoing a fundamental transformation. This transformation is not only technical but also conceptual, redefining how we understand, protect, and interact with our cultural legacy. AI no longer functions solely as a tool for automation or computation; it now plays a central role in knowledge production, decision-making, and creative processes. These capacities are driving a paradigm shift in cultural heritage work——from reactive, static models to proactive, adaptive systems powered by data and learning. The cultural heritage sector, historically reliant on manual preservation, scholarly interpretation, and traditional dissemination methods, is currently being transformed by advanced algorithms, machine learning models, and intelligent data processing frameworks. The profound capabilities of AI——in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), data mining, semantic segmentation, and 3D reconstruction——are increasingly being leveraged to support the digitization, restoration, analysis, management, and public engagement of cultural heritage. These developments, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, are poised to reshape the entire lifecycle of cultural relics—from their initial discovery and documentation to their long-term preservation and dynamic presentation to the public. The key challenge that currently arises—and forms the central concern of this paper—is the effective, responsible, and innovative application of AI within the cultural heritage field. While the potential of AI is undeniable, its implementation must be carefully aligned with the values, sensitivities, and interdisciplinary nature of cultural preservation. In particular, the complex materiality, symbolic importance, and contextual uniqueness of cultural relics demand AI approaches that are interpretable, ethical, and inclusive of human expertise. Ethical considerations, such as bias in training data, the risks of over-reliance on automated interpretations, and the protection of indigenous knowledge systems, must be at the forefront of AI deployment in cultural domains. This paper explores five critical dimensions of AI applications in the cultural heritage sector: prevention, preservation, research, management, and utilization. The five aspects collectively form a holistic framework for understanding how AI technologies can support the sustained vitality and accessibility of cultural resources. In terms of prevention, AI can play a crucial role in developing early warning systems to identify environmental changes and potential threats to cultural relics. By integrating sensor networks with AI-driven monitoring tools, institutions can proactively detect fluctuations in humidity, temperature, light exposure, and other environmental factors that may contribute to material deterioration. Additionally, predictive models based on historical data can be employed to forecast risks and guide strategic conservation efforts. For instance, machine learning algorithms have been employed in several European museums to predict mold outbreaks in organic cultural relics based on microclimatic data, enabling timely interventions. In terms of preservation, AI contributes to digital restoration, 3D reconstruction, and non-invasive diagnostics. For example, deep learning models can help reconstruct missing parts of fragmented murals or manuscripts by learning visual patterns from intact sections. Additionally, hyperspectral imaging combined with AI analysis can uncover faded texts or underdrawings that are invisible to the human eye. These technologies not only extend the physical lifespan of cultural relics but also introduce innovative approaches to virtual preservation. Some institutions are already using AI in the reconstruction of historical architecture through photogrammetry and simulation of ancient environments for educational use. In the domain of research, AI notably enhances the capabilities of scholars to extract knowledge from vast, heterogeneous datasets. Natural language processing facilitates the digitization and analysis of ancient texts, while computer vision supports the classification of cultural relics based on style, origin, and function. Semantic knowledge graphs and AI-assisted databases promote cross-referencing across disciplines and collections, fostering highly integrated and interdisciplinary research outcomes. These tools are proving essential in digital humanities projects that aim to map large cultural corpora or trace stylistic influences across time and geography. The management of cultural heritage institutions and resources also benefits substantially from AI. Intelligent information systems can optimize inventory tracking, automate metadata tagging, and streamline exhibition logistics. Recommendation systems can be tailored to guide curatorial decisions and enhance user interaction. AI can also help balance conservation needs with public access by dynamically regulating visitor flow in sensitive exhibition areas. Moreover, the integration of blockchain with AI for provenance tracking is emerging as a promising area, enhancing the security and transparency of cultural relic records. In terms of utilization, AI is reshaping how cultural heritage is accessed and experienced—particularly in education, tourism, and public engagement. Virtual museums, intelligent chatbots, augmented reality (AR), and personalized content delivery are making cultural experiences highly interactive and accessible. AI-generated reconstructions and immersive simulations allow audiences to engage with history in immersive ways, expanding the reach of cultural heritage to new demographics and global audiences. Platforms such as Google Arts & Culture, along with various national museum initiatives, are increasingly leveraging AI for context-aware storytelling and multilingual access, making culture more inclusive and dynamic. Beyond practical applications, this paper also examines how traditional research methodologies are evolving in response to AI integration. The paper highlights the epistemological shifts occur as cultural interpretation moves from purely human-centered approaches to hybrid models that combine human expertise with computational inference. While AI presents powerful tools, it also raises critical questions about authenticity, authorship, and cultural sovereignty——especially when applied across diverse cultural contexts and communities. The co-construction of meaning between human curators and intelligent systems may enrich interpretations, but it also demands careful calibration of roles and responsibilities. Overall, the integration of AI into the field of cultural heritage presents an unprecedented opportunity and a profound responsibility. As we navigate this new landscape, balancing technological innovation and cultural sensitivity is essential, ensuring that AI serves as a tool for cultural empowerment, rather than erasure. This paper ultimately offers insights into the current landscape and future trajectory of AI in cultural heritage, advocating for collaborative, interdisciplinary efforts to harness the potential of AI while honoring the depth, diversity, and dignity of the world’s cultural legacies.关键词:cultural heritage;artificial intelligence (AI);deep learning;museums;cultural relic preservation305|524|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “卫星视频单目标跟踪技术在军事和民用领域具有重要应用,面临目标尺寸小、相似目标干扰等挑战。专家总结了典型跟踪方法,为该领域研究提供新方向。”
 摘要:In recent years, single-object tracking in satellite videos has gained substantial attention and plays a pivotal role in military and civilian domains. This tracking has found applications in urban-scale disaster relief, public security surveillance, and the monitoring of emergency events, among others. However, due to a combination of factors, such as small target size, interference from similar targets, motion blur, and complex backgrounds, single-object tracking in satellite videos presents numerous challenges. Aiming to promote further exploration in this domain by scholars domestically and internationally, this paper comprehensively reviews and critically analyzes the current state of the art in satellite video-based single-object tracking. Considering challenges and advantages, video satellites offer an expansive field of view. Targets such as vehicles typically occupy only a few to a dozen pixels in satellite videos, with limited distinguishing features or textures. Additionally, satellite videos contain many targets, and the distinguishability between the targets of interest and interfering objects is poor, presenting a high degree of similarity. Moreover, target blurring may occur due to their rapid target movement or satellite platform jitter. When the moving target is inconspicuous and background information overshadows target features, tracking failure is likely to occur. However, compared to ground-based or low-altitude videos, satellite video-based object tracking offers certain advantages. For example, external factors related to the target, such as the camera perspective, are relatively stable, aiding tracking algorithms in maintaining a consistent lock on the target. Most objects in satellite videos are rigid and rarely undergo substantial deformation during tracking. Additionally, the aspect ratios of targets remain approximately consistent across video frames, reducing the potential for algorithmic confusion. The motion of targets is typically straightforward, with trajectories generally following straight lines or smooth curves, enabling the prediction of target positions based on historical motion data. Regarding the development of tracking methods, this paper reviews the evolution of single-object tracking methods for satellite videos and highlights typical tracking paradigms, including generative-based approaches, correlation filter-based methods, and deep learning-based techniques. Deep learning-based tracking methods can be further classified into convolutional neural network (CNN)-based and Transformer-based methods. In contrast to the hand-crafted features employed in correlation filter-based methods, CNNs can extract more comprehensive and robust features, thereby enhancing target tracking performance. In recent years, an increasing number of scholars have applied CNNs to satellite video object tracking tasks. However, when processing high-resolution images, long time-series data, and complex backgrounds, which are common in satellite videos, CNNs exhibit certain limitations. Aiming to address these limitations, Transformers have been gradually introduced into satellite video object tracking. Transformers can capture global spatial information and long-term temporal dependencies, offering a promising alternative for improving tracking accuracy in complex scenarios. Regarding datasets and evaluation metrics, this study compiles existing single-object tracking datasets for satellite videos, along with commonly adopted performance evaluation metrics. Prominent datasets in this field include XDU-BDSTU, video satellite objects(VISO), SatSOT, and the oriented object tracking benchmark(OOTB). Among them, the VISO dataset is the largest in scale, comprising training and test subsets. The XDU-BDSTU dataset features images with a large swath width, making it suitable for long-term tracking tasks. The OOTB dataset provides annotations using rotated bounding boxes, which accurately represents the actual target geometry. The main performance evaluation metrics include precision, success rate, and frame rate, which collectively assess tracking methods in terms of tracking accuracy and speed. Aiming to evaluate the applicability of various tracking algorithms across different scenarios, this paper selects 18 algorithms for performance evaluation and analysis on a self-constructed test set. Experimental results highlight the critical roles of motion estimation, temporal information utilization, and background information exploitation in satellite video object tracking. Specifically, the correlation filter with motion estimation(CFME) algorithm leverages historical motion information of the target to enhance tracking performance, while the Trdimp algorithm incorporates temporal and background information, yielding favorable outcomes. When a vehicle makes a turn, the hand-crafted features employed by the correlation filter-based method CFME lack rotational invariance and are poorly equipped to handle changes in the target’s bounding box due to rotation, resulting in suboptimal tracking performance. Conversely, methods such as Trdimp and Trsiam directly estimate the target’s bounding box, while approaches such as siamese region proposal network(SiamRPN) and SiamRPN++ predefine anchor boxes with different aspect ratios, effectively addressing the challenge of in-plane rotation. Finally, in terms of future perspectives, this paper outlines the anticipated trajectory of single-object tracking algorithms for satellite videos across several key dimensions: standardizing evaluation metrics for tracking results, developing large-scale and high-quality satellite video object tracking datasets, devising models specifically tailored to satellite video tracking challenges, and enabling robust long-term tracking capabilities. In the domain of general video target tracking, commonly used evaluation metrics include those from the OTB and VOT benchmarks. For satellite video target tracking, scholars predominantly adopt the precision and success rate metrics defined by the OTB evaluation framework. In the OTB metrics for general videos, the precision threshold is customarily set to 20 pixels, and the success rate is evaluated based on the area under the curve (AUC) of the overlap score. However, in satellite video target tracking, researchers often adopt varying threshold settings, which hinders the objective evaluation of algorithms under a unified standard. Thus, standardizing evaluation metrics for tracking results is essential for the advancement of satellite video single-object tracking. Before the emergence of large-scale test datasets, most studies in satellite video object tracking verified algorithms using only a few targets, which restricted comprehensive algorithm performance assessment. Moreover, the use of different test dataset across studies has further hindered direct comparisons between algorithms. Consequently, the development of large-scale, high-quality satellite video object tracking datasets is urgently needed, not only for effective model training, but also for model testing and performance benchmarking. Future research could benefit from rapidly assimilating the latest advancements in general video object tracking domain and adapting them to the unique characteristics of satellite videos. Given the rich background information and the continuous, linear nature of target motion trajectories between adjacent frames in satellite videos, these priors can be fully leveraged to explore global spatial and temporal information, thereby enhancing tracking accuracy. Furthermore, techniques such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, and neural architecture search hold considerable potential for autonomously constructing streamlined, low-complexity models specifically tailored to satellite video single-object tracking. These approaches can enable high-precision, real-time target tracking under constrained computation resources. In contrast to ground-based surveillance videos, satellite videos offer broad coverage, making it possible to track trajectories across entire urban areas. However, in such large-scale scenarios, multiple challenges, such as occlusion, interference from similar objects, motion blur, illumination variation, and target rotation, often occur simultaneously. Aiming to address the demands of real-world applications, the development of satellite video tracking algorithms capable of simultaneously addressing these challenges is imperative.关键词:satellite video;single object tracking;correlation filtering;deep learning;Jilin-1 satellite163|161|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:In recent years, single-object tracking in satellite videos has gained substantial attention and plays a pivotal role in military and civilian domains. This tracking has found applications in urban-scale disaster relief, public security surveillance, and the monitoring of emergency events, among others. However, due to a combination of factors, such as small target size, interference from similar targets, motion blur, and complex backgrounds, single-object tracking in satellite videos presents numerous challenges. Aiming to promote further exploration in this domain by scholars domestically and internationally, this paper comprehensively reviews and critically analyzes the current state of the art in satellite video-based single-object tracking. Considering challenges and advantages, video satellites offer an expansive field of view. Targets such as vehicles typically occupy only a few to a dozen pixels in satellite videos, with limited distinguishing features or textures. Additionally, satellite videos contain many targets, and the distinguishability between the targets of interest and interfering objects is poor, presenting a high degree of similarity. Moreover, target blurring may occur due to their rapid target movement or satellite platform jitter. When the moving target is inconspicuous and background information overshadows target features, tracking failure is likely to occur. However, compared to ground-based or low-altitude videos, satellite video-based object tracking offers certain advantages. For example, external factors related to the target, such as the camera perspective, are relatively stable, aiding tracking algorithms in maintaining a consistent lock on the target. Most objects in satellite videos are rigid and rarely undergo substantial deformation during tracking. Additionally, the aspect ratios of targets remain approximately consistent across video frames, reducing the potential for algorithmic confusion. The motion of targets is typically straightforward, with trajectories generally following straight lines or smooth curves, enabling the prediction of target positions based on historical motion data. Regarding the development of tracking methods, this paper reviews the evolution of single-object tracking methods for satellite videos and highlights typical tracking paradigms, including generative-based approaches, correlation filter-based methods, and deep learning-based techniques. Deep learning-based tracking methods can be further classified into convolutional neural network (CNN)-based and Transformer-based methods. In contrast to the hand-crafted features employed in correlation filter-based methods, CNNs can extract more comprehensive and robust features, thereby enhancing target tracking performance. In recent years, an increasing number of scholars have applied CNNs to satellite video object tracking tasks. However, when processing high-resolution images, long time-series data, and complex backgrounds, which are common in satellite videos, CNNs exhibit certain limitations. Aiming to address these limitations, Transformers have been gradually introduced into satellite video object tracking. Transformers can capture global spatial information and long-term temporal dependencies, offering a promising alternative for improving tracking accuracy in complex scenarios. Regarding datasets and evaluation metrics, this study compiles existing single-object tracking datasets for satellite videos, along with commonly adopted performance evaluation metrics. Prominent datasets in this field include XDU-BDSTU, video satellite objects(VISO), SatSOT, and the oriented object tracking benchmark(OOTB). Among them, the VISO dataset is the largest in scale, comprising training and test subsets. The XDU-BDSTU dataset features images with a large swath width, making it suitable for long-term tracking tasks. The OOTB dataset provides annotations using rotated bounding boxes, which accurately represents the actual target geometry. The main performance evaluation metrics include precision, success rate, and frame rate, which collectively assess tracking methods in terms of tracking accuracy and speed. Aiming to evaluate the applicability of various tracking algorithms across different scenarios, this paper selects 18 algorithms for performance evaluation and analysis on a self-constructed test set. Experimental results highlight the critical roles of motion estimation, temporal information utilization, and background information exploitation in satellite video object tracking. Specifically, the correlation filter with motion estimation(CFME) algorithm leverages historical motion information of the target to enhance tracking performance, while the Trdimp algorithm incorporates temporal and background information, yielding favorable outcomes. When a vehicle makes a turn, the hand-crafted features employed by the correlation filter-based method CFME lack rotational invariance and are poorly equipped to handle changes in the target’s bounding box due to rotation, resulting in suboptimal tracking performance. Conversely, methods such as Trdimp and Trsiam directly estimate the target’s bounding box, while approaches such as siamese region proposal network(SiamRPN) and SiamRPN++ predefine anchor boxes with different aspect ratios, effectively addressing the challenge of in-plane rotation. Finally, in terms of future perspectives, this paper outlines the anticipated trajectory of single-object tracking algorithms for satellite videos across several key dimensions: standardizing evaluation metrics for tracking results, developing large-scale and high-quality satellite video object tracking datasets, devising models specifically tailored to satellite video tracking challenges, and enabling robust long-term tracking capabilities. In the domain of general video target tracking, commonly used evaluation metrics include those from the OTB and VOT benchmarks. For satellite video target tracking, scholars predominantly adopt the precision and success rate metrics defined by the OTB evaluation framework. In the OTB metrics for general videos, the precision threshold is customarily set to 20 pixels, and the success rate is evaluated based on the area under the curve (AUC) of the overlap score. However, in satellite video target tracking, researchers often adopt varying threshold settings, which hinders the objective evaluation of algorithms under a unified standard. Thus, standardizing evaluation metrics for tracking results is essential for the advancement of satellite video single-object tracking. Before the emergence of large-scale test datasets, most studies in satellite video object tracking verified algorithms using only a few targets, which restricted comprehensive algorithm performance assessment. Moreover, the use of different test dataset across studies has further hindered direct comparisons between algorithms. Consequently, the development of large-scale, high-quality satellite video object tracking datasets is urgently needed, not only for effective model training, but also for model testing and performance benchmarking. Future research could benefit from rapidly assimilating the latest advancements in general video object tracking domain and adapting them to the unique characteristics of satellite videos. Given the rich background information and the continuous, linear nature of target motion trajectories between adjacent frames in satellite videos, these priors can be fully leveraged to explore global spatial and temporal information, thereby enhancing tracking accuracy. Furthermore, techniques such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, and neural architecture search hold considerable potential for autonomously constructing streamlined, low-complexity models specifically tailored to satellite video single-object tracking. These approaches can enable high-precision, real-time target tracking under constrained computation resources. In contrast to ground-based surveillance videos, satellite videos offer broad coverage, making it possible to track trajectories across entire urban areas. However, in such large-scale scenarios, multiple challenges, such as occlusion, interference from similar objects, motion blur, illumination variation, and target rotation, often occur simultaneously. Aiming to address the demands of real-world applications, the development of satellite video tracking algorithms capable of simultaneously addressing these challenges is imperative.关键词:satellite video;single object tracking;correlation filtering;deep learning;Jilin-1 satellite163|161|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在自然语言处理领域,大语言模型取得显著进展,但在视频问答领域仍面临挑战。本文系统回顾了视频问答模型的研究进展,为多模态人工智能发展提供新思路。”
 摘要:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in natural language processing (NLP), demonstrating exceptional capabilities in language understanding and generation. These advancements have driven widespread applications in tasks such as text generation, machine translation, question answering, text summarization, and text classification. However, despite their impressive performance in handling and generating text, LLMs face notable limitations when handling highly complex multimodal tasks, particularly in the domain of video question answering (Video QA). Video QA is a particularly challenging task that requires models to comprehend and generate responses based on dynamic visual content, which often includes temporal and auditory information. Unlike static images or purely textual contents, video data contains inherent temporal dependencies, where the meaning of events and actions unfolds over time. This temporal dimension adds substantial complexity to the understanding process because models must not only interpret individual frames but also maintain coherent understanding across sequences of frames within the broader video context. Consequently, effective Video QA demands advanced temporal information processing capabilities that many LLMs, primarily designed for static text, often struggle to handle adequately. Moreover, the multimodal nature of video, which often involves the integration of visual, auditory, and occasionally textual cues, further complicates the task. Effective Video QA requires the model to seamlessly fuse information across these different modalities, ensuring accurate interpretation and response to questions regarding video content. This process involves understanding visual scenes, recognizing speech or background sounds, and correlating them with the corresponding textual information. The challenge lies not only in processing each modality independently but also in establishing meaningful connections between them to generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the current state of research on Video QA models based on large language models. The technical characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of non-real-time and real-time Video QA models are also investigated. Non-real-time Video QA models typically operate on pre-recorded video content, allowing them to access and analyze the entire video sequence before generating responses. These models can leverage global contextual information, making such models particularly effective for tasks that require video content analysis, such as video summarization or detailed scene interpretation. However, they may struggle with efficiency and scalability, particularly when handling long videos or large datasets. In contrast, real-time Video QA models are designed to process video streams as they are received, increasing their suitability for applications requiring immediate responses, such as live video monitoring or interactive video systems. However, these models must maintain a balance between processing speed and accuracy due to their frequently limited access to the full temporal context of the video. The paper discusses the challenges encountered by these models in maintaining performance under real-time constraints, including efficient computation and prediction capability based on partial information. Additionally, the paper explores the commonly used datasets in Video QA research, highlighting their features, limitations, and the types of tasks they are designed to address. The evaluation of Video QA models is also examined, focusing on the metrics and benchmarks used to assess their performance. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different datasets is crucial for advancing the field, helping in the identification of gaps in current research and guiding the development of robust and versatile models. Finally, the paper addresses the extensive challenges and bottlenecks in the field of Video QA, including the difficulties in scaling models to handle large and diverse video datasets, the need for efficient multimodal fusion techniques, and the computational demands associated with video data processing in real-time. The discussion is further extended to consider the potential future research directions in Video QA, with particular emphasis on improving the temporal reasoning capabilities of LLMs, enhancing their multimodal integration, and developing efficient model architectures that can operate effectively under resource constraints. Overall, while large language models have presented new possibilities in the field of video interpretation, considerable challenges remain in adapting these models to the specific demands of Video QA. Through the systematic review of the current advancements and the presentation of the key obstacles and future directions, this paper aims to contribute to the ongoing efforts to develop highly capable and intelligent multimodal AI systems. The field must continue innovations in the following areas: temporal modeling, where novel architectures that can effectively capture long-range dependencies in video sequences are needed; multimodal representation learning, where sophisticated approaches for integrating visual, auditory, and textual features could yield substantial improvements. Furthermore, the development of highly efficient training paradigms that can address the computational intensity of video processing while retaining model performance is essential for practical applications. Another critical area for future work focuses on the creation of highly comprehensive and challenging benchmark datasets that effectively reflect real-world scenarios, pushing the boundaries of what current models can achieve. As research in this area progresses, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of LLMs in video interpretation applications. Achieving this goal will require AI systems that can interpret and reason about dynamic visual content with a level of proficiency comparable to human cognition. The integration of advanced techniques from computer vision, speech processing, and natural language understanding will be pivotal in developing truly multimodal systems capable of managing the complexity and variability in real-world video data. Through continued innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration, the field can overcome current limitations and drive the development of next-generation video understanding technologies with broad applicability across domains such as education, entertainment, surveillance, and human-computer interaction.关键词:large language models(LLMs);video question answering(Video QA);multimodal information fusion;temporal information processing;video understanding168|183|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in natural language processing (NLP), demonstrating exceptional capabilities in language understanding and generation. These advancements have driven widespread applications in tasks such as text generation, machine translation, question answering, text summarization, and text classification. However, despite their impressive performance in handling and generating text, LLMs face notable limitations when handling highly complex multimodal tasks, particularly in the domain of video question answering (Video QA). Video QA is a particularly challenging task that requires models to comprehend and generate responses based on dynamic visual content, which often includes temporal and auditory information. Unlike static images or purely textual contents, video data contains inherent temporal dependencies, where the meaning of events and actions unfolds over time. This temporal dimension adds substantial complexity to the understanding process because models must not only interpret individual frames but also maintain coherent understanding across sequences of frames within the broader video context. Consequently, effective Video QA demands advanced temporal information processing capabilities that many LLMs, primarily designed for static text, often struggle to handle adequately. Moreover, the multimodal nature of video, which often involves the integration of visual, auditory, and occasionally textual cues, further complicates the task. Effective Video QA requires the model to seamlessly fuse information across these different modalities, ensuring accurate interpretation and response to questions regarding video content. This process involves understanding visual scenes, recognizing speech or background sounds, and correlating them with the corresponding textual information. The challenge lies not only in processing each modality independently but also in establishing meaningful connections between them to generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses. This paper presents a comprehensive review of the current state of research on Video QA models based on large language models. The technical characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of non-real-time and real-time Video QA models are also investigated. Non-real-time Video QA models typically operate on pre-recorded video content, allowing them to access and analyze the entire video sequence before generating responses. These models can leverage global contextual information, making such models particularly effective for tasks that require video content analysis, such as video summarization or detailed scene interpretation. However, they may struggle with efficiency and scalability, particularly when handling long videos or large datasets. In contrast, real-time Video QA models are designed to process video streams as they are received, increasing their suitability for applications requiring immediate responses, such as live video monitoring or interactive video systems. However, these models must maintain a balance between processing speed and accuracy due to their frequently limited access to the full temporal context of the video. The paper discusses the challenges encountered by these models in maintaining performance under real-time constraints, including efficient computation and prediction capability based on partial information. Additionally, the paper explores the commonly used datasets in Video QA research, highlighting their features, limitations, and the types of tasks they are designed to address. The evaluation of Video QA models is also examined, focusing on the metrics and benchmarks used to assess their performance. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different datasets is crucial for advancing the field, helping in the identification of gaps in current research and guiding the development of robust and versatile models. Finally, the paper addresses the extensive challenges and bottlenecks in the field of Video QA, including the difficulties in scaling models to handle large and diverse video datasets, the need for efficient multimodal fusion techniques, and the computational demands associated with video data processing in real-time. The discussion is further extended to consider the potential future research directions in Video QA, with particular emphasis on improving the temporal reasoning capabilities of LLMs, enhancing their multimodal integration, and developing efficient model architectures that can operate effectively under resource constraints. Overall, while large language models have presented new possibilities in the field of video interpretation, considerable challenges remain in adapting these models to the specific demands of Video QA. Through the systematic review of the current advancements and the presentation of the key obstacles and future directions, this paper aims to contribute to the ongoing efforts to develop highly capable and intelligent multimodal AI systems. The field must continue innovations in the following areas: temporal modeling, where novel architectures that can effectively capture long-range dependencies in video sequences are needed; multimodal representation learning, where sophisticated approaches for integrating visual, auditory, and textual features could yield substantial improvements. Furthermore, the development of highly efficient training paradigms that can address the computational intensity of video processing while retaining model performance is essential for practical applications. Another critical area for future work focuses on the creation of highly comprehensive and challenging benchmark datasets that effectively reflect real-world scenarios, pushing the boundaries of what current models can achieve. As research in this area progresses, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of LLMs in video interpretation applications. Achieving this goal will require AI systems that can interpret and reason about dynamic visual content with a level of proficiency comparable to human cognition. The integration of advanced techniques from computer vision, speech processing, and natural language understanding will be pivotal in developing truly multimodal systems capable of managing the complexity and variability in real-world video data. Through continued innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration, the field can overcome current limitations and drive the development of next-generation video understanding technologies with broad applicability across domains such as education, entertainment, surveillance, and human-computer interaction.关键词:large language models(LLMs);video question answering(Video QA);multimodal information fusion;temporal information processing;video understanding168|183|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “点云深度学习网络在三维视觉领域取得显著进展,但面临旋转变换挑战。专家系统整理了旋转不变点云网络的研究内容和方法,为未来发展提供新方向。”
 摘要:In recent years, deep learning networks for point clouds have achieved remarkable advancements, with their robust semantic understanding capabilities propelling research across the entire field of three-dimensional (3D) computer vision. These advancements have enabled accurate and efficient processing of 3D data, supporting applications in autonomous driving, robotics, remote sensing and mapping, and augmented reality. However, 3D point clouds often exhibit complex transformation symmetries, with rotation being a particularly challenging yet critical factor. The spatial coordinates of point clouds, which are the fundamental input to point cloud networks, undergo substantial changes, resulting in feature output variations. However, the semantic information embedded within point clouds theoretically remains consistent under various rotational transformations. This spatial variability substantially impacts the stability and reliability of conventional point cloud deep learning networks in semantic perception tasks, such as recognition, classification, and segmentation, reducing their effectiveness in real-world scenarios characterized by arbitrary orientations and poses. Early studies primarily relied on rotational data augmentation to enhance the robustness of point cloud networks against rotational variations. While data augmentation can improve generalization to some extent, it falls short of addressing the fundamental issue posed by the infinite and continuous nature of the rotation group. Acknowledging these limitations, an increasing number of researchers have shifted their focus toward designing rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, which aim to mitigate the impact of rotation on feature extraction at the architectural level. Therefore, researchers seek to achieve consistent semantic perception regardless of point cloud orientation, thereby enhancing the applicability of deep learning models in real-world scenarios where data can be encountered in arbitrary poses. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the current state of research on rotation-invariant point cloud networks. The research background is first outlined to highlight the importance of rotation invariance in 3D vision tasks and the challenges posed by rotational symmetries in point cloud data. Then, a systematic categorization of the prevailing mainstream methods is investigated. Particularly, the rotation-invariant point cloud networks can be broadly classified into the following three categories: 1) geometric-guided rotation-invariant methods: Using the traditional geometric analysis algorithms, these methods extract rotation-invariant geometric representations such as relative distances, angles, local reference frames, and canonical poses. These representations are then integrated into point cloud networks, facilitating learning of high-level semantic features and maintaining robustness to rotational transformations simultaneously. 2) Feature-guided rotation-invariant methods: These methods employ rotation-equivariant point cloud networks to extract point cloud representations that contain shape and pose information. Leveraging the inherent principles of equivariant networks, they subsequently remove the pose information from the rotation-equivariant representations, obtaining rotation-invariant point cloud features. 3) Training-guided rotation-invariant methods: These methods focus on designing sophisticated and highly generalizable rotational data augmentation training schemes, allowing non-rotation-invariant point cloud networks to gradually acquire robustness of rotations and achieve stable performance simultaneously. An in-depth analysis of the core concepts and algorithmic improvements that support these methods is provided for each category. The current research content on this issue and methodologies within the academic community are outlined, and the advantages and disadvantages of each method are summarized and compared. Subsequently, a comprehensive overview of the prevalent downstream tasks in the research of rotation-invariant point cloud networks is presented. These tasks include point cloud classification, point cloud segmentation, and point cloud retrieval. For each of these tasks, an in-depth discussion of the commonly employed datasets and evaluation metrics, which are essential for assessing network performance, is provided. Additionally, the quantitative performance metrics of mainstream rotation-invariant point cloud networks applied to these tasks are summarized and analyzed, offering a comparative perspective on their efficacy and robustness under rotational variations. Afterward, the downstream application prospects of rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, including point cloud self-supervised representation learning, end-to-end point cloud registration, and point cloud completion, are examined and summarized. Finally, an outlook on future developments and research hotspots is presented. In addition to the ongoing development of new rotation-invariant point cloud networks, three primary issues warrant further research: 1) discrimination of effective geometric attributes. Current approaches are limited by the design of geometric attribute extraction algorithms. An in-depth discussion and determination of the effectiveness of different rotation-invariant geometric attributes within deep learning frameworks could yield novel insights and foster the development of innovative strategies to advance this field. 2) Highly integratable rotation-invariant mechanism. On the one hand, existing non-rotation-invariant point cloud networks continue to demonstrate strong performance on aligned data. The challenge lies in incorporating rotation invariance into these networks in a straightforward manner degrading their original performance. This challenge remains a key research topic because seamless integration requires innovative architectural designs and methodological approaches. On the other hand, rotation-invariant point cloud networks should also exhibit simplicity and reusability, enabling their direct application to downstream tasks with minimal adaptation. 3) High computational efficiency in invariant feature extraction modules. Although many existing methods demonstrate commendable performance, they often incur substantial time and computational costs, making it challenging to efficiently process large-scale point cloud data. Therefore, designing more efficient rotation-invariant point cloud networks that maintain robust feature extraction capabilities while minimizing computational overhead is crucial. Addressing the aforementioned challenges will notably enhance the effectiveness and practicality of rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, facilitating their widespread adoption in complex 3D environments. This survey aims to provide researchers in 3D computer vision with a foundational understanding of current methodologies, highlight key challenges, and suggest potential avenues for future research.关键词:three-dimensional vision;deep learning;Point cloud network;rotation invariance;Rotation equivariance115|138|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:In recent years, deep learning networks for point clouds have achieved remarkable advancements, with their robust semantic understanding capabilities propelling research across the entire field of three-dimensional (3D) computer vision. These advancements have enabled accurate and efficient processing of 3D data, supporting applications in autonomous driving, robotics, remote sensing and mapping, and augmented reality. However, 3D point clouds often exhibit complex transformation symmetries, with rotation being a particularly challenging yet critical factor. The spatial coordinates of point clouds, which are the fundamental input to point cloud networks, undergo substantial changes, resulting in feature output variations. However, the semantic information embedded within point clouds theoretically remains consistent under various rotational transformations. This spatial variability substantially impacts the stability and reliability of conventional point cloud deep learning networks in semantic perception tasks, such as recognition, classification, and segmentation, reducing their effectiveness in real-world scenarios characterized by arbitrary orientations and poses. Early studies primarily relied on rotational data augmentation to enhance the robustness of point cloud networks against rotational variations. While data augmentation can improve generalization to some extent, it falls short of addressing the fundamental issue posed by the infinite and continuous nature of the rotation group. Acknowledging these limitations, an increasing number of researchers have shifted their focus toward designing rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, which aim to mitigate the impact of rotation on feature extraction at the architectural level. Therefore, researchers seek to achieve consistent semantic perception regardless of point cloud orientation, thereby enhancing the applicability of deep learning models in real-world scenarios where data can be encountered in arbitrary poses. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the current state of research on rotation-invariant point cloud networks. The research background is first outlined to highlight the importance of rotation invariance in 3D vision tasks and the challenges posed by rotational symmetries in point cloud data. Then, a systematic categorization of the prevailing mainstream methods is investigated. Particularly, the rotation-invariant point cloud networks can be broadly classified into the following three categories: 1) geometric-guided rotation-invariant methods: Using the traditional geometric analysis algorithms, these methods extract rotation-invariant geometric representations such as relative distances, angles, local reference frames, and canonical poses. These representations are then integrated into point cloud networks, facilitating learning of high-level semantic features and maintaining robustness to rotational transformations simultaneously. 2) Feature-guided rotation-invariant methods: These methods employ rotation-equivariant point cloud networks to extract point cloud representations that contain shape and pose information. Leveraging the inherent principles of equivariant networks, they subsequently remove the pose information from the rotation-equivariant representations, obtaining rotation-invariant point cloud features. 3) Training-guided rotation-invariant methods: These methods focus on designing sophisticated and highly generalizable rotational data augmentation training schemes, allowing non-rotation-invariant point cloud networks to gradually acquire robustness of rotations and achieve stable performance simultaneously. An in-depth analysis of the core concepts and algorithmic improvements that support these methods is provided for each category. The current research content on this issue and methodologies within the academic community are outlined, and the advantages and disadvantages of each method are summarized and compared. Subsequently, a comprehensive overview of the prevalent downstream tasks in the research of rotation-invariant point cloud networks is presented. These tasks include point cloud classification, point cloud segmentation, and point cloud retrieval. For each of these tasks, an in-depth discussion of the commonly employed datasets and evaluation metrics, which are essential for assessing network performance, is provided. Additionally, the quantitative performance metrics of mainstream rotation-invariant point cloud networks applied to these tasks are summarized and analyzed, offering a comparative perspective on their efficacy and robustness under rotational variations. Afterward, the downstream application prospects of rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, including point cloud self-supervised representation learning, end-to-end point cloud registration, and point cloud completion, are examined and summarized. Finally, an outlook on future developments and research hotspots is presented. In addition to the ongoing development of new rotation-invariant point cloud networks, three primary issues warrant further research: 1) discrimination of effective geometric attributes. Current approaches are limited by the design of geometric attribute extraction algorithms. An in-depth discussion and determination of the effectiveness of different rotation-invariant geometric attributes within deep learning frameworks could yield novel insights and foster the development of innovative strategies to advance this field. 2) Highly integratable rotation-invariant mechanism. On the one hand, existing non-rotation-invariant point cloud networks continue to demonstrate strong performance on aligned data. The challenge lies in incorporating rotation invariance into these networks in a straightforward manner degrading their original performance. This challenge remains a key research topic because seamless integration requires innovative architectural designs and methodological approaches. On the other hand, rotation-invariant point cloud networks should also exhibit simplicity and reusability, enabling their direct application to downstream tasks with minimal adaptation. 3) High computational efficiency in invariant feature extraction modules. Although many existing methods demonstrate commendable performance, they often incur substantial time and computational costs, making it challenging to efficiently process large-scale point cloud data. Therefore, designing more efficient rotation-invariant point cloud networks that maintain robust feature extraction capabilities while minimizing computational overhead is crucial. Addressing the aforementioned challenges will notably enhance the effectiveness and practicality of rotation-invariant point cloud deep learning networks, facilitating their widespread adoption in complex 3D environments. This survey aims to provide researchers in 3D computer vision with a foundational understanding of current methodologies, highlight key challenges, and suggest potential avenues for future research.关键词:three-dimensional vision;deep learning;Point cloud network;rotation invariance;Rotation equivariance115|138|0更新时间:2025-12-18
Review
- “在人脸图像年龄估计领域,研究者提出了一种新的开集半监督多任务学习方法,有效提升了年龄估计精度,并充分利用无标签数据集优化性能。”
 摘要:ObjectiveFacial age estimation from images constitutes a prominent area of research within the field of computer vision, offering extensive potential applications in fields such as biometrics, digital marketing, healthcare, and human-computer interaction. Despite substantial efforts by numerous researchers in this field, achieving accurate facial age estimation remains a formidable challenge, primarily due to the lack of high-quality, large-scale labeled datasets for facial age estimation. The manual annotation of facial datasets necessitates considerable time and financial costs. Semi-supervised learning has emerged as a promising strategy for solving this problem because it enables the simultaneous utilization of labeled and unlabeled data. However, achieving satisfactory results in the domain of facial age estimation using semi-supervised learning methods is difficult. This difficulty arises from the limited accuracy of the pseudo-labels produced by these methods, as well as their susceptibility to the influence of outlier data. These factors hinder the effective utilization of unlabeled data, consequently limiting overall performance. Aiming to address these challenges, optimizing the capability of the model to extract features is essential. Such improvements will facilitate the effective acquisition of valuable representations from unlabeled data, thereby yielding highly precise pseudo-labels. Additionally, establishing a semi-supervised learning framework that can adeptly manage the challenges associated with outlier data while optimizing the utilization of the unlabeled dataset is crucial. Consequently, this study presents an open-set semi-supervised multi-task approach for facial age estimation.MethodThis research presents the SwinLEDF model to optimize the capability of the model to extract local and global features from facial images. This model is based on the Swin Transformer architecture and integrates local enhanced feedforward (LEFF) modules along with dynamic filter networks (DFNs). The Swin Transformer demonstrates proficient capabilities in capturing long-range dependencies and global characteristics, particularly in the analysis of age-related trends and the overall morphology of facial structures. The LEFF module incorporates non-linear transformations at the feature level, facilitating the identification of local patterns within images or feature representations. This capability is essential for differentiating age-related attributes, including intricate details such as wrinkles and skin texture. The DFN module implements a dynamic filtering operation within the spatial dimension of the model’s output, thereby enhancing model flexibility and adaptability. Furthermore, this research presents an open-set semi-supervised multitask learning algorithm to optimize the use of labeled and unlabeled data. In this algorithm, the model assesses the probability of unlabeled data being classified as outliers by integrating the outcomes of a closed-set classifier and a multi-class binary classifier. Subsequently, the model generates pseudo-labels for non-outlier data that meet a specified confidence threshold. Additionally, the model simultaneously learns to estimate sex, race, and age using labeled and unlabeled data. Through this process, the model learns not only the unique characteristics associated with each specific task but also the interrelationships among gender, race, and age, thereby enhancing the capability of the model to process diverse data and increases its expressive power and robustness. Furthermore, the process enables the effective utilization of unlabeled datasets, addressing the challenge of limited labeled data in the field of age estimation. This study employs an adaptive threshold mechanism and a negative learning strategy to optimize the use of unlabeled data. The adaptive threshold mechanism dynamically adjusts the confidence threshold for pseudo-labels based on the model’s training performance across different categories, effectively addressing category imbalance and improving the precision of pseudo-label production. The negative learning strategy enhances the handling of unlabeled data by identifying categories to which the input data does not belong, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of false pseudo-labels on model performance.ResultThis study assesses the proposed methodology using the MORPH and UTKface datasets. On the MORPH dataset, the model exhibits a mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.908 when trained solely on labeled data. This error is further reduced to 1.885 with the inclusion of labeled and unlabeled datasets. Similarly, for the UTKface dataset, the initial MAE is recorded at 4.343 using only labeled datasets, which subsequently reduces to 4.246 following the integration of labeled and unlabeled datasets. Compared to current facial age estimation methods, the proposed approach exhibits superior performance and further optimizes its accuracy by leveraging unlabeled facial datasets.ConclusionThis study introduces an open-set semi-supervised multi-task learning method for facial age estimation. The proposed method effectively extracts gender, race, and age attributes from facial images while leveraging unlabeled data and appropriately handling potential outliers. This approach addresses the challenges associated with limited labeled data, thereby enhancing the accuracy of facial age estimation. Furthermore, the methodology presents innovative strategies for achieving precise results and holds strong potential for practical applications.关键词:facial age estimation;open-set semi-supervised learning;multi-task learning;SwinLEDF model;pseudo-label156|197|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveFacial age estimation from images constitutes a prominent area of research within the field of computer vision, offering extensive potential applications in fields such as biometrics, digital marketing, healthcare, and human-computer interaction. Despite substantial efforts by numerous researchers in this field, achieving accurate facial age estimation remains a formidable challenge, primarily due to the lack of high-quality, large-scale labeled datasets for facial age estimation. The manual annotation of facial datasets necessitates considerable time and financial costs. Semi-supervised learning has emerged as a promising strategy for solving this problem because it enables the simultaneous utilization of labeled and unlabeled data. However, achieving satisfactory results in the domain of facial age estimation using semi-supervised learning methods is difficult. This difficulty arises from the limited accuracy of the pseudo-labels produced by these methods, as well as their susceptibility to the influence of outlier data. These factors hinder the effective utilization of unlabeled data, consequently limiting overall performance. Aiming to address these challenges, optimizing the capability of the model to extract features is essential. Such improvements will facilitate the effective acquisition of valuable representations from unlabeled data, thereby yielding highly precise pseudo-labels. Additionally, establishing a semi-supervised learning framework that can adeptly manage the challenges associated with outlier data while optimizing the utilization of the unlabeled dataset is crucial. Consequently, this study presents an open-set semi-supervised multi-task approach for facial age estimation.MethodThis research presents the SwinLEDF model to optimize the capability of the model to extract local and global features from facial images. This model is based on the Swin Transformer architecture and integrates local enhanced feedforward (LEFF) modules along with dynamic filter networks (DFNs). The Swin Transformer demonstrates proficient capabilities in capturing long-range dependencies and global characteristics, particularly in the analysis of age-related trends and the overall morphology of facial structures. The LEFF module incorporates non-linear transformations at the feature level, facilitating the identification of local patterns within images or feature representations. This capability is essential for differentiating age-related attributes, including intricate details such as wrinkles and skin texture. The DFN module implements a dynamic filtering operation within the spatial dimension of the model’s output, thereby enhancing model flexibility and adaptability. Furthermore, this research presents an open-set semi-supervised multitask learning algorithm to optimize the use of labeled and unlabeled data. In this algorithm, the model assesses the probability of unlabeled data being classified as outliers by integrating the outcomes of a closed-set classifier and a multi-class binary classifier. Subsequently, the model generates pseudo-labels for non-outlier data that meet a specified confidence threshold. Additionally, the model simultaneously learns to estimate sex, race, and age using labeled and unlabeled data. Through this process, the model learns not only the unique characteristics associated with each specific task but also the interrelationships among gender, race, and age, thereby enhancing the capability of the model to process diverse data and increases its expressive power and robustness. Furthermore, the process enables the effective utilization of unlabeled datasets, addressing the challenge of limited labeled data in the field of age estimation. This study employs an adaptive threshold mechanism and a negative learning strategy to optimize the use of unlabeled data. The adaptive threshold mechanism dynamically adjusts the confidence threshold for pseudo-labels based on the model’s training performance across different categories, effectively addressing category imbalance and improving the precision of pseudo-label production. The negative learning strategy enhances the handling of unlabeled data by identifying categories to which the input data does not belong, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of false pseudo-labels on model performance.ResultThis study assesses the proposed methodology using the MORPH and UTKface datasets. On the MORPH dataset, the model exhibits a mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.908 when trained solely on labeled data. This error is further reduced to 1.885 with the inclusion of labeled and unlabeled datasets. Similarly, for the UTKface dataset, the initial MAE is recorded at 4.343 using only labeled datasets, which subsequently reduces to 4.246 following the integration of labeled and unlabeled datasets. Compared to current facial age estimation methods, the proposed approach exhibits superior performance and further optimizes its accuracy by leveraging unlabeled facial datasets.ConclusionThis study introduces an open-set semi-supervised multi-task learning method for facial age estimation. The proposed method effectively extracts gender, race, and age attributes from facial images while leveraging unlabeled data and appropriately handling potential outliers. This approach addresses the challenges associated with limited labeled data, thereby enhancing the accuracy of facial age estimation. Furthermore, the methodology presents innovative strategies for achieving precise results and holds strong potential for practical applications.关键词:facial age estimation;open-set semi-supervised learning;multi-task learning;SwinLEDF model;pseudo-label156|197|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在轨道缺陷检测领域,研究者提出了LPCANet模型,有效提升了检测速度和精度,具有实际应用价值。”
 摘要:ObjectiveMost existing vision-based rail defect detection methods face challenges such as high parameter counts, computational complexity, slow detection speeds, and limited accuracy. Aiming to overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a lightweight pyramid cross-attention network (LPCANet) for orbital image defect detection using RGB images and depth images.MethodLPCANet adopts MobileNetv2 as its backbone network to extract multiscale feature maps from RGB images. Simultaneously, a lightweight pyramid module (LPM) is employed to extract similarly-sized feature maps from depth images. Each stage of the LPM comprises a sequence of operations including max pooling, a 3 × 3 convolutional layer, batch normalization, and ReLU activation, enabling efficient extraction of features from depth images. By leveraging deep learning, RGB-D technology, and salient object detection, LPCANet efficiently extracts multiscale feature representations from RGB and depth data. The LPM handles depth image features, while the backbone captures detailed pyramid features from RGB images. Subsequently, a cross-attention mechanism (CAM) is applied to integrate the feature maps from both modalities, enhancing the network’s focus on relevant defect regions. Additionally, a spatial feature extractor (SFE) is introduced to further boost defect detection performance. Finally, a “pixel shuffle” operation is used to restore the output to the original image resolution.ResultThe proposed scheme was computationally evaluated using the PyTorch library in an environment equipped with an NVIDIA 3090 GPU, alongside several benchmark models for comparison. For the evaluation of LPCANet, three publicly available unsupervised RGB-D rail datasets were used: NEU-RSDDS-AUG, RSDD-TYPE1, and RSDD-TYPE2. Experimental results on the NEU-RSDDS-AUG dataset indicate that LPCANet achieves excellent efficiency, with 9.90 million parameters, a computational complexity of 2.50 G, a model size of 37.95 MB, and a running speed of 162.60 frames per second. Compared to 18 existing rail defect detection schemes, LPCANet exhibits superior lightness in performance. In particular, when compared against CSEPNet, the current best-performing model, LPCANet achieves improvements across several evaluation metrics: +1.48% in
摘要:ObjectiveMost existing vision-based rail defect detection methods face challenges such as high parameter counts, computational complexity, slow detection speeds, and limited accuracy. Aiming to overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a lightweight pyramid cross-attention network (LPCANet) for orbital image defect detection using RGB images and depth images.MethodLPCANet adopts MobileNetv2 as its backbone network to extract multiscale feature maps from RGB images. Simultaneously, a lightweight pyramid module (LPM) is employed to extract similarly-sized feature maps from depth images. Each stage of the LPM comprises a sequence of operations including max pooling, a 3 × 3 convolutional layer, batch normalization, and ReLU activation, enabling efficient extraction of features from depth images. By leveraging deep learning, RGB-D technology, and salient object detection, LPCANet efficiently extracts multiscale feature representations from RGB and depth data. The LPM handles depth image features, while the backbone captures detailed pyramid features from RGB images. Subsequently, a cross-attention mechanism (CAM) is applied to integrate the feature maps from both modalities, enhancing the network’s focus on relevant defect regions. Additionally, a spatial feature extractor (SFE) is introduced to further boost defect detection performance. Finally, a “pixel shuffle” operation is used to restore the output to the original image resolution.ResultThe proposed scheme was computationally evaluated using the PyTorch library in an environment equipped with an NVIDIA 3090 GPU, alongside several benchmark models for comparison. For the evaluation of LPCANet, three publicly available unsupervised RGB-D rail datasets were used: NEU-RSDDS-AUG, RSDD-TYPE1, and RSDD-TYPE2. Experimental results on the NEU-RSDDS-AUG dataset indicate that LPCANet achieves excellent efficiency, with 9.90 million parameters, a computational complexity of 2.50 G, a model size of 37.95 MB, and a running speed of 162.60 frames per second. Compared to 18 existing rail defect detection schemes, LPCANet exhibits superior lightness in performance. In particular, when compared against CSEPNet, the current best-performing model, LPCANet achieves improvements across several evaluation metrics: +1.48% in
Image Analysis and Recognition
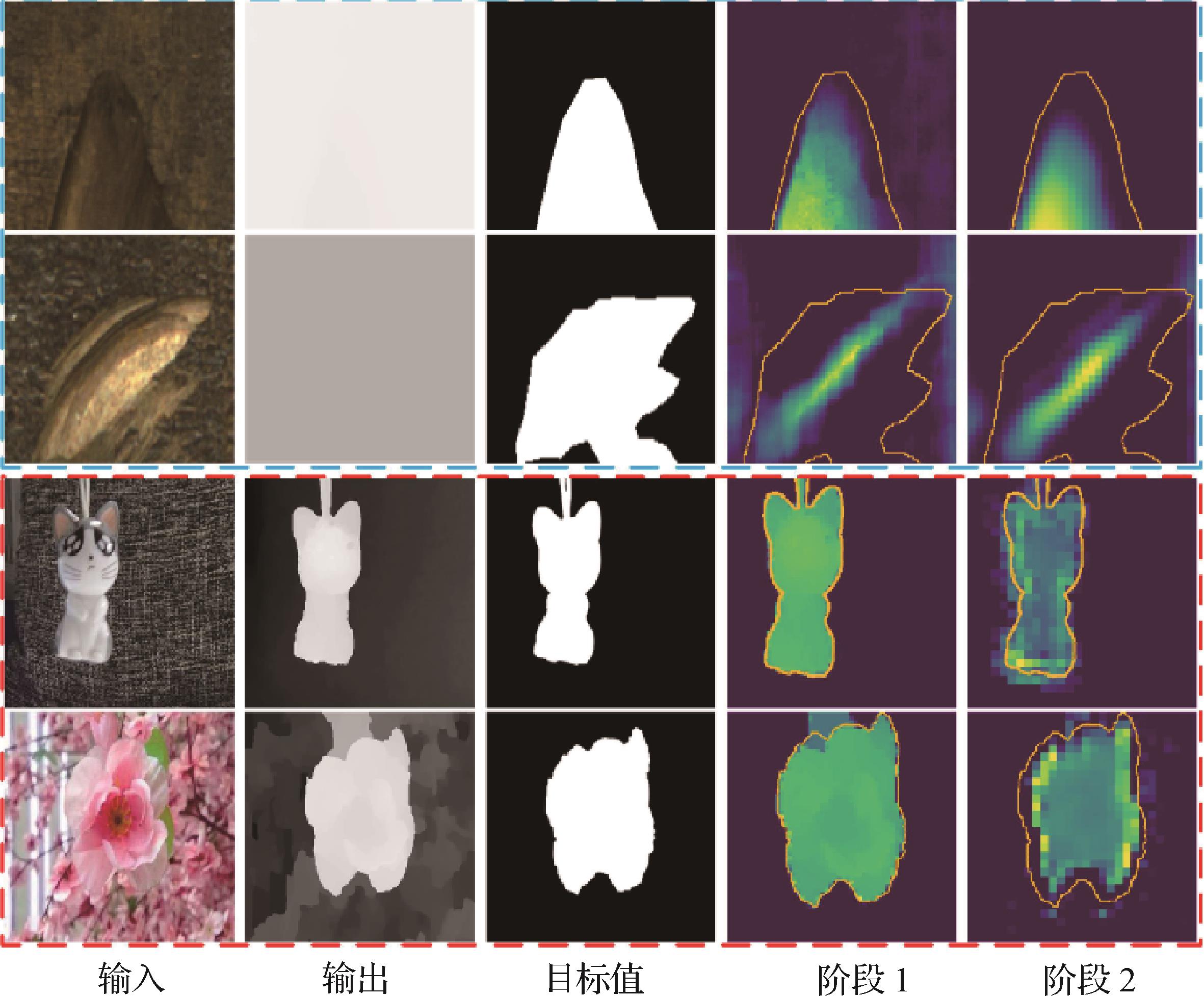
- “在显著目标检测领域,研究者提出了一种RGB-D显著目标检测方法,通过跨模态特征融合与边缘细节增强,有效提高了检测性能。”
 摘要:ObjectiveRGB-D salient object detection (SOD) combines complementary information from RGB and depth images, offering substantially enhanced performance in complex and challenging scenes compared to RGB-only models. This technique has gained considerable attention in the academic community due to its capability to effectively capture salient objects by leveraging visual and spatial information. However, existing RGB-D detection models face several key challenges. First, efficiently utilizing and fusing multi-modal information from RGB and depth inputs remains a difficult task due to the inherent differences between the two modalities. RGB images provide rich color and texture details but lack depth information, whereas depth maps offer spatial cues but are often noisy or of low quality. Second, achieving accurate boundary detection is particularly challenging in cluttered or noisy environments. Noisy depth maps and cluttered backgrounds can obscure object contours, making it difficult to predict sharp and precise boundaries. These challenges highlight the urgent need for a robust model that can effectively integrate RGB and depth information while simultaneously addressing noise and enhancing boundary precision.MethodAiming to address these challenges, a novel method, the cross-modal feature fusion and detail-enhanced RGB-D salient object detection network (CFADNet), is introduced. The proposed network incorporates two innovative modules: the cross-modal attention fusion enhancement module (CAFEM) and the boundary feature extraction module (BFEM). The CAFEM is designed to enhance the integration of RGB and depth features by leveraging attention mechanisms that emphasize the most informative aspects of each modality. Specifically, channel attention is applied to the RGB features to suppress noise and enhance critical color and texture details. Similarly, spatial attention is applied to the depth features to emphasize spatial regions that are relevant for salient object detection. This attention-based fusion mechanism ensures that the model effectively retains global semantic information from the depth map while preserving fine-grained details from the RGB image. The fusion process is structured in multiple layers, progressively integrating features at different scales to fully utilize the complementary strengths of RGB and depth modalities. In contrast, the BFEM is specifically designed to improve the accuracy of salient object boundaries. Accurate contour detection is crucial for generating high-quality saliency maps; thus, BFEM leverages low-level CNN features, which are rich in edge and texture information. These features are refined through channel attention, which filters out noise and irrelevant details, enhancing the clarity of boundary-related cues. The refined features are then used to guide cross-modal feature decoding, ensuring that the final saliency maps exhibit sharp and accurate boundaries. By combining the edge-extraction capabilities of low-level CNN features with the semantic richness of cross-modal features, BFEM notably improves boundary precision in RGB-D salient object detection.ResultAiming to evaluate the performance of CFADNet, extensive experiments are conducted on four widely used RGB-D salient object detection datasets: NJU2K, NLPR, STERE, and SIP. These datasets encompass a wide range of diverse and challenging scenes, making them ideal for evaluating the generalization capability of the proposed model. CFADNet is compared against 16 state-of-the-art RGB-D salient object detection methods, including DCF, CIRNet, and CAVER, using standard quantitative metrics such as mean absolute error (MAE), F-measure(Fβ), and structural similarity (Sα). CFADNet demonstrated superior performance across all datasets, particularly excelling in the MAE metric. Specifically, this network outperformed the second-best method by 6.9%, 10.5%, 9.7%, and 2.4% on the NJU2K, NLPR, STERE, and SIP datasets, respectively. These substantial improvements highlight the effectiveness of the attention-based fusion strategy and edge refinement mechanisms. Furthermore, CFADNet consistently achieved higher F-measure and Sα scores, indicating that the model not only reduces pixel-level errors but also more accurately preserves the overall structure and shape of salient objects compared to competing methods. In addition to quantitative evaluations, qualitative comparisons are conducted to visually assess the performance of CFADNet in various challenging scenarios. Results show that the proposed method generates saliency maps with sharp and accurate boundaries, even in cases where salient objects exhibit complex edges or are embedded in cluttered and noisy backgrounds. This finding demonstrates the robustness of CFADNet in handling difficult scenes by effectively separating salient objects from their background while preserving fine boundary details. The visual results further confirm that CFADNet successfully captures global semantic information and local detail, ensuring accurate identification and clear isolation of salient objects from the background.ConclusionThis paper presents CFADNet, a cross-modal feature fusion and detail-enhancement network for RGB-D SOD, designed to address the two major challenges: effective multimodal feature fusion and accurate boundary detection. CFADNet introduces two novel modules, the CAFEM and the BFEM. CFADNet effectively integrates RGB and depth information while notably enhancing the precision of salient object boundaries. The attention mechanisms used in the CAF0EM enable the network to fully leverage the complementary information from RGB and depth modalities. Simultaneously, the BFEM module focuses on refining edge details, resulting in sharper and more accurate saliency predictions. Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that CFADNet consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance across key evaluation metric, including MAE, F-measure, and structural similarity index. These findings highlight the robustness and strong generalization capability of CFADNet in diverse and challenging environments. By combining attention-based feature fusion with effective edge refinement, CFADNet emerges as a powerful and reliable solution for RGB-D salient object detection into complex scenarios. Future research could explore extending this approach to other multi-modal tasks, such as RGB-Thermal or multi-spectral image processing, where challenges related to multi-modal fusion and boundary detection are also prevalent. Additionally, optimizing the computational efficiency of CFADNet for real-time deployment represents a potential research direction, enabling its application in time-sensitive applications such as autonomous driving and robotics.关键词:salient object detection(SOD);attention mechanism;cross-modal;feature fusion;edge detail-enhancement255|198|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveRGB-D salient object detection (SOD) combines complementary information from RGB and depth images, offering substantially enhanced performance in complex and challenging scenes compared to RGB-only models. This technique has gained considerable attention in the academic community due to its capability to effectively capture salient objects by leveraging visual and spatial information. However, existing RGB-D detection models face several key challenges. First, efficiently utilizing and fusing multi-modal information from RGB and depth inputs remains a difficult task due to the inherent differences between the two modalities. RGB images provide rich color and texture details but lack depth information, whereas depth maps offer spatial cues but are often noisy or of low quality. Second, achieving accurate boundary detection is particularly challenging in cluttered or noisy environments. Noisy depth maps and cluttered backgrounds can obscure object contours, making it difficult to predict sharp and precise boundaries. These challenges highlight the urgent need for a robust model that can effectively integrate RGB and depth information while simultaneously addressing noise and enhancing boundary precision.MethodAiming to address these challenges, a novel method, the cross-modal feature fusion and detail-enhanced RGB-D salient object detection network (CFADNet), is introduced. The proposed network incorporates two innovative modules: the cross-modal attention fusion enhancement module (CAFEM) and the boundary feature extraction module (BFEM). The CAFEM is designed to enhance the integration of RGB and depth features by leveraging attention mechanisms that emphasize the most informative aspects of each modality. Specifically, channel attention is applied to the RGB features to suppress noise and enhance critical color and texture details. Similarly, spatial attention is applied to the depth features to emphasize spatial regions that are relevant for salient object detection. This attention-based fusion mechanism ensures that the model effectively retains global semantic information from the depth map while preserving fine-grained details from the RGB image. The fusion process is structured in multiple layers, progressively integrating features at different scales to fully utilize the complementary strengths of RGB and depth modalities. In contrast, the BFEM is specifically designed to improve the accuracy of salient object boundaries. Accurate contour detection is crucial for generating high-quality saliency maps; thus, BFEM leverages low-level CNN features, which are rich in edge and texture information. These features are refined through channel attention, which filters out noise and irrelevant details, enhancing the clarity of boundary-related cues. The refined features are then used to guide cross-modal feature decoding, ensuring that the final saliency maps exhibit sharp and accurate boundaries. By combining the edge-extraction capabilities of low-level CNN features with the semantic richness of cross-modal features, BFEM notably improves boundary precision in RGB-D salient object detection.ResultAiming to evaluate the performance of CFADNet, extensive experiments are conducted on four widely used RGB-D salient object detection datasets: NJU2K, NLPR, STERE, and SIP. These datasets encompass a wide range of diverse and challenging scenes, making them ideal for evaluating the generalization capability of the proposed model. CFADNet is compared against 16 state-of-the-art RGB-D salient object detection methods, including DCF, CIRNet, and CAVER, using standard quantitative metrics such as mean absolute error (MAE), F-measure(Fβ), and structural similarity (Sα). CFADNet demonstrated superior performance across all datasets, particularly excelling in the MAE metric. Specifically, this network outperformed the second-best method by 6.9%, 10.5%, 9.7%, and 2.4% on the NJU2K, NLPR, STERE, and SIP datasets, respectively. These substantial improvements highlight the effectiveness of the attention-based fusion strategy and edge refinement mechanisms. Furthermore, CFADNet consistently achieved higher F-measure and Sα scores, indicating that the model not only reduces pixel-level errors but also more accurately preserves the overall structure and shape of salient objects compared to competing methods. In addition to quantitative evaluations, qualitative comparisons are conducted to visually assess the performance of CFADNet in various challenging scenarios. Results show that the proposed method generates saliency maps with sharp and accurate boundaries, even in cases where salient objects exhibit complex edges or are embedded in cluttered and noisy backgrounds. This finding demonstrates the robustness of CFADNet in handling difficult scenes by effectively separating salient objects from their background while preserving fine boundary details. The visual results further confirm that CFADNet successfully captures global semantic information and local detail, ensuring accurate identification and clear isolation of salient objects from the background.ConclusionThis paper presents CFADNet, a cross-modal feature fusion and detail-enhancement network for RGB-D SOD, designed to address the two major challenges: effective multimodal feature fusion and accurate boundary detection. CFADNet introduces two novel modules, the CAFEM and the BFEM. CFADNet effectively integrates RGB and depth information while notably enhancing the precision of salient object boundaries. The attention mechanisms used in the CAF0EM enable the network to fully leverage the complementary information from RGB and depth modalities. Simultaneously, the BFEM module focuses on refining edge details, resulting in sharper and more accurate saliency predictions. Extensive experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that CFADNet consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance across key evaluation metric, including MAE, F-measure, and structural similarity index. These findings highlight the robustness and strong generalization capability of CFADNet in diverse and challenging environments. By combining attention-based feature fusion with effective edge refinement, CFADNet emerges as a powerful and reliable solution for RGB-D salient object detection into complex scenarios. Future research could explore extending this approach to other multi-modal tasks, such as RGB-Thermal or multi-spectral image processing, where challenges related to multi-modal fusion and boundary detection are also prevalent. Additionally, optimizing the computational efficiency of CFADNet for real-time deployment represents a potential research direction, enabling its application in time-sensitive applications such as autonomous driving and robotics.关键词:salient object detection(SOD);attention mechanism;cross-modal;feature fusion;edge detail-enhancement255|198|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在弱监督语义分割领域,研究者提出了基于知识蒸馏的端到端框架,通过双阶段知识交互和高斯修正模块,有效降低噪声干扰,提升伪标签质量,展现出优越性能。”
 摘要:ObjectiveWeakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) aims to reduce the cost associated with annotating “strong” pixel-level labels by using “weak” labels, such as points, bounding boxes, image-level class labels, and scribbles. Among these, image-level class labels are the most cost-effective and readily available; however, leveraging them for precise segmentation remains a considerable challenge. A widely used WSSS approach based on image-level class labels generally comprises the following steps: 1) training a neural network for image classification using the class labels; 2) using the trained network to generate class activation maps (CAMs), which serve as seed regions for the segmentation task; and 3) refining these CAMs into pseudo-labels, which are then used as the ground truth to supervise a segmentation network. These steps can be integrated into a single collaborative stage; typically, single-stage frameworks are highly efficient due to their simplified training pipeline. However, the quality of pseudo-labels is crucial to the overall performance of semantic segmentation. High-quality pseudo-labels result in superior segmentation outcomes, whereas noisy or inaccurate pseudo-labels hinder the capability of the model to learn meaningful features. WSSS based on image-level labels faces considerable challenges due to the absence of precise positional and shape-related information, making it difficult to generate accurate segmentation maps. These challenges have led to the development of various approaches, which can be broadly categorized into two types: single-stage methods and multistage methods. Although single-stage methods offer greater efficiency and simplify the overall training process, they often produce less accurate pseudo-labels. This condition is due to the limited refinement of CAMs, resulting in imprecise supervision signals that ultimately degrade segmentation performance. Aiming to alleviate these limitations, a simple yet novel single-stage WSSS framework that incorporates knowledge distillation is introduced to enhance pseudo-label quality without relying on any additional external supervision. The framework enhances the feature learning process within the teacher-student network using a dual-stage knowledge distillation module. This module allows the student network to acquire more dynamic and informative knowledge from the teacher network while preserving key features, thereby enhancing the overall robustness of the student model. Moreover, to further improve segmentation accuracy, a pseudo-label correction module based on a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is introduced. This module refines the pseudo-labels by modeling the distribution of the CAMs, resulting in highly accurate and reliable supervision signals. The combination of dual-stage knowledge distillation and the Gaussian correction module ensures accurate learning and improved segmentation results, even under weak supervision signals such as image-level labels. Ultimately, the proposed method effectively mitigates the impact of noise during training and enhances the accuracy of the generated pseudo-labels, resulting in superior semantic segmentation outcomes in WSSS tasks.MethodA novel weakly-supervised semantic segmentation method, aimed at addressing the challenges posed by noisy data points and weak supervision, is proposed. First, a dual-stage knowledge interaction module is introduced to enhance the feature learning process of the teacher and student networks. By enabling highly effective knowledge exchange between the two networks, the proposed approach notably reduces the impact of noise during training, leading to robust feature extraction. Additionally, a Gaussian correction module is proposed to enhance the quality of pseudo-labels. This module refines the pseudo-labels by modeling the distribution of class activation maps. By fitting the distribution more accurately, the module corrects potential errors in the pseudo-labels, ensuring that the model learns from high-quality, refined labels. Therefore, the method boosts the overall performance of weakly-supervised semantic segmentation, making it more robust to noise and improving segmentation accuracy. This method provides a promising solution for weakly-supervised segmentation tasks.ResultThe mIoU values of this method on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets were 74.8% and 42.3%, respectively, surpassing other comparative methods. Specifically, on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset, the proposed method achieved a 3.7% improvement over ToCo, an 8.8% enhancement compared to AFA, a 7.5% increase relative to TSCD, and 1.1% compared to BECO. On the MS COCO 2014 dataset, the method improved performance by 2.2% compared to TSCD, 3.4% compared to AFA, and 5.3% compared to AuxSegNet+. Additionally, the mIoU values of different categories are compared on the PASCAL VOC 2012 validation set. The experimental results showed that the method outperformed the competing methods in 16 categories. Notably, for the background class, the method achieved an mIoU of 92.4%, the highest among all methods evaluated. This result indicates that the method effectively leverages the Gaussian correction module to reduce misclassification of background regions, thereby improving segmentation performance. Furthermore, the method achieved notable improvements in categories such as bird, bottle, car, chair, and cow, further demonstrating its effectiveness.ConclusionThe proposed method effectively mitigates the impact of noise during training and address the issue of incomplete pseudo-label generation through the integration of a dual-stage knowledge distillation module and a Gaussian correction module. This approach achieves remarkable performance improvements compared to existing methods. Overall, the results demonstrate notable advantages in end-to-end weakly supervised semantic segmentation and holds considerable research value.关键词:deep learning;end-to-end weakly supervised semantic segmentation;Gaussian mixture model (GMM);knowledge distillation;class activation map (CAM)90|108|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveWeakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) aims to reduce the cost associated with annotating “strong” pixel-level labels by using “weak” labels, such as points, bounding boxes, image-level class labels, and scribbles. Among these, image-level class labels are the most cost-effective and readily available; however, leveraging them for precise segmentation remains a considerable challenge. A widely used WSSS approach based on image-level class labels generally comprises the following steps: 1) training a neural network for image classification using the class labels; 2) using the trained network to generate class activation maps (CAMs), which serve as seed regions for the segmentation task; and 3) refining these CAMs into pseudo-labels, which are then used as the ground truth to supervise a segmentation network. These steps can be integrated into a single collaborative stage; typically, single-stage frameworks are highly efficient due to their simplified training pipeline. However, the quality of pseudo-labels is crucial to the overall performance of semantic segmentation. High-quality pseudo-labels result in superior segmentation outcomes, whereas noisy or inaccurate pseudo-labels hinder the capability of the model to learn meaningful features. WSSS based on image-level labels faces considerable challenges due to the absence of precise positional and shape-related information, making it difficult to generate accurate segmentation maps. These challenges have led to the development of various approaches, which can be broadly categorized into two types: single-stage methods and multistage methods. Although single-stage methods offer greater efficiency and simplify the overall training process, they often produce less accurate pseudo-labels. This condition is due to the limited refinement of CAMs, resulting in imprecise supervision signals that ultimately degrade segmentation performance. Aiming to alleviate these limitations, a simple yet novel single-stage WSSS framework that incorporates knowledge distillation is introduced to enhance pseudo-label quality without relying on any additional external supervision. The framework enhances the feature learning process within the teacher-student network using a dual-stage knowledge distillation module. This module allows the student network to acquire more dynamic and informative knowledge from the teacher network while preserving key features, thereby enhancing the overall robustness of the student model. Moreover, to further improve segmentation accuracy, a pseudo-label correction module based on a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is introduced. This module refines the pseudo-labels by modeling the distribution of the CAMs, resulting in highly accurate and reliable supervision signals. The combination of dual-stage knowledge distillation and the Gaussian correction module ensures accurate learning and improved segmentation results, even under weak supervision signals such as image-level labels. Ultimately, the proposed method effectively mitigates the impact of noise during training and enhances the accuracy of the generated pseudo-labels, resulting in superior semantic segmentation outcomes in WSSS tasks.MethodA novel weakly-supervised semantic segmentation method, aimed at addressing the challenges posed by noisy data points and weak supervision, is proposed. First, a dual-stage knowledge interaction module is introduced to enhance the feature learning process of the teacher and student networks. By enabling highly effective knowledge exchange between the two networks, the proposed approach notably reduces the impact of noise during training, leading to robust feature extraction. Additionally, a Gaussian correction module is proposed to enhance the quality of pseudo-labels. This module refines the pseudo-labels by modeling the distribution of class activation maps. By fitting the distribution more accurately, the module corrects potential errors in the pseudo-labels, ensuring that the model learns from high-quality, refined labels. Therefore, the method boosts the overall performance of weakly-supervised semantic segmentation, making it more robust to noise and improving segmentation accuracy. This method provides a promising solution for weakly-supervised segmentation tasks.ResultThe mIoU values of this method on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets were 74.8% and 42.3%, respectively, surpassing other comparative methods. Specifically, on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset, the proposed method achieved a 3.7% improvement over ToCo, an 8.8% enhancement compared to AFA, a 7.5% increase relative to TSCD, and 1.1% compared to BECO. On the MS COCO 2014 dataset, the method improved performance by 2.2% compared to TSCD, 3.4% compared to AFA, and 5.3% compared to AuxSegNet+. Additionally, the mIoU values of different categories are compared on the PASCAL VOC 2012 validation set. The experimental results showed that the method outperformed the competing methods in 16 categories. Notably, for the background class, the method achieved an mIoU of 92.4%, the highest among all methods evaluated. This result indicates that the method effectively leverages the Gaussian correction module to reduce misclassification of background regions, thereby improving segmentation performance. Furthermore, the method achieved notable improvements in categories such as bird, bottle, car, chair, and cow, further demonstrating its effectiveness.ConclusionThe proposed method effectively mitigates the impact of noise during training and address the issue of incomplete pseudo-label generation through the integration of a dual-stage knowledge distillation module and a Gaussian correction module. This approach achieves remarkable performance improvements compared to existing methods. Overall, the results demonstrate notable advantages in end-to-end weakly supervised semantic segmentation and holds considerable research value.关键词:deep learning;end-to-end weakly supervised semantic segmentation;Gaussian mixture model (GMM);knowledge distillation;class activation map (CAM)90|108|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在人体姿态估计领域,专家提出了自适应真值热力图生成方法,有效提高了关键点检测准确率。”
 摘要:ObjectiveHuman pose estimation aims to locate skeletal keypoints of individuals in a given image. As a fundamental task in computer vision, human pose estimation has wide applications in human activity recognition, person re-identification, pose tracking, and related fields. Two main approaches for human pose estimation are available: top-down and bottom-up. Top-down methods first detect human bodies in the image, crop out each person, and then estimate the keypoint coordinates. While effective, these methods perform poorly in cases of occlusion, and their computation cost increases with the number of people in the image. In contrast, bottom-up methods detect all identity-independent keypoints simultaneously and then group them into individual poses. These methods are typically lightweight and fast but must handle varying human scales. Bottom-up human pose estimation methods commonly use 2D Gaussian kernels to generate keypoint heatmaps as regression targets because they provide rich spatial information. However, conventional approaches apply Gaussian kernels with a fixed variance across all keypoints, resulting in uniform heatmap structures. This uniformity is problematic given the existing scale variability in bottom-up methods. On the one hand, different keypoints cover different pixel areas in images, and using large Gaussian kernels may introduce semantic ambiguity, particularly for small joints. On the other hand, differences in keypoint scale imply different levels of annotation uncertainty, which the heatmap variance should ideally reflect. The variance of the Gaussian kernel represents uncertainty; thus, it should be proportional to the scale and ambiguity associated with each keypoint. Aiming to address these issues, an adaptive heatmap generation network (AHGNet) for bottom-up human pose estimation is proposed. AHGNet estimates the appropriate radius of the Gaussian kernel for each keypoint by integrating inherent scale information and geometric relationships. Through formula derivation, the relationship between the radius and the Gaussian kernel variance is established, enabling the creation of customized, scale-adaptive ground-truth heatmaps. This approach improves localization accuracy by effectively aligning the heatmap structure with the spatial characteristics of each keypoint.MethodFirst, an adaptive heatmap generation module is introduced. This module combines the inherent scale information from image features and the geometric relationship between adjacent keypoints to constrain the coverage areas of kernels. Keypoint scale is defined by semantic coverage areas in images. However, in the actual scene, accurately allowing pixel areas to occupy keypoints is almost impossible, and determining the potential relationship between Gaussian kernels and coverage areas is difficult. Interestingly, the areas occupied by keypoints are found to be related to geometric distance from adjacent keypoints. Therefore, an adaptive heatmap generation module is introduced to generate kernel scale maps of keypoints. This module combine the geometric relationship between adjacent keypoints and inherent scale information from image features. Second, local probabilistic consistency loss is presented to define the distance between the predicted and ground truth heatmaps globally and locally. Most methods based on heatmap regression use L2 loss for supervised learning. However, as the loss function for heatmap regression, L2 loss assumes that each pixel point is independent and overlooks the local structural correlation, making it difficult to describe the probability distribution of heatmaps. A keypoint heatmap is a probability distribution that describes pixels belonging to a certain joint. Thus, KL Divergence must be added to describe local probability consistency. Moreover, samples with large prediction errors are difficult to predict; thus, the weight of difficult samples should be increased. Similarly, the weight of easily detected samples should be reduced. Therefore, the dynamic weight is added to balance the contribution of different samples. Inspired by focal loss, which allows the model to actively focus on hard-to-detect samples, this paper utilizes dynamic weights to reduce the contribution of easily detected samples while enhancing the contribution of hard-to-detect samples.ResultHrHRNet is used as the baseline to establish AHGNet for bottom-up human pose estimation. The model is tested on two public datasets: MS COCO and CrowdPose. Experimental results reveal that AHGNet surpasses HrHRNet in terms of average precision (AP), achieving 72.1% AP and 74.1% AP on COCO test-dev and CrowdPose dataset, providing improvements of +1.6% AP and +6.5% AP, respectively. In addition, the substantial improvement on the CrowdPose dataset with crowded scenes indicates that AHGNet helps alleviate the problem of human scale changes in complex crowded scenes. Simultaneously, the ablation experiments verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.ConclusionAHGNet leverages geometric features between adjacent keypoints and inherent scale information within the image to generate adaptive heatmaps as groundtruth. This network further employs a local probability consistency loss function to address the challenges posed by various human scales, effectively improving the accuracy of bottom-up human pose estimation. AHGNet provides a new paradigm for optimizing supervision signals in bottom-up pose estimation. By dynamically adjusting the Gaussian kernel scale and enforcing local probability constraints, it effectively reduces multiscale ambiguity in complex scenarios.关键词:human pose estimation;adaptive scale;bottom-up;heatmap regression;dynamic weight88|105|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveHuman pose estimation aims to locate skeletal keypoints of individuals in a given image. As a fundamental task in computer vision, human pose estimation has wide applications in human activity recognition, person re-identification, pose tracking, and related fields. Two main approaches for human pose estimation are available: top-down and bottom-up. Top-down methods first detect human bodies in the image, crop out each person, and then estimate the keypoint coordinates. While effective, these methods perform poorly in cases of occlusion, and their computation cost increases with the number of people in the image. In contrast, bottom-up methods detect all identity-independent keypoints simultaneously and then group them into individual poses. These methods are typically lightweight and fast but must handle varying human scales. Bottom-up human pose estimation methods commonly use 2D Gaussian kernels to generate keypoint heatmaps as regression targets because they provide rich spatial information. However, conventional approaches apply Gaussian kernels with a fixed variance across all keypoints, resulting in uniform heatmap structures. This uniformity is problematic given the existing scale variability in bottom-up methods. On the one hand, different keypoints cover different pixel areas in images, and using large Gaussian kernels may introduce semantic ambiguity, particularly for small joints. On the other hand, differences in keypoint scale imply different levels of annotation uncertainty, which the heatmap variance should ideally reflect. The variance of the Gaussian kernel represents uncertainty; thus, it should be proportional to the scale and ambiguity associated with each keypoint. Aiming to address these issues, an adaptive heatmap generation network (AHGNet) for bottom-up human pose estimation is proposed. AHGNet estimates the appropriate radius of the Gaussian kernel for each keypoint by integrating inherent scale information and geometric relationships. Through formula derivation, the relationship between the radius and the Gaussian kernel variance is established, enabling the creation of customized, scale-adaptive ground-truth heatmaps. This approach improves localization accuracy by effectively aligning the heatmap structure with the spatial characteristics of each keypoint.MethodFirst, an adaptive heatmap generation module is introduced. This module combines the inherent scale information from image features and the geometric relationship between adjacent keypoints to constrain the coverage areas of kernels. Keypoint scale is defined by semantic coverage areas in images. However, in the actual scene, accurately allowing pixel areas to occupy keypoints is almost impossible, and determining the potential relationship between Gaussian kernels and coverage areas is difficult. Interestingly, the areas occupied by keypoints are found to be related to geometric distance from adjacent keypoints. Therefore, an adaptive heatmap generation module is introduced to generate kernel scale maps of keypoints. This module combine the geometric relationship between adjacent keypoints and inherent scale information from image features. Second, local probabilistic consistency loss is presented to define the distance between the predicted and ground truth heatmaps globally and locally. Most methods based on heatmap regression use L2 loss for supervised learning. However, as the loss function for heatmap regression, L2 loss assumes that each pixel point is independent and overlooks the local structural correlation, making it difficult to describe the probability distribution of heatmaps. A keypoint heatmap is a probability distribution that describes pixels belonging to a certain joint. Thus, KL Divergence must be added to describe local probability consistency. Moreover, samples with large prediction errors are difficult to predict; thus, the weight of difficult samples should be increased. Similarly, the weight of easily detected samples should be reduced. Therefore, the dynamic weight is added to balance the contribution of different samples. Inspired by focal loss, which allows the model to actively focus on hard-to-detect samples, this paper utilizes dynamic weights to reduce the contribution of easily detected samples while enhancing the contribution of hard-to-detect samples.ResultHrHRNet is used as the baseline to establish AHGNet for bottom-up human pose estimation. The model is tested on two public datasets: MS COCO and CrowdPose. Experimental results reveal that AHGNet surpasses HrHRNet in terms of average precision (AP), achieving 72.1% AP and 74.1% AP on COCO test-dev and CrowdPose dataset, providing improvements of +1.6% AP and +6.5% AP, respectively. In addition, the substantial improvement on the CrowdPose dataset with crowded scenes indicates that AHGNet helps alleviate the problem of human scale changes in complex crowded scenes. Simultaneously, the ablation experiments verified the effectiveness of the proposed method.ConclusionAHGNet leverages geometric features between adjacent keypoints and inherent scale information within the image to generate adaptive heatmaps as groundtruth. This network further employs a local probability consistency loss function to address the challenges posed by various human scales, effectively improving the accuracy of bottom-up human pose estimation. AHGNet provides a new paradigm for optimizing supervision signals in bottom-up pose estimation. By dynamically adjusting the Gaussian kernel scale and enforcing local probability constraints, it effectively reduces multiscale ambiguity in complex scenarios.关键词:human pose estimation;adaptive scale;bottom-up;heatmap regression;dynamic weight88|105|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在煤矿图像处理领域,专家提出了基于自适应掩码的矿井图像自监督去噪算法,有效去除噪声并保留图像细节,展现出优越的鲁棒性和广泛的适用性。”
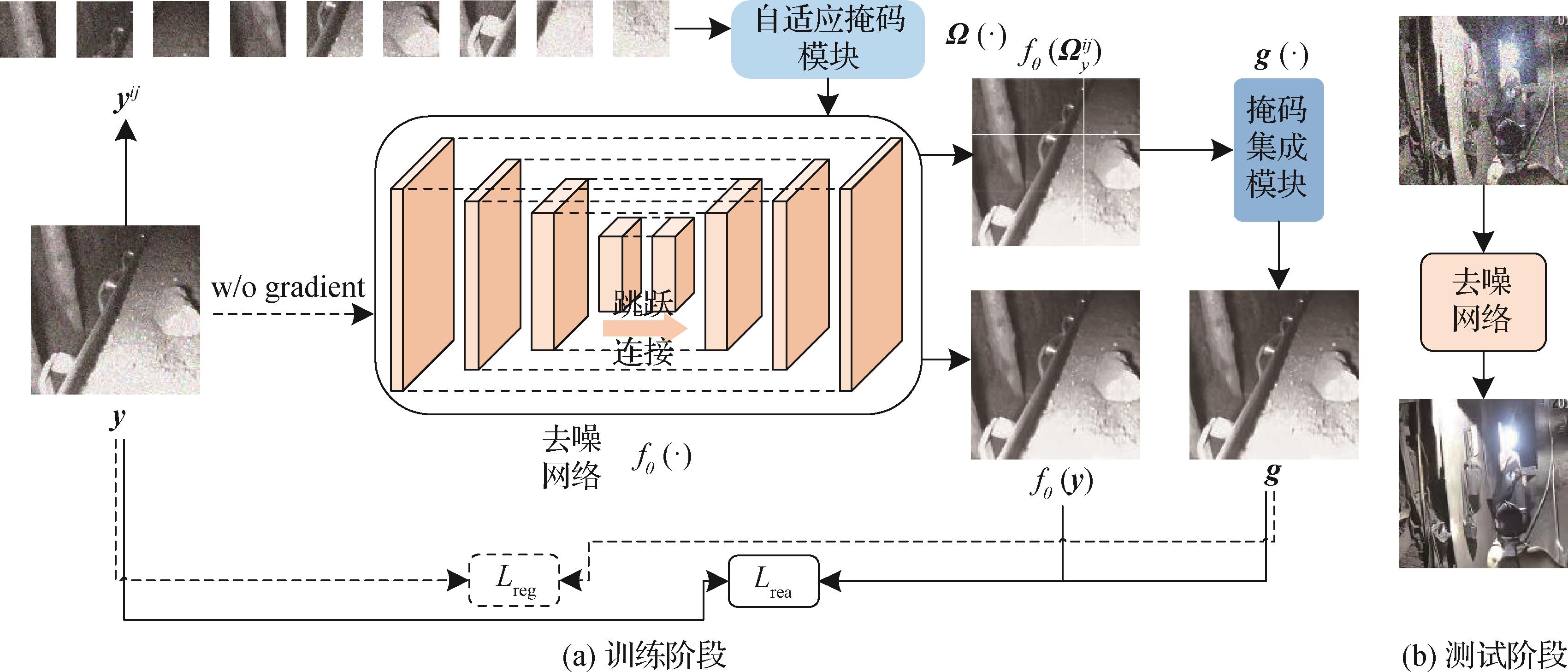 摘要:ObjectiveThe objective of this research is to enhance the quality and accuracy of information extracted from coal mine images, which are often degraded by high dust concentrations and uneven lighting conditions. These challenging environmental conditions introduce noise, reduce local contrast, and lead to the loss of fine details and edge textures, ultimately compromising the visual quality and the reliability of information extraction. Aiming to address these challenges, this study proposes a self-supervised coal mine image denoising algorithm based on adaptive masking. Designed to handle a wide range of noise levels and types, this algorithm aims to restore the original integrity of the image while preserving critical visual features. The proposed algorithm is divided into three main components: adaptive masking, mask integration, and an adaptive integrated loss function. Each component plays a vital role in enhancing the denoising process, ensuring that the final output is accurate and visually appealing.MethodThe adaptive masking component is the cornerstone of the proposed algorithm, enabling segmented processing of coal mine images. This segmentation not only reduces computational overhead but also allows for more targeted and effective denoising. By dividing each image into smaller blocks, the algorithm can analyze and process each section independently, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the denoising process. The module operates by sequentially applying a mask to the edge and corner pixels of each block, while deliberately excluding the central pixels. This method prevents the network from performing a trivial identity mapping that fails to enhance image quality. Instead, this approach introduces data variability that boosts the generalization capability and robustness of the neural network model, making it adaptable to previously unknown images. The adaptive nature of the mask ensures that the module responds dynamically to varying noise levels and image features. By analyzing local variance and texture complexity, the mask can adaptively determine the optimal masking strategy for each block. This tailored approach ensures that the denoising process is responsive to the specific characteristics of each image, substantially improving its effectiveness. Subsequently, once the masking process is complete, the mask integration module is employed. This module is responsible for fusing the neural network’s output with the masked areas to reconstruct a coherent and denoised image. The integration involves calculating the Hadamard product (element-wise multiplication) between the network’s output and the masked image. This strategic operation enhances the network’s capability to distinguish between actual image content and noise, especially around edges and texture boundaries. In this stage, considering local and global features of the coal mine images is crucial. Effective integration of these features allows the algorithm effectively interpret image context, leading in denoised outputs that are coherent and structurally complete. The mask integration module also ensures that denoised areas seamlessly blend into the rest of the image, preserving the overall visual flow and structural integrity. Furthermore, this module incorporates a quality evaluation mechanism to assess the effectiveness of the integration. The feedback from these evaluations is used to iteratively refine the integration process. The final component of the algorithm is an adaptive integrated loss function, which guides the model during training. This loss function is specifically designed to address the unique challenges of coal mine image denoising, including complex noise patterns and the need to preserve subtle image details. The adaptive integrated loss uses the integrated image as a training label, allowing the model to learn effectively from the differences between the noisy input images and the denoised outputs. Additionally, by incorporating the original noisy image, the loss function increases the model’s sensitivity to signal changes, enhancing its adaptability across various denoising scenarios and noise conditions.ResultThe proposed algorithm was rigorously tested using an underground coal mine image dataset alongside four additional public datasets, including Kodak24 (Kodak lossless true color image suite), BSD300 (Berkeley segmentation dataset 300), and BSDS500 (Berkeley segmentation dataset 500). The experiments were specifically designed to simulate real-world conditions, with a particular emphasis on dimly lit environments commonly encountered in coal mines. The results of these experiments demonstrated that the algorithm substantially outperformed other comparative denoising algorithms, in terms of subjective evaluations and objective metrics such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM). In tunnel scenes with a high level of Gaussian noise (level 50), the algorithm achieved substantial improvements in PSNR/SSIM values compared to existing methods such as B2U and NBR2NBR, with increases of 4.2 dB/0.055 and 2.99 dB/0.077, respectively. Furthermore, when tested on images corrupted with Gaussian noise levels ranging from 5 to 50 on the public datasets, the algorithm consistently demonstrated substantial PSNR improvements over the second-best method, with increases of 1.09%, 0.72%, and 0.68% for Kodak24, BSD300, and BSDS500, respectively.ConclusionThe proposed self-supervised denoising algorithm has demonstrated a strong capability to remove noise while preserving overall image information from single coal mine images, across various noise levels and types. This finding highlights the algorithm’s robustness and generalization capabilities, making it a promising tool for real-world applications in coal mine monitoring and safety systems. The effectiveness of the algorithm in enhancing image quality and improving the accuracy of information extraction, even under challenging conditions, underscores its potential to make a substantial contribution to the field of coal mine image processing and analysis.The code in this paper can be obtained by https://www.sciclb.cn/anonymous/skpswk56.关键词:self-supervised learning;mine image denoising;adaptive masking;Hadamard product;adaptive integrated loss109|145|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveThe objective of this research is to enhance the quality and accuracy of information extracted from coal mine images, which are often degraded by high dust concentrations and uneven lighting conditions. These challenging environmental conditions introduce noise, reduce local contrast, and lead to the loss of fine details and edge textures, ultimately compromising the visual quality and the reliability of information extraction. Aiming to address these challenges, this study proposes a self-supervised coal mine image denoising algorithm based on adaptive masking. Designed to handle a wide range of noise levels and types, this algorithm aims to restore the original integrity of the image while preserving critical visual features. The proposed algorithm is divided into three main components: adaptive masking, mask integration, and an adaptive integrated loss function. Each component plays a vital role in enhancing the denoising process, ensuring that the final output is accurate and visually appealing.MethodThe adaptive masking component is the cornerstone of the proposed algorithm, enabling segmented processing of coal mine images. This segmentation not only reduces computational overhead but also allows for more targeted and effective denoising. By dividing each image into smaller blocks, the algorithm can analyze and process each section independently, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the denoising process. The module operates by sequentially applying a mask to the edge and corner pixels of each block, while deliberately excluding the central pixels. This method prevents the network from performing a trivial identity mapping that fails to enhance image quality. Instead, this approach introduces data variability that boosts the generalization capability and robustness of the neural network model, making it adaptable to previously unknown images. The adaptive nature of the mask ensures that the module responds dynamically to varying noise levels and image features. By analyzing local variance and texture complexity, the mask can adaptively determine the optimal masking strategy for each block. This tailored approach ensures that the denoising process is responsive to the specific characteristics of each image, substantially improving its effectiveness. Subsequently, once the masking process is complete, the mask integration module is employed. This module is responsible for fusing the neural network’s output with the masked areas to reconstruct a coherent and denoised image. The integration involves calculating the Hadamard product (element-wise multiplication) between the network’s output and the masked image. This strategic operation enhances the network’s capability to distinguish between actual image content and noise, especially around edges and texture boundaries. In this stage, considering local and global features of the coal mine images is crucial. Effective integration of these features allows the algorithm effectively interpret image context, leading in denoised outputs that are coherent and structurally complete. The mask integration module also ensures that denoised areas seamlessly blend into the rest of the image, preserving the overall visual flow and structural integrity. Furthermore, this module incorporates a quality evaluation mechanism to assess the effectiveness of the integration. The feedback from these evaluations is used to iteratively refine the integration process. The final component of the algorithm is an adaptive integrated loss function, which guides the model during training. This loss function is specifically designed to address the unique challenges of coal mine image denoising, including complex noise patterns and the need to preserve subtle image details. The adaptive integrated loss uses the integrated image as a training label, allowing the model to learn effectively from the differences between the noisy input images and the denoised outputs. Additionally, by incorporating the original noisy image, the loss function increases the model’s sensitivity to signal changes, enhancing its adaptability across various denoising scenarios and noise conditions.ResultThe proposed algorithm was rigorously tested using an underground coal mine image dataset alongside four additional public datasets, including Kodak24 (Kodak lossless true color image suite), BSD300 (Berkeley segmentation dataset 300), and BSDS500 (Berkeley segmentation dataset 500). The experiments were specifically designed to simulate real-world conditions, with a particular emphasis on dimly lit environments commonly encountered in coal mines. The results of these experiments demonstrated that the algorithm substantially outperformed other comparative denoising algorithms, in terms of subjective evaluations and objective metrics such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM). In tunnel scenes with a high level of Gaussian noise (level 50), the algorithm achieved substantial improvements in PSNR/SSIM values compared to existing methods such as B2U and NBR2NBR, with increases of 4.2 dB/0.055 and 2.99 dB/0.077, respectively. Furthermore, when tested on images corrupted with Gaussian noise levels ranging from 5 to 50 on the public datasets, the algorithm consistently demonstrated substantial PSNR improvements over the second-best method, with increases of 1.09%, 0.72%, and 0.68% for Kodak24, BSD300, and BSDS500, respectively.ConclusionThe proposed self-supervised denoising algorithm has demonstrated a strong capability to remove noise while preserving overall image information from single coal mine images, across various noise levels and types. This finding highlights the algorithm’s robustness and generalization capabilities, making it a promising tool for real-world applications in coal mine monitoring and safety systems. The effectiveness of the algorithm in enhancing image quality and improving the accuracy of information extraction, even under challenging conditions, underscores its potential to make a substantial contribution to the field of coal mine image processing and analysis.The code in this paper can be obtained by https://www.sciclb.cn/anonymous/skpswk56.关键词:self-supervised learning;mine image denoising;adaptive masking;Hadamard product;adaptive integrated loss109|145|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “最新研究揭示行人轨迹预测新方法,PSEN网络结合社会约束与轨迹终点,显著提升预测准确性。”
 摘要:ObjectivePedestrian trajectory prediction constitutes a critical research challenge in autonomous driving systems, intelligent security surveillance, and human-robot interaction frameworks. The capability to accurately anticipate pedestrian movement patterns directly influences the operational safety of autonomous vehicles, the responsiveness of surveillance systems, and the adaptability of social robots in dynamic environments. While existing approaches predominantly focus on leveraging sequential data patterns and optimizing model architectures through recurrent neural networks, they often overlook the intrinsic social-semantic characteristics embedded in real-world pedestrian interactions. Current methodologies tend to treat trajectory prediction as a purely sequential modeling task, overlooking three fundamental aspects: 1) the social constraints governing crowd movement patterns, 2) the intentional, destination-oriented nature of human locomotion, and 3) the dynamic adaptation mechanisms pedestrians employ during path navigation. This oversight leads to suboptimal performance, particularly in dense pedestrian scenarios where social interactions and environmental adaptability notably influence movement decisions. Aiming to address these limitations, this paper proposes path stepwise estimation network (PSEN), a novel framework that systematically integrates social relationship modeling, endpoint-aware trajectory planning, and environment-adaptive path refinement. The proposed model bridges the gap between conventional sequence prediction paradigms and the complex socio-spatial dynamics inherent in real-world pedestrian navigation scenarios.MethodThis paper incorporates the characteristics of path planning observed in daily human walking, which can be broadly divided into three key aspects. First, social restrictions are considered. The crowd is categorized based on movement direction, speed, and distance to demonstrate these reflections. Intra-class feature learning is then performed on the classified groups. The social relationships between predicted pedestrians and other pedestrians are calculated using social weights to obtain social attention, which affects the subsequent path estimation network. Second, an endpoint estimation network is introduced by stimulating the feature that pedestrians typically identify a destination and then purposefully plan their walking path. This network leverages the strengths of serialized prediction tasks by using spatiotemporal sequences to predict an endpoint. The estimated endpoint serves as a reference condition within the overall network model, guiding the complete path planning process. Third, this paper address the fact that pedestrians constantly fine-tune their local paths and adjust their focus based on environmental context and destination. Aiming to model this behavior, an endpoint and path fine-tuning network is constructed using conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) and multilayer perceptron (MLP). This module takes the output of the endpoint estimation network as a condition and uses the output from the social restriction module, along with the historical trajectory, as inputs for feature learning. After every three frames of prediction, the social restriction and endpoint module outputs are updated according to the current environment of the pedestrians. This update allows the model to automatically fine-tune the planned path in response to dynamic surroundings.ResultThe experiments are conducted by comparing the proposed method with six baseline methods on the ETH/UCY dataset, five baseline methods on the SDD dataset, and four baseline methods on the NBA SportVU dataset. The evaluation metrics used are average displacement error (ADE) and final displacement error (FDE). On the entire ETH/UCY dataset, ADE and FDE are reduced by an average of 5.1% and 7.5%, respectively. On the SDD dataset, reductions of 1% in ADE and 2% in FDE are observed on average. When analyzing individual datasets, the performance improvements are highly pronounced in scenarios with denser pedestrian traffic. Notably, in the ZARA1, ZARA2, and UNIV datasets, the proposed method achieves improvements of over 10% in prediction accuracy. Ablation experiments are also conducted on the ETH/UCY dataset to evaluate the contributions of individual components of the PSEN framework. The experimental results demonstrate that each module of PSEN notably improves the effectiveness of pedestrian trajectory prediction, achieving average reductions of 19% and 31% in ADE and final displacement error FDE, respectively. Ablation experiments are performed in parameters such as social distance, social attention weights, and the number of frames used in stepwise trajectory generation. These experiments confirm that all aspects of the network design positively impact pedestrian trajectory prediction. However, the model does not perform as well on the NBAsportVU dataset. This dataset is characterized by 10 players moving at high speeds, with trajectory endpoints changing dynamically based on in-game situations and players’ intentions. Different from ETH/UCY and SDD datasets, where movement is predictable and socially constrained, the varying roles and tactical decisions of agent in NBA dataset play a crucial role in path planning, making prediction highly challenging. Therefore, achieving accurate predictions by relying solely on time-position information is difficult because the characteristics of pedestrians in this setting notably differ from those in typical pedestrian scenes. In sports scenes, athletes actively seek collisions and obstructions as part of their strategic movement. PSEN does not consider the role-specific behaviors of agents, limiting its effectiveness in such environments.ConclusionThe PSEN model proposed in this paper integrates the serialization task with three key features of real-world pedestrian scenes. By combining recurrent neural networks with a CVAE, PSEN effectively reflects the complex features of pedestrian trajectory prediction in realistic scenarios. The model achieves superior performance on the ETH/UCY and SDD datasets, providing a new direction for subsequent tasks in pedestrian trajectory prediction. However, this study focuses only on interactions among pedestrians and does not consider the relationship between pedestrians and other objects, such as vehicles and obstacles. In novel environments, or in scenes where pedestrians are sparse but other dynamic or static objects are abundant, the performance of the model may degrade. Further research is needed in terms of the relationships between pedestrians and objects, along with their associated feature information.关键词:pedestrian trajectory prediction;sequential prediction;recurrent neural network (RNN);conditional variational autoencoder(CVAE);social constraints;ETH/UCY dataset84|129|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectivePedestrian trajectory prediction constitutes a critical research challenge in autonomous driving systems, intelligent security surveillance, and human-robot interaction frameworks. The capability to accurately anticipate pedestrian movement patterns directly influences the operational safety of autonomous vehicles, the responsiveness of surveillance systems, and the adaptability of social robots in dynamic environments. While existing approaches predominantly focus on leveraging sequential data patterns and optimizing model architectures through recurrent neural networks, they often overlook the intrinsic social-semantic characteristics embedded in real-world pedestrian interactions. Current methodologies tend to treat trajectory prediction as a purely sequential modeling task, overlooking three fundamental aspects: 1) the social constraints governing crowd movement patterns, 2) the intentional, destination-oriented nature of human locomotion, and 3) the dynamic adaptation mechanisms pedestrians employ during path navigation. This oversight leads to suboptimal performance, particularly in dense pedestrian scenarios where social interactions and environmental adaptability notably influence movement decisions. Aiming to address these limitations, this paper proposes path stepwise estimation network (PSEN), a novel framework that systematically integrates social relationship modeling, endpoint-aware trajectory planning, and environment-adaptive path refinement. The proposed model bridges the gap between conventional sequence prediction paradigms and the complex socio-spatial dynamics inherent in real-world pedestrian navigation scenarios.MethodThis paper incorporates the characteristics of path planning observed in daily human walking, which can be broadly divided into three key aspects. First, social restrictions are considered. The crowd is categorized based on movement direction, speed, and distance to demonstrate these reflections. Intra-class feature learning is then performed on the classified groups. The social relationships between predicted pedestrians and other pedestrians are calculated using social weights to obtain social attention, which affects the subsequent path estimation network. Second, an endpoint estimation network is introduced by stimulating the feature that pedestrians typically identify a destination and then purposefully plan their walking path. This network leverages the strengths of serialized prediction tasks by using spatiotemporal sequences to predict an endpoint. The estimated endpoint serves as a reference condition within the overall network model, guiding the complete path planning process. Third, this paper address the fact that pedestrians constantly fine-tune their local paths and adjust their focus based on environmental context and destination. Aiming to model this behavior, an endpoint and path fine-tuning network is constructed using conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) and multilayer perceptron (MLP). This module takes the output of the endpoint estimation network as a condition and uses the output from the social restriction module, along with the historical trajectory, as inputs for feature learning. After every three frames of prediction, the social restriction and endpoint module outputs are updated according to the current environment of the pedestrians. This update allows the model to automatically fine-tune the planned path in response to dynamic surroundings.ResultThe experiments are conducted by comparing the proposed method with six baseline methods on the ETH/UCY dataset, five baseline methods on the SDD dataset, and four baseline methods on the NBA SportVU dataset. The evaluation metrics used are average displacement error (ADE) and final displacement error (FDE). On the entire ETH/UCY dataset, ADE and FDE are reduced by an average of 5.1% and 7.5%, respectively. On the SDD dataset, reductions of 1% in ADE and 2% in FDE are observed on average. When analyzing individual datasets, the performance improvements are highly pronounced in scenarios with denser pedestrian traffic. Notably, in the ZARA1, ZARA2, and UNIV datasets, the proposed method achieves improvements of over 10% in prediction accuracy. Ablation experiments are also conducted on the ETH/UCY dataset to evaluate the contributions of individual components of the PSEN framework. The experimental results demonstrate that each module of PSEN notably improves the effectiveness of pedestrian trajectory prediction, achieving average reductions of 19% and 31% in ADE and final displacement error FDE, respectively. Ablation experiments are performed in parameters such as social distance, social attention weights, and the number of frames used in stepwise trajectory generation. These experiments confirm that all aspects of the network design positively impact pedestrian trajectory prediction. However, the model does not perform as well on the NBAsportVU dataset. This dataset is characterized by 10 players moving at high speeds, with trajectory endpoints changing dynamically based on in-game situations and players’ intentions. Different from ETH/UCY and SDD datasets, where movement is predictable and socially constrained, the varying roles and tactical decisions of agent in NBA dataset play a crucial role in path planning, making prediction highly challenging. Therefore, achieving accurate predictions by relying solely on time-position information is difficult because the characteristics of pedestrians in this setting notably differ from those in typical pedestrian scenes. In sports scenes, athletes actively seek collisions and obstructions as part of their strategic movement. PSEN does not consider the role-specific behaviors of agents, limiting its effectiveness in such environments.ConclusionThe PSEN model proposed in this paper integrates the serialization task with three key features of real-world pedestrian scenes. By combining recurrent neural networks with a CVAE, PSEN effectively reflects the complex features of pedestrian trajectory prediction in realistic scenarios. The model achieves superior performance on the ETH/UCY and SDD datasets, providing a new direction for subsequent tasks in pedestrian trajectory prediction. However, this study focuses only on interactions among pedestrians and does not consider the relationship between pedestrians and other objects, such as vehicles and obstacles. In novel environments, or in scenes where pedestrians are sparse but other dynamic or static objects are abundant, the performance of the model may degrade. Further research is needed in terms of the relationships between pedestrians and objects, along with their associated feature information.关键词:pedestrian trajectory prediction;sequential prediction;recurrent neural network (RNN);conditional variational autoencoder(CVAE);social constraints;ETH/UCY dataset84|129|0更新时间:2025-12-18
Image Understanding and Computer Vision
- “在3D点云语义-实例联合分割领域,研究者提出了一种基于增强注意力的语义实例联合分割网络,有效融合提取的语义特征与实例特征,其准确性明显优于现有方法。”
 摘要:ObjectiveWith the rapid advancement of 3D sensing technologies such as LiDAR (light detection and ranging) and depth cameras, large-scale 3D point clouds have emerged as a crucial data source for a wide range of applications, including autonomous driving, robotic navigation, augmented reality, and urban scene reconstruction. Compared to 2D images, point clouds offer precise spatial geometry and provide a comprehensive representation of the environment without perspective distortion. Additionally, they are robust to variations in lighting and texture. Point cloud segmentation plays a crucial role in scene analysis and interpretation. The segmentation can be categorized into three types: semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, and joint semantic-instance segmentation. Semantic segmentation partitions a 3D scene into informative regions and assigns each region to a specific class. Instance segmentation identifies and separates individual objects at the point level, including those that belong to the same semantic category. In recent years, researchers have increasingly focused on combining the two tasks to achieve more consistent and informative scene-level interpretations. Joint semantic-instance segmentation leverages the intrinsic correlation between semantic and instance-level segmentation, enabling the two tasks to complement and reinforce each other. In 3D point cloud contexts, this joint approach substantially improves the capability of the system to comprehend complex environments and offers strong technical support for the development of intelligent systems. Consequently, this approach has become an area of growing interest and active research. However, most existing methods for joint semantic-instance segmentation rely on simplistic feature fusion strategies, which limit their effectiveness in fully capturing the potential relationship between semantic and instance features. Aiming to address this limitation, an enhanced attention-based joint semantic-instance segmentation network is proposed. This network is designed to effectively model and utilize the correlation between semantic and instance information.MethodThe enhanced attention-based joint semantic-instance segmentation neural network (EAJS-Net) incorporates a semantic feature extraction module based on an attention mechanism. This module focuses on the local neighborhood of each point and dynamically adjusts attention weights to emphasize key information, thereby enhancing the extraction of semantic features across points. Additionally, an attention-enhanced semantic/instance feature fusion module is introduced, which adaptively learns the similarity between central and adjacent features. This design reinforces key characteristics and effectively captures the correlation between instance and semantic segmentation, ultimately improving overall segmentation accuracy. EAJS-Net integrates PointNet++ and PointConv as its backbone network and comprises three main components: a point feature enhancement module, an encoder-decoder module, and an enhanced attention-based joint segmentation module. The input to EAJS-Net includes N × 9 dimensional point cloud data, where N represents the number of points, and the nine dimensions include coordinate values (XYZ), color information (RGB), and normalized coordinates. A semantic feature extraction module based on an attention mechanism is employed to effectively capture local contextual information between points. The enhanced features extracted by this module are then fed into the encoding layer, which includes four encoding modules: one attention pooling-based set abstraction layer adapted from PointNet++ and three feature encoding layers derived from PointConv. The corresponding decoding layer comprises four decoding modules: three deep feature decoding layers derived from PointConv and one feature propagation layer from PointNet++. By utilizing the attention pooling-based set abstraction layer from PointNet++, the network effectively captures spatial geometric relationships among features. Through the combination of the encoding and decoding layers, the initial semantic and instance features of the point cloud are extracted, laying the foundation for accurate joint segmentation. An enhanced attention module is designed to adaptively learn the similarity between central and neighboring features through dual attention mechanisms, which dynamically compute attention weights. These dual attention weights are summed and applied to the initial semantic features, resulting in enhanced semantic representations. This module is embedded within the semantic branch of the joint segmentation module, enabling more effective integration of semantic and instance features to improve joint segmentation accuracy. The encoded features are then upsampled through two parallel decoder branches to generate an instance feature matrix and a semantic feature matrix, which serve as inputs to the joint segmentation module. Within this module, the semantic and instance branches are integrated using the enhanced attention mechanism. The final output comprises instance embeddings and semantic predictions, supporting precise and consistent segmentation results.ResultThe proposed network is evaluated on the Stanford large-scale 3D indoor spaces (S3DIS) dataset and ScanNet V2 to assess its performance on point cloud segmentation tasks. Six fold cross-validation is performed on the S3DIS dataset, and the results of EAJS-Net are compared with those of the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. For semantic segmentation on the S3DIS dataset, EAJS-Net achieves a mean intersection over union (mIoU) of 65.9%, overall accuracy (oAcc) of 89.1%, and mean accuracy (mAcc) of 76.0%. Compared to JSNet++, these results represent improvements of 3.5% (mIoU), 0.4% (oAcc), and 3.2% (mAcc). For instance segmentation, EAJS-Net reaches a weighted coverage rate of 61.1%, outperforming JSNet++ by 4.1% (mean weighted coverage, mWCov), 4.6% (mean coverage, mCov), and 1.2% (mean recall, mRec). On the ScanNet dataset, EAJS-Net improves the mIoU for semantic segmentation by 3.2% and increases the weighted coverage rate for instance segmentation by 2.8% compared to JSNet. Visual comparisons between EAJS-Net and other SOTA methods are also presented, demonstrating that EAJS-Net consistently achieves superior segmentation results, even in complex indoor scenes. In addition, ablation experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of individual modules within the network. The enhanced attention-based joint segmentation module in EAJS-Net dynamically adjusts attention weights to effectively capture various features, successfully integrating semantic and instance features into the semantic feature space. This integration notably enhances the performance of the semantic segmentation task.ConclusionAiming to address the limitations of existing feature fusion strategies that fail to fully capture inter-instance semantic correlations, this paper proposes a novel semantic-instance joint segmentation network, EAJS-Net, based on an enhanced attention mechanism. A new semantic feature extraction module is designed to capture contextual relationships among points. Additionally, an enhanced attention module is introduced to effectively aggregate instance features into the semantic feature space. This improved feature fusion strategy boosts the performance of joint semantic-instance segmentation. Experimental results demonstrate that EAJS-Net effectively integrates semantic and instance features, substantially improving the accuracy of both segmentation tasks compared to SOTA methods.关键词:deep learning;point cloud;semantic segmentation;instance segmentation;enhanced attention-based mechanism35|22|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveWith the rapid advancement of 3D sensing technologies such as LiDAR (light detection and ranging) and depth cameras, large-scale 3D point clouds have emerged as a crucial data source for a wide range of applications, including autonomous driving, robotic navigation, augmented reality, and urban scene reconstruction. Compared to 2D images, point clouds offer precise spatial geometry and provide a comprehensive representation of the environment without perspective distortion. Additionally, they are robust to variations in lighting and texture. Point cloud segmentation plays a crucial role in scene analysis and interpretation. The segmentation can be categorized into three types: semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, and joint semantic-instance segmentation. Semantic segmentation partitions a 3D scene into informative regions and assigns each region to a specific class. Instance segmentation identifies and separates individual objects at the point level, including those that belong to the same semantic category. In recent years, researchers have increasingly focused on combining the two tasks to achieve more consistent and informative scene-level interpretations. Joint semantic-instance segmentation leverages the intrinsic correlation between semantic and instance-level segmentation, enabling the two tasks to complement and reinforce each other. In 3D point cloud contexts, this joint approach substantially improves the capability of the system to comprehend complex environments and offers strong technical support for the development of intelligent systems. Consequently, this approach has become an area of growing interest and active research. However, most existing methods for joint semantic-instance segmentation rely on simplistic feature fusion strategies, which limit their effectiveness in fully capturing the potential relationship between semantic and instance features. Aiming to address this limitation, an enhanced attention-based joint semantic-instance segmentation network is proposed. This network is designed to effectively model and utilize the correlation between semantic and instance information.MethodThe enhanced attention-based joint semantic-instance segmentation neural network (EAJS-Net) incorporates a semantic feature extraction module based on an attention mechanism. This module focuses on the local neighborhood of each point and dynamically adjusts attention weights to emphasize key information, thereby enhancing the extraction of semantic features across points. Additionally, an attention-enhanced semantic/instance feature fusion module is introduced, which adaptively learns the similarity between central and adjacent features. This design reinforces key characteristics and effectively captures the correlation between instance and semantic segmentation, ultimately improving overall segmentation accuracy. EAJS-Net integrates PointNet++ and PointConv as its backbone network and comprises three main components: a point feature enhancement module, an encoder-decoder module, and an enhanced attention-based joint segmentation module. The input to EAJS-Net includes N × 9 dimensional point cloud data, where N represents the number of points, and the nine dimensions include coordinate values (XYZ), color information (RGB), and normalized coordinates. A semantic feature extraction module based on an attention mechanism is employed to effectively capture local contextual information between points. The enhanced features extracted by this module are then fed into the encoding layer, which includes four encoding modules: one attention pooling-based set abstraction layer adapted from PointNet++ and three feature encoding layers derived from PointConv. The corresponding decoding layer comprises four decoding modules: three deep feature decoding layers derived from PointConv and one feature propagation layer from PointNet++. By utilizing the attention pooling-based set abstraction layer from PointNet++, the network effectively captures spatial geometric relationships among features. Through the combination of the encoding and decoding layers, the initial semantic and instance features of the point cloud are extracted, laying the foundation for accurate joint segmentation. An enhanced attention module is designed to adaptively learn the similarity between central and neighboring features through dual attention mechanisms, which dynamically compute attention weights. These dual attention weights are summed and applied to the initial semantic features, resulting in enhanced semantic representations. This module is embedded within the semantic branch of the joint segmentation module, enabling more effective integration of semantic and instance features to improve joint segmentation accuracy. The encoded features are then upsampled through two parallel decoder branches to generate an instance feature matrix and a semantic feature matrix, which serve as inputs to the joint segmentation module. Within this module, the semantic and instance branches are integrated using the enhanced attention mechanism. The final output comprises instance embeddings and semantic predictions, supporting precise and consistent segmentation results.ResultThe proposed network is evaluated on the Stanford large-scale 3D indoor spaces (S3DIS) dataset and ScanNet V2 to assess its performance on point cloud segmentation tasks. Six fold cross-validation is performed on the S3DIS dataset, and the results of EAJS-Net are compared with those of the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. For semantic segmentation on the S3DIS dataset, EAJS-Net achieves a mean intersection over union (mIoU) of 65.9%, overall accuracy (oAcc) of 89.1%, and mean accuracy (mAcc) of 76.0%. Compared to JSNet++, these results represent improvements of 3.5% (mIoU), 0.4% (oAcc), and 3.2% (mAcc). For instance segmentation, EAJS-Net reaches a weighted coverage rate of 61.1%, outperforming JSNet++ by 4.1% (mean weighted coverage, mWCov), 4.6% (mean coverage, mCov), and 1.2% (mean recall, mRec). On the ScanNet dataset, EAJS-Net improves the mIoU for semantic segmentation by 3.2% and increases the weighted coverage rate for instance segmentation by 2.8% compared to JSNet. Visual comparisons between EAJS-Net and other SOTA methods are also presented, demonstrating that EAJS-Net consistently achieves superior segmentation results, even in complex indoor scenes. In addition, ablation experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of individual modules within the network. The enhanced attention-based joint segmentation module in EAJS-Net dynamically adjusts attention weights to effectively capture various features, successfully integrating semantic and instance features into the semantic feature space. This integration notably enhances the performance of the semantic segmentation task.ConclusionAiming to address the limitations of existing feature fusion strategies that fail to fully capture inter-instance semantic correlations, this paper proposes a novel semantic-instance joint segmentation network, EAJS-Net, based on an enhanced attention mechanism. A new semantic feature extraction module is designed to capture contextual relationships among points. Additionally, an enhanced attention module is introduced to effectively aggregate instance features into the semantic feature space. This improved feature fusion strategy boosts the performance of joint semantic-instance segmentation. Experimental results demonstrate that EAJS-Net effectively integrates semantic and instance features, substantially improving the accuracy of both segmentation tasks compared to SOTA methods.关键词:deep learning;point cloud;semantic segmentation;instance segmentation;enhanced attention-based mechanism35|22|0更新时间:2025-12-18 - “在三维模型分类领域,研究者提出了一种基于Transformer注意力引导的最优视图选择与分类方法,有效提高了分类性能并选出代表性视图。”
 摘要:Objective3D model classification is a fundamental problem in the fields of computer graphics and computer vision, with wide-ranging applications in areas such as computer-aided design, mixed reality, autonomous driving, and robotic navigation. The challenges associated with 3D model classification primarily arise from three key aspects: the difficulty in representing 3D surface geometric features, the diversity of 3D transformations and deformations, and the incompleteness of geometric and topological structures. Existing multi-view-based 3D model classification methods typically render 3D models from multiple preset viewpoints and input all rendered views into a neural network for classification. However, due to the presence of redundant and ineffective views, not all views contribute equally to the classification task. Selecting views that substantially enhance classification performance can not only improve the overall accuracy of multi-view 3D model classification but also help identify representative views that effectively capture the essential characteristics of the 3D model.MethodThis paper proposes a Transformer attention-guided approach for optimal view selection and classification of 3D models. The 3D model is first rendered from 20 viewpoints arranged on a regular icosahedron. A convolutional neural network is then employed to extract feature information from these multiple views, producing a sequence of local multi-view feature tokens. Aiming to retain spatial location information, position encoding is applied to the token sequence. Next, a learnable global classification token is introduced and concatenated with the multi-view feature tokens, forming the input to a Transformer encoder that performs global view feature fusion and generates an initial global classification feature. Subsequently, the optimal view selection module calculates the contribution of each view to the initial global classification token using the attention score matrix from the feature fusion process. The highest-scoring views are selected as the optimal views. These optimal view feature tokens are then concatenated with the initial global classification token and input into the Transformer encoder for a second round of feature fusion, producing the final global classification token. This final token is passed through a classifier to generate the classification probabilities and simultaneously output the selected optimal views. Aiming to enhance generalization during training, the model incorporates random view dropping and contrastive learning strategies.ResultThis study experiments on the ModelNet40 dataset, which comprises 40 object categories. The dataset is suitable for research in 3D object recognition and is widely used for benchmarking algorithm performance. Evaluation metrics include overall accuracy (OA), average accuracy (AA), and speed. OA measures classification accuracy across the entire dataset, while AA calculates the mean accuracy across all categories, addressing issues related to class imbalance. The dataset, created by Stanford University, is widely used for performance evaluation of algorithms. First, the Transformer-based multi-view selection and 3D model classification method proposed in this paper are compared with other state-of-the-art deep learning-based 3D model classification methods to validate its effectiveness. Subsequently, ablation experiments are conducted to analyze the impact of different parameter settings on the performance of the proposed method, including multi-view representation, feature extraction backbone, Transformer hidden layer dimension, number of attention heads, contrastive learning strategy, and random view dropout module. On the ModelNet40 benchmark dataset, the proposed method achieves an overall recognition accuracy of 97.61% and an average recognition accuracy of 96.36%. In addition to reaching state-of-the-art classification performance, the optimal views selected based on the Transformer attention score matrix are shown to be highly representative.ConclusionThe proposed method leverages the Transformer architecture to perform feature fusion across different views. By employing mechanisms such as self-attention, residual connections, and multi-layer stacking, the Transformer effectively learns complex features and captures global contextual relationships among different views. Furthermore, the attention score matrix generated by the Transformer serves as a basis for optimal view selection, enabling efficient classification while identifying the most representative views.关键词:3D model classification;Transformer;optimal view selection;contrastive learning;multi-view learning151|148|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:Objective3D model classification is a fundamental problem in the fields of computer graphics and computer vision, with wide-ranging applications in areas such as computer-aided design, mixed reality, autonomous driving, and robotic navigation. The challenges associated with 3D model classification primarily arise from three key aspects: the difficulty in representing 3D surface geometric features, the diversity of 3D transformations and deformations, and the incompleteness of geometric and topological structures. Existing multi-view-based 3D model classification methods typically render 3D models from multiple preset viewpoints and input all rendered views into a neural network for classification. However, due to the presence of redundant and ineffective views, not all views contribute equally to the classification task. Selecting views that substantially enhance classification performance can not only improve the overall accuracy of multi-view 3D model classification but also help identify representative views that effectively capture the essential characteristics of the 3D model.MethodThis paper proposes a Transformer attention-guided approach for optimal view selection and classification of 3D models. The 3D model is first rendered from 20 viewpoints arranged on a regular icosahedron. A convolutional neural network is then employed to extract feature information from these multiple views, producing a sequence of local multi-view feature tokens. Aiming to retain spatial location information, position encoding is applied to the token sequence. Next, a learnable global classification token is introduced and concatenated with the multi-view feature tokens, forming the input to a Transformer encoder that performs global view feature fusion and generates an initial global classification feature. Subsequently, the optimal view selection module calculates the contribution of each view to the initial global classification token using the attention score matrix from the feature fusion process. The highest-scoring views are selected as the optimal views. These optimal view feature tokens are then concatenated with the initial global classification token and input into the Transformer encoder for a second round of feature fusion, producing the final global classification token. This final token is passed through a classifier to generate the classification probabilities and simultaneously output the selected optimal views. Aiming to enhance generalization during training, the model incorporates random view dropping and contrastive learning strategies.ResultThis study experiments on the ModelNet40 dataset, which comprises 40 object categories. The dataset is suitable for research in 3D object recognition and is widely used for benchmarking algorithm performance. Evaluation metrics include overall accuracy (OA), average accuracy (AA), and speed. OA measures classification accuracy across the entire dataset, while AA calculates the mean accuracy across all categories, addressing issues related to class imbalance. The dataset, created by Stanford University, is widely used for performance evaluation of algorithms. First, the Transformer-based multi-view selection and 3D model classification method proposed in this paper are compared with other state-of-the-art deep learning-based 3D model classification methods to validate its effectiveness. Subsequently, ablation experiments are conducted to analyze the impact of different parameter settings on the performance of the proposed method, including multi-view representation, feature extraction backbone, Transformer hidden layer dimension, number of attention heads, contrastive learning strategy, and random view dropout module. On the ModelNet40 benchmark dataset, the proposed method achieves an overall recognition accuracy of 97.61% and an average recognition accuracy of 96.36%. In addition to reaching state-of-the-art classification performance, the optimal views selected based on the Transformer attention score matrix are shown to be highly representative.ConclusionThe proposed method leverages the Transformer architecture to perform feature fusion across different views. By employing mechanisms such as self-attention, residual connections, and multi-layer stacking, the Transformer effectively learns complex features and captures global contextual relationships among different views. Furthermore, the attention score matrix generated by the Transformer serves as a basis for optimal view selection, enabling efficient classification while identifying the most representative views.关键词:3D model classification;Transformer;optimal view selection;contrastive learning;multi-view learning151|148|0更新时间:2025-12-18
Computer Graphics
- “数字化口腔正畸领域取得新进展,专家提出牙弓线拟合新方法,有效提升正畸效果。”
 摘要:ObjectiveIn recent years, rapid advancements in digital technology have positioned digital orthodontics as a critical research focus within the field of dentistry. Among the numerous challenges encountered during orthodontic treatment, designing an accurate dental arch line is fundamental for precisely calculating the target positions of teeth after treatment. The dental arch line should not only follow the natural growth patterns of the teeth but also satisfy aesthetic and functional requirements essential for optimal orthodontic outcomes. However, current automated tooth alignment methods typically model the dental arch line using Beta functions, which are inherently limited by their restricted degrees of freedom. This limitation often prevents these methods from generating curves that accurately capture the ideal dental arch form, especially when dealing with complex or irregular tooth arrangements. Moreover, orthodontists frequently require customized dental arch lines tailored to each patient’s unique oral condition. However, arch lines fitted solely from the patient’s initial intraoral scan may not always align with therapeutic or aesthetic expectations, necessitating labor-intensive manual adjustments. These challenges highlight the need for a flexible and precise approach to dental arch line design that effectively meets clinical standards and patient-specific requirements. Aiming to address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel dental arch line fitting method based on cumulative chord length parameterization combined with Hermite interpolation. This approach aims to enhance control over the dental arch shape, improve fitting accuracy, and provide orthodontists with a highly effective and efficient tool for designing and adjusting dental arch lines during orthodontic treatment planning.MethodThe proposed method begins by inputting the patient’s intraoral scan data, which undergoes a series of preprocessing steps to ensure data quality and consistency. A tooth segmentation algorithm is then applied to accurately isolate each individual tooth, following internationally recognized dental segmentation standards. After segmentation, a landmark detection algorithm is employed to extract key landmarks from each tooth, capturing essential geometric and morphological features. These landmarks serve as the foundation for subsequent dental arch line fitting. Aiming to facilitate the interpolation process, the extracted landmarks are initially reparameterized using cumulative chord length parameterization. This process generates a naturally distributed set of interpolation points along the dental arch by accounting for the varying distances between adjacent landmarks, thereby preserving the true spatial relationships among teeth. Subsequently, Hermite interpolation is employed to construct the dental arch line through the parameterized points. By incorporating position and tangent information, Hermite interpolation enables the construction of smooth, continuous curves with enhanced local control. Aiming to ensure fitting accuracy and smoothness, a coefficient matrix is constructed to formulate a system of linear equations. Solving this system yields the final dental arch line, represented as a piecewise continuous function. This piecewise structure allows for precise local adjustments, making the method particularly effectively for accommodating complicated or irregular tooth arrangements. Furthermore, this paper introduces two new mathematical evaluation metrics: the mean shortest distance and the maximum shortest distance between the extracted landmarks and the fitted curve. These metrics offer an objective and robust means of assessing how accurately the generated dental arch line conforms to the patient’s actual dental morphology.ResultThe proposed fitting method, which integrates cumulative chord length parameterization with Hermite interpolation, exhibits substantial improvements over traditional approaches in dental arch line fitting. First, compared to conventional Beta function-based methods, the proposed approach offers substantially greater flexibility by allowing the inclusion of additional control points. This increased degree of freedom directly addresses the limitations of Beta functions, particularly their inability to support localized shape modifications. The resulting dental arch line provides orthodontists with the flexibility to manually adjust specific, predefined control points, enabling localized adjustments tailored to individual patient needs. The proposed method excels in offering excellent controllability for global and local morphology adjustments of the dental arch line while maintaining high accuracy and smoothness across all regions, attributed to the use of its piecewise functional structure. Experimental evaluations further highlight the advantages of the proposed method. Qualitative analyses show that the generated curves more naturally align with actual dental arch shapes than those produced by conventional methods. Quantitative results, assessed using the proposed shortest distance-based evaluation metrics, confirm a notable improvement in fitting accuracy and alignment with natural tooth arrangements. Additionally, the proposed method enhances clinical flexibility, allowing orthodontists to efficiently adjust the dental arch line by manipulating a limited number of control points, minimizing the need for extensive manual corrections. In practical scenarios, the proposed fitting method is integrated into an existing automated tooth alignment system. This integration led to noticeably improved orthodontic outcomes, further validating the practical effectiveness and clinical applicability of the proposed method.ConclusionCompared to existing dental arch fitting methods, the proposed method based on cumulative chord length parameterization and Hermite interpolation demonstrates clear advantages in fitting accuracy and flexibility. This method effectively addresses key limitations of traditional approaches, such as difficulty in achieving an ideal dental arch line and limited adaptability to patient-specific variations. By notably increasing the degrees of freedom and enhancing the controllability of the fitting function, the method produces dental arch lines that are not only smooth and accurate but also highly customizable to meet the diverse clinical requirements of modern orthodontic practice. Furthermore, the introduction of quantitative evaluation metrics offers a systematic and objective framework for assessing fitting quality, ensuring that the resulting dental arch lines are aesthetically aligned and functionally sound. Beyond its technical advantages, the method also improves clinical efficiency by reducing the time and effort typically required for dental arch adjustments during treatment planning. Overall, the proposed method offers strong technical support for the advancement of digital orthodontics and holds substantial potential for broader clinical adoption. This paper establishes a solid foundation for further innovations in automated orthodontic treatment systems, opening new possibilities for personalized and precise dental care.关键词:dental arch line;Hermite interpolation;orthodontic treatment;parameterization;piecewise function90|158|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveIn recent years, rapid advancements in digital technology have positioned digital orthodontics as a critical research focus within the field of dentistry. Among the numerous challenges encountered during orthodontic treatment, designing an accurate dental arch line is fundamental for precisely calculating the target positions of teeth after treatment. The dental arch line should not only follow the natural growth patterns of the teeth but also satisfy aesthetic and functional requirements essential for optimal orthodontic outcomes. However, current automated tooth alignment methods typically model the dental arch line using Beta functions, which are inherently limited by their restricted degrees of freedom. This limitation often prevents these methods from generating curves that accurately capture the ideal dental arch form, especially when dealing with complex or irregular tooth arrangements. Moreover, orthodontists frequently require customized dental arch lines tailored to each patient’s unique oral condition. However, arch lines fitted solely from the patient’s initial intraoral scan may not always align with therapeutic or aesthetic expectations, necessitating labor-intensive manual adjustments. These challenges highlight the need for a flexible and precise approach to dental arch line design that effectively meets clinical standards and patient-specific requirements. Aiming to address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel dental arch line fitting method based on cumulative chord length parameterization combined with Hermite interpolation. This approach aims to enhance control over the dental arch shape, improve fitting accuracy, and provide orthodontists with a highly effective and efficient tool for designing and adjusting dental arch lines during orthodontic treatment planning.MethodThe proposed method begins by inputting the patient’s intraoral scan data, which undergoes a series of preprocessing steps to ensure data quality and consistency. A tooth segmentation algorithm is then applied to accurately isolate each individual tooth, following internationally recognized dental segmentation standards. After segmentation, a landmark detection algorithm is employed to extract key landmarks from each tooth, capturing essential geometric and morphological features. These landmarks serve as the foundation for subsequent dental arch line fitting. Aiming to facilitate the interpolation process, the extracted landmarks are initially reparameterized using cumulative chord length parameterization. This process generates a naturally distributed set of interpolation points along the dental arch by accounting for the varying distances between adjacent landmarks, thereby preserving the true spatial relationships among teeth. Subsequently, Hermite interpolation is employed to construct the dental arch line through the parameterized points. By incorporating position and tangent information, Hermite interpolation enables the construction of smooth, continuous curves with enhanced local control. Aiming to ensure fitting accuracy and smoothness, a coefficient matrix is constructed to formulate a system of linear equations. Solving this system yields the final dental arch line, represented as a piecewise continuous function. This piecewise structure allows for precise local adjustments, making the method particularly effectively for accommodating complicated or irregular tooth arrangements. Furthermore, this paper introduces two new mathematical evaluation metrics: the mean shortest distance and the maximum shortest distance between the extracted landmarks and the fitted curve. These metrics offer an objective and robust means of assessing how accurately the generated dental arch line conforms to the patient’s actual dental morphology.ResultThe proposed fitting method, which integrates cumulative chord length parameterization with Hermite interpolation, exhibits substantial improvements over traditional approaches in dental arch line fitting. First, compared to conventional Beta function-based methods, the proposed approach offers substantially greater flexibility by allowing the inclusion of additional control points. This increased degree of freedom directly addresses the limitations of Beta functions, particularly their inability to support localized shape modifications. The resulting dental arch line provides orthodontists with the flexibility to manually adjust specific, predefined control points, enabling localized adjustments tailored to individual patient needs. The proposed method excels in offering excellent controllability for global and local morphology adjustments of the dental arch line while maintaining high accuracy and smoothness across all regions, attributed to the use of its piecewise functional structure. Experimental evaluations further highlight the advantages of the proposed method. Qualitative analyses show that the generated curves more naturally align with actual dental arch shapes than those produced by conventional methods. Quantitative results, assessed using the proposed shortest distance-based evaluation metrics, confirm a notable improvement in fitting accuracy and alignment with natural tooth arrangements. Additionally, the proposed method enhances clinical flexibility, allowing orthodontists to efficiently adjust the dental arch line by manipulating a limited number of control points, minimizing the need for extensive manual corrections. In practical scenarios, the proposed fitting method is integrated into an existing automated tooth alignment system. This integration led to noticeably improved orthodontic outcomes, further validating the practical effectiveness and clinical applicability of the proposed method.ConclusionCompared to existing dental arch fitting methods, the proposed method based on cumulative chord length parameterization and Hermite interpolation demonstrates clear advantages in fitting accuracy and flexibility. This method effectively addresses key limitations of traditional approaches, such as difficulty in achieving an ideal dental arch line and limited adaptability to patient-specific variations. By notably increasing the degrees of freedom and enhancing the controllability of the fitting function, the method produces dental arch lines that are not only smooth and accurate but also highly customizable to meet the diverse clinical requirements of modern orthodontic practice. Furthermore, the introduction of quantitative evaluation metrics offers a systematic and objective framework for assessing fitting quality, ensuring that the resulting dental arch lines are aesthetically aligned and functionally sound. Beyond its technical advantages, the method also improves clinical efficiency by reducing the time and effort typically required for dental arch adjustments during treatment planning. Overall, the proposed method offers strong technical support for the advancement of digital orthodontics and holds substantial potential for broader clinical adoption. This paper establishes a solid foundation for further innovations in automated orthodontic treatment systems, opening new possibilities for personalized and precise dental care.关键词:dental arch line;Hermite interpolation;orthodontic treatment;parameterization;piecewise function90|158|0更新时间:2025-12-18
Medical Image Processing
-
Lightweight spaceborne remote sensing object detection algorithm with multi-attention mechanism AI导读
“在遥感图像目标检测领域,专家提出了一种轻量化算法,有效降低模型参数量并提高检测精度,为星上部署提供技术支持。” 摘要:ObjectiveWith the advancement of image processing and artificial intelligence, deep learning-based algorithms have become increasingly important in the tasks of image target detection and recognition. In the aerospace domain, satellite remote sensing object detection consistently confronts challenges, including cluttered imaging backgrounds, numerous minuscule targets, and wide dynamic imaging ranges. In recent years, convolutional neural network-based approaches have witnessed significant progress in satellite remote sensing object detection, particularly in fine-grained target recognition. These advancements play crucial roles across domains such as military reconnaissance, postdisaster reconstruction, and resource exploration. Given the challenges of large coverage, small and dense targets, and complex imaging backgrounds in satellite-based remote sensing images, large and complex neural networks have been utilized to represent image features for further target detection. Although large neural networks exhibit certain detection capabilities, they are difficult to deploy in space-based remote sensing tasks because of the high real-time requirements and limited computing resources. To address these issues, this study proposes a lightweight space-based remote sensing image target detection algorithm that integrates multiattention mechanisms in the spatial domain and channels. It deploys remote sensing image data processing and target detection algorithms to a remote sensing edge intelligent computing platform, achieving efficient and accurate target recognition and analysis for remote sensing images. This approach provides a solution for future in-orbit fast target detection algorithm processing and real-time tracking of detection targets.MethodBased on a You Only Look Once version 11 model (i.e., YOLOv11n), the proposed algorithm integrates the channel prior convolutional attention (CPCA) mechanism, which combines channel and spatial attention mechanisms. It utilizes the channel attention mechanism to generate a channel attention map. Subsequently, this map is multiplied element-wise with the model’s input feature map to produce a channel-weighted feature map. This channel-weighted feature map is then fed into a depthwise convolution module to generate a spatial attention feature map. The CPCA mechanism can dynamically allocate attention weights across channel and spatial dimensions, enriching the network’s target features by extracting channel-wise and spatial attention features, thereby enhancing the network’s feature extraction capability. By employing a 2D convolutional layer based on partial convolution (Pconv), which convolves only a subset of input channels, it leverages redundant compression in interchannel feature maps. This approach avoids the issue of excessive parameters typically introduced by adding attention modules. Consequently, the improved model reduces the parameter count by 0.48 M (approximately 18.53%) compared with the original YOLOv11n. This approach partially addresses the challenge of deploying network models on embedded devices. For ensuring consistent dimensions between the two branches of Pconv, a max-pooling operation is applied to the nonconvolved channels, downsizing the feature maps to half their original dimensions. Through leveraging pointwise convolution to fully utilize the representational capacity of channel-wise features, this design reduces the computational load while preventing significant degradation in the model’s feature extraction capability.ResultDuring validation on the DIOR dataset, the proposed algorithm was compared with various YOLO algorithms for object detection. Experimental results demonstrate that real-time detection transformer(RTDETR) has the largest parameter count at 9.42 M, YOLOv11n has 2.59 M parameters, and YOLOv11n_CBAM has 2.74 M. By contrast, the proposed model contains only 2.11 M parameters, accounting for 81.47% of those of the original YOLOv11n. Meanwhile, compared with the original YOLOv11n algorithm, the proposed method achieves a mean improvement of 1.9% in accuracy and 1.2% in recall. The neural network processing unit (NPU) inference latency of YOLOv11n is 19.6 ms, whereas the proposed algorithm achieves only 14.8 ms. This result indicates a reduction of 4.8 ms in comparison with the original model, representing a 24.49% speed improvement. Additionally, the NPU-deployed YOLOv11n model attains an accuracy of 0.799 and a recall of 0.642, whereas the proposed algorithm achieves 0.819 accuracy and 0.652 recall. Accordingly, no potential accuracy degradation occurs during model migration and deployment. Compared with merely adding the CPCA module, the proposed algorithm exhibits a slight accuracy decrease of 0.10% but reduces the parameter count by 0.66 M. When contrasted with solely incorporating the Pconv module, it shows a marginal parameter increase of 0.08 M, yet it improves the accuracy by 1.7%.ConclusionTargeting space-based remote sensing minute object detection tasks, this study draws inspiration from the YOLOv11n model to propose a lightweight object detection algorithm that integrates multiattention mechanisms in the spatial domain and channels and contextual information. This approach significantly enhances detection accuracy while effectively reducing model parameters. By refining the attention mechanism in YOLOv11n, we introduce an improved architecture incorporating the CPCA module. This architecture enables comprehensive feature extraction for minute objects across spatial and channel dimensions, effectively mitigating missed detections and false alarms in spaceborne imagery. The conventional 2D convolutional layers in YOLO are replaced with Pconv-based designs, circumventing parameter inflation typically caused by attention modules. This replacement achieves an 18.53% parameter reduction and model lightweighting. Finally, through NPU-optimized deployment, the model’s hardware compatibility is enhanced. Compared with the original YOLOv11n, the proposed algorithm reduces inference time by 4.8 ms while maintaining detection accuracy, meeting real-time monitoring requirements. The solution proves exceptionally resource efficient for space-based engineering deployment with constrained computational resources and memory, providing crucial technical support for onboard implementation in spaceborne remote sensing systems.关键词:Space-based remote sensing images;YOLOv11n;attention mechanism;target detection;Model lightweighting;Algorithm deployment124|114|0更新时间:2025-12-18
摘要:ObjectiveWith the advancement of image processing and artificial intelligence, deep learning-based algorithms have become increasingly important in the tasks of image target detection and recognition. In the aerospace domain, satellite remote sensing object detection consistently confronts challenges, including cluttered imaging backgrounds, numerous minuscule targets, and wide dynamic imaging ranges. In recent years, convolutional neural network-based approaches have witnessed significant progress in satellite remote sensing object detection, particularly in fine-grained target recognition. These advancements play crucial roles across domains such as military reconnaissance, postdisaster reconstruction, and resource exploration. Given the challenges of large coverage, small and dense targets, and complex imaging backgrounds in satellite-based remote sensing images, large and complex neural networks have been utilized to represent image features for further target detection. Although large neural networks exhibit certain detection capabilities, they are difficult to deploy in space-based remote sensing tasks because of the high real-time requirements and limited computing resources. To address these issues, this study proposes a lightweight space-based remote sensing image target detection algorithm that integrates multiattention mechanisms in the spatial domain and channels. It deploys remote sensing image data processing and target detection algorithms to a remote sensing edge intelligent computing platform, achieving efficient and accurate target recognition and analysis for remote sensing images. This approach provides a solution for future in-orbit fast target detection algorithm processing and real-time tracking of detection targets.MethodBased on a You Only Look Once version 11 model (i.e., YOLOv11n), the proposed algorithm integrates the channel prior convolutional attention (CPCA) mechanism, which combines channel and spatial attention mechanisms. It utilizes the channel attention mechanism to generate a channel attention map. Subsequently, this map is multiplied element-wise with the model’s input feature map to produce a channel-weighted feature map. This channel-weighted feature map is then fed into a depthwise convolution module to generate a spatial attention feature map. The CPCA mechanism can dynamically allocate attention weights across channel and spatial dimensions, enriching the network’s target features by extracting channel-wise and spatial attention features, thereby enhancing the network’s feature extraction capability. By employing a 2D convolutional layer based on partial convolution (Pconv), which convolves only a subset of input channels, it leverages redundant compression in interchannel feature maps. This approach avoids the issue of excessive parameters typically introduced by adding attention modules. Consequently, the improved model reduces the parameter count by 0.48 M (approximately 18.53%) compared with the original YOLOv11n. This approach partially addresses the challenge of deploying network models on embedded devices. For ensuring consistent dimensions between the two branches of Pconv, a max-pooling operation is applied to the nonconvolved channels, downsizing the feature maps to half their original dimensions. Through leveraging pointwise convolution to fully utilize the representational capacity of channel-wise features, this design reduces the computational load while preventing significant degradation in the model’s feature extraction capability.ResultDuring validation on the DIOR dataset, the proposed algorithm was compared with various YOLO algorithms for object detection. Experimental results demonstrate that real-time detection transformer(RTDETR) has the largest parameter count at 9.42 M, YOLOv11n has 2.59 M parameters, and YOLOv11n_CBAM has 2.74 M. By contrast, the proposed model contains only 2.11 M parameters, accounting for 81.47% of those of the original YOLOv11n. Meanwhile, compared with the original YOLOv11n algorithm, the proposed method achieves a mean improvement of 1.9% in accuracy and 1.2% in recall. The neural network processing unit (NPU) inference latency of YOLOv11n is 19.6 ms, whereas the proposed algorithm achieves only 14.8 ms. This result indicates a reduction of 4.8 ms in comparison with the original model, representing a 24.49% speed improvement. Additionally, the NPU-deployed YOLOv11n model attains an accuracy of 0.799 and a recall of 0.642, whereas the proposed algorithm achieves 0.819 accuracy and 0.652 recall. Accordingly, no potential accuracy degradation occurs during model migration and deployment. Compared with merely adding the CPCA module, the proposed algorithm exhibits a slight accuracy decrease of 0.10% but reduces the parameter count by 0.66 M. When contrasted with solely incorporating the Pconv module, it shows a marginal parameter increase of 0.08 M, yet it improves the accuracy by 1.7%.ConclusionTargeting space-based remote sensing minute object detection tasks, this study draws inspiration from the YOLOv11n model to propose a lightweight object detection algorithm that integrates multiattention mechanisms in the spatial domain and channels and contextual information. This approach significantly enhances detection accuracy while effectively reducing model parameters. By refining the attention mechanism in YOLOv11n, we introduce an improved architecture incorporating the CPCA module. This architecture enables comprehensive feature extraction for minute objects across spatial and channel dimensions, effectively mitigating missed detections and false alarms in spaceborne imagery. The conventional 2D convolutional layers in YOLO are replaced with Pconv-based designs, circumventing parameter inflation typically caused by attention modules. This replacement achieves an 18.53% parameter reduction and model lightweighting. Finally, through NPU-optimized deployment, the model’s hardware compatibility is enhanced. Compared with the original YOLOv11n, the proposed algorithm reduces inference time by 4.8 ms while maintaining detection accuracy, meeting real-time monitoring requirements. The solution proves exceptionally resource efficient for space-based engineering deployment with constrained computational resources and memory, providing crucial technical support for onboard implementation in spaceborne remote sensing systems.关键词:Space-based remote sensing images;YOLOv11n;attention mechanism;target detection;Model lightweighting;Algorithm deployment124|114|0更新时间:2025-12-18
Remote Sensing Image Processing
0

