
最新刊期
卷 28 , 期 8 , 2023
-
 摘要:Document analysis and recognition (called document recognition in brief) is aimed to covert non-structured documents (typically, document images and online handwriting) into structured texts for facilitating computer processing and understanding. It is needed in wide applications due to the pervasive communication and usage of documents. The field of document recognition has attracted intensive attention and produced enormous progress in research and applications since 1960s. Particularly, the recent development of deep learning technology has boosted the performance of document recognition remarkably compared to traditional methods, and the technology has been applied successfully to document digitization, form processing, handwriting input, intelligent transportation, document retrieval and information extraction.In this article, we first introduce the background and involved techniques of document recognition, give an overview of the history of research (divided into four periods according to the objects of research, the methods and applications), and then review the main research progress with emphasis on deep learning based methods developed in recent years. After identifying the insufficiency of current technology, we finally suggest some important issues for future research.The review of recent progress is divided into sections corresponding to main processing steps, namely image pre-processing, layout analysis, scene text detection, text recognition, structured symbol and graphics recognition, document retrieval and information extraction.The review of recent progress is divided into sections corresponding to the main processing steps, namely image pre-processing, layout analysis, scene text detection, text recognition, structured symbol and graphics recognition, document retrieval and information extraction. 1) Due to the popularity of camera-captured document images, the current main task in image pre-processing is the rectification of distorted image while the task of binarization is still concerned. Recent methods are mostly end-to-end deep learning based transformation methods. 2) Layout analysis is dichotomized into physical layout analysis (page segmentation) and logical layout analysis (semantic region segmentation and reading order prediction). Recent page segmentation methods based on fully convolutional network (FCN) or graph neural network (GNN) have shown promises. Logical layout analysis has been addressed by deep neural networks fusing multi-modal information. Table structure analysis is a special task of layout analysis and has been studied intensively in recent years. 3) Scene text detection is a hot topic in document analysis and computer vision fields. Deep learning based methods for text methods can be divided into regression-based methods, segmentation-based methods and hybrid methods. FCN is prevalently used for extracting visual features, based on which models are built to predict text regions. 4) Text recognition is the core task in document analysis. We review recent works for handwritten text recognition and scene text recognition, which share some common strategies but also show different preferences. There are two main streams of methods: segmentation-based and sequence-to-sequence learning methods. The convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) model has received high attention in recent years and is being extended in respect of encoding, decoding or learning strategies, while segmentation-based methods combining deep learning are still performing competitively. A noteworthy tendency is the extension of text line recognition to page-level recognition. Following text recognition, we also review the works of end-to-end scene text recognition (also called as text spotting), for which text detection and recognition models are learned jointly. 5) Among symbol and graphics in documents, mathematical expressions and flowcharts have received increasing attention. Recent methods for mathematical expression recognition are mostly image-to-markup generation methods using encoder-decoder models, while graph-based methods promise in generating both recognition and segmentation results. Flowchart recognition is addressed using structured prediction models such as GNN. 6) Document retrieval concerned mainly keyword spotting in pre-deep learning era, while recent works focus on information extraction (spotting semantic entities) by fusing layout and language information. Pre-trained layout and multi-modal language models are showing promises, while visual information is not considered adequately.Overall, the recent progress shows that the objects of recognition are expanded in breadth and depth, the methods are getting closer to deep neural networks and deep learning, the recognition performance is improved constantly, and the technology is applied to extensive scenes. The review also reveals the insufficiencies of the current technology in accuracy and reliability on various tasks, the interpretability, the learning ability and adaptability.Future works are suggested in respect of performance promotion, application extension, and improved learning. Issues of performance promotion include the reliability of recognition, interpretability, omni-element recognition, long-tailed recognition, multi-lingual documents, complex layout analysis and understanding, recognition of distorted documents. Issues related to applications include new applications (such as robotic process automation (RPA), text scription in natural scenes, archeology), new technical problems involved in applications (such as semantic information extraction, cross-modal fusion, reasoning and decision related to application scenes). Aiming to improve the automatic system design, learning ability and adaptability, the involved learning problems/methods include small sample learning, transfer learning, multi-task learning, domain adaptation, structured prediction, weakly-supervised learning, self-supervised learning, open set learning, and cross-modal learning.关键词:document analysis and recognition;document intelligence;layout analysis;text detection;text recognition;graphics and symbol recognition;document information extraction353|2383|4更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:Document analysis and recognition (called document recognition in brief) is aimed to covert non-structured documents (typically, document images and online handwriting) into structured texts for facilitating computer processing and understanding. It is needed in wide applications due to the pervasive communication and usage of documents. The field of document recognition has attracted intensive attention and produced enormous progress in research and applications since 1960s. Particularly, the recent development of deep learning technology has boosted the performance of document recognition remarkably compared to traditional methods, and the technology has been applied successfully to document digitization, form processing, handwriting input, intelligent transportation, document retrieval and information extraction.In this article, we first introduce the background and involved techniques of document recognition, give an overview of the history of research (divided into four periods according to the objects of research, the methods and applications), and then review the main research progress with emphasis on deep learning based methods developed in recent years. After identifying the insufficiency of current technology, we finally suggest some important issues for future research.The review of recent progress is divided into sections corresponding to main processing steps, namely image pre-processing, layout analysis, scene text detection, text recognition, structured symbol and graphics recognition, document retrieval and information extraction.The review of recent progress is divided into sections corresponding to the main processing steps, namely image pre-processing, layout analysis, scene text detection, text recognition, structured symbol and graphics recognition, document retrieval and information extraction. 1) Due to the popularity of camera-captured document images, the current main task in image pre-processing is the rectification of distorted image while the task of binarization is still concerned. Recent methods are mostly end-to-end deep learning based transformation methods. 2) Layout analysis is dichotomized into physical layout analysis (page segmentation) and logical layout analysis (semantic region segmentation and reading order prediction). Recent page segmentation methods based on fully convolutional network (FCN) or graph neural network (GNN) have shown promises. Logical layout analysis has been addressed by deep neural networks fusing multi-modal information. Table structure analysis is a special task of layout analysis and has been studied intensively in recent years. 3) Scene text detection is a hot topic in document analysis and computer vision fields. Deep learning based methods for text methods can be divided into regression-based methods, segmentation-based methods and hybrid methods. FCN is prevalently used for extracting visual features, based on which models are built to predict text regions. 4) Text recognition is the core task in document analysis. We review recent works for handwritten text recognition and scene text recognition, which share some common strategies but also show different preferences. There are two main streams of methods: segmentation-based and sequence-to-sequence learning methods. The convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) model has received high attention in recent years and is being extended in respect of encoding, decoding or learning strategies, while segmentation-based methods combining deep learning are still performing competitively. A noteworthy tendency is the extension of text line recognition to page-level recognition. Following text recognition, we also review the works of end-to-end scene text recognition (also called as text spotting), for which text detection and recognition models are learned jointly. 5) Among symbol and graphics in documents, mathematical expressions and flowcharts have received increasing attention. Recent methods for mathematical expression recognition are mostly image-to-markup generation methods using encoder-decoder models, while graph-based methods promise in generating both recognition and segmentation results. Flowchart recognition is addressed using structured prediction models such as GNN. 6) Document retrieval concerned mainly keyword spotting in pre-deep learning era, while recent works focus on information extraction (spotting semantic entities) by fusing layout and language information. Pre-trained layout and multi-modal language models are showing promises, while visual information is not considered adequately.Overall, the recent progress shows that the objects of recognition are expanded in breadth and depth, the methods are getting closer to deep neural networks and deep learning, the recognition performance is improved constantly, and the technology is applied to extensive scenes. The review also reveals the insufficiencies of the current technology in accuracy and reliability on various tasks, the interpretability, the learning ability and adaptability.Future works are suggested in respect of performance promotion, application extension, and improved learning. Issues of performance promotion include the reliability of recognition, interpretability, omni-element recognition, long-tailed recognition, multi-lingual documents, complex layout analysis and understanding, recognition of distorted documents. Issues related to applications include new applications (such as robotic process automation (RPA), text scription in natural scenes, archeology), new technical problems involved in applications (such as semantic information extraction, cross-modal fusion, reasoning and decision related to application scenes). Aiming to improve the automatic system design, learning ability and adaptability, the involved learning problems/methods include small sample learning, transfer learning, multi-task learning, domain adaptation, structured prediction, weakly-supervised learning, self-supervised learning, open set learning, and cross-modal learning.关键词:document analysis and recognition;document intelligence;layout analysis;text detection;text recognition;graphics and symbol recognition;document information extraction353|2383|4更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:Text can be as one of the key carriers for information transmission. Digital media-related text has been widely developing for such image aspects of document and scene contexts. To extract and analyze these text information-involved images automatically, Conventional researches are mainly focused on automatic text extraction techniques like scene text detection and recognition. However, text-centric images-based semantic information recognition or analysis as a downstream task of spotting text, remains a challenge due to the difficulty of fully leveraging multi-modal features from both vision and language. To this end, text-centric image understanding has been an emerging research topic and many related tasks have been proposed. For example, the visual information extraction technique is capable of extracting the specified content from the given image, which can be used to improve productivity in finance, social media, and other fields. In this paper, we introduce five representative text-centric image understanding tasks and conduct a systematic survey on them. According to the understanding level, these tasks can be broadly classified into two categories. The first category requires the basic understanding ability to extract and distinguish information, such as visual information extraction and scene text retrieval. In contrast, besides the fundamental understanding ability, the second category is more concerned with high-level semantic understanding capabilities like information aggregation and logical reasoning. With the research progress in deep learning and multimodal learning, the second category has attracted considerable attention recently. For the second category, this survey mainly introduces document visual question answering, scene text visual question answering, and scene text image captioning tasks. Over the past few decades, the development of text-centric image understanding techniques has gone through several stages. Earlier approaches are based on heuristic rules and may only utilize unimodal features. Currently, deep learning methods have gained wide popularity and dominated this area. Meanwhile, multimodal features are valued and exploited to improve performance. To be more specific, traditional visual information extraction depends on pre-defined templates or specific rules. Traditional text retrieval task tends to represent words with pyramid histograms of character vectors and predict the matched image according to the representation distance. Expanded from the conventional visual question answering framework, earlier document visual question answering, and scene text visual question answering approaches simply add an optical character recognition branch to extract text information. As integrating knowledge from multimodal signals helps to better understand images, graph neural networks and Transformer-based frameworks are used to fuse multi-modal features recently. Furthermore, self-supervised pre-training schemes are applied to learn the alignment between different modalities, thus boosting model capabilities by a large margin. For each text-centric image understanding task, we summarize classical methods and further elaborate the pros and cons of them. In addition, we also discuss the potential problems and further research directions for the community. Firstly, due to the complexity of different modality features, such as mutative layout and diverse fonts, current deep learning architectures still fail to complete the interaction of multi-modal information efficiently. Secondly, existing text-centric image understanding methods are still limited in their reasoning abilities, involving counting, sorting, and arithmetic operations. For instance, in document visual question answering and scene text visual question answering tasks, current models have difficulty predicting accurate answers when they require to jointly reason over image layout, textual content, and visual art, etc. Finally, the current text-centric understanding tasks are often trained independently and the correlation between different tasks has not been effectively leveraged. We hope this survey can help researchers capture the latest progress in text-centric image understanding and inspire the new design of advanced models and algorithms.关键词:text image understanding;visual information extraction;scene text retrieval;document visual question answering;scene text visual question answering;scene text image captioning198|513|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:Text can be as one of the key carriers for information transmission. Digital media-related text has been widely developing for such image aspects of document and scene contexts. To extract and analyze these text information-involved images automatically, Conventional researches are mainly focused on automatic text extraction techniques like scene text detection and recognition. However, text-centric images-based semantic information recognition or analysis as a downstream task of spotting text, remains a challenge due to the difficulty of fully leveraging multi-modal features from both vision and language. To this end, text-centric image understanding has been an emerging research topic and many related tasks have been proposed. For example, the visual information extraction technique is capable of extracting the specified content from the given image, which can be used to improve productivity in finance, social media, and other fields. In this paper, we introduce five representative text-centric image understanding tasks and conduct a systematic survey on them. According to the understanding level, these tasks can be broadly classified into two categories. The first category requires the basic understanding ability to extract and distinguish information, such as visual information extraction and scene text retrieval. In contrast, besides the fundamental understanding ability, the second category is more concerned with high-level semantic understanding capabilities like information aggregation and logical reasoning. With the research progress in deep learning and multimodal learning, the second category has attracted considerable attention recently. For the second category, this survey mainly introduces document visual question answering, scene text visual question answering, and scene text image captioning tasks. Over the past few decades, the development of text-centric image understanding techniques has gone through several stages. Earlier approaches are based on heuristic rules and may only utilize unimodal features. Currently, deep learning methods have gained wide popularity and dominated this area. Meanwhile, multimodal features are valued and exploited to improve performance. To be more specific, traditional visual information extraction depends on pre-defined templates or specific rules. Traditional text retrieval task tends to represent words with pyramid histograms of character vectors and predict the matched image according to the representation distance. Expanded from the conventional visual question answering framework, earlier document visual question answering, and scene text visual question answering approaches simply add an optical character recognition branch to extract text information. As integrating knowledge from multimodal signals helps to better understand images, graph neural networks and Transformer-based frameworks are used to fuse multi-modal features recently. Furthermore, self-supervised pre-training schemes are applied to learn the alignment between different modalities, thus boosting model capabilities by a large margin. For each text-centric image understanding task, we summarize classical methods and further elaborate the pros and cons of them. In addition, we also discuss the potential problems and further research directions for the community. Firstly, due to the complexity of different modality features, such as mutative layout and diverse fonts, current deep learning architectures still fail to complete the interaction of multi-modal information efficiently. Secondly, existing text-centric image understanding methods are still limited in their reasoning abilities, involving counting, sorting, and arithmetic operations. For instance, in document visual question answering and scene text visual question answering tasks, current models have difficulty predicting accurate answers when they require to jointly reason over image layout, textual content, and visual art, etc. Finally, the current text-centric understanding tasks are often trained independently and the correlation between different tasks has not been effectively leveraged. We hope this survey can help researchers capture the latest progress in text-centric image understanding and inspire the new design of advanced models and algorithms.关键词:text image understanding;visual information extraction;scene text retrieval;document visual question answering;scene text visual question answering;scene text image captioning198|513|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:A huge amount of big data-driven documents are required to be digitalized, stored and distributed in relation to images contexts. Such of application scenarios are concerned of document images-oriented key information, such as receipt understanding, card recognition, automatic paper scoring and document matching. Such process is called visual information extraction (VIE), which is focused on information mining, analysis, and extraction from visually rich documents. Documents-related text objects are diverse and varied, multi-language documents can be also commonly-used incorporated with single language scenario. Furthermore, text corpus differs from field to field. For example, a difference in the text content is required to be handled between legal files and medical documents. A complex layout may exist when a variety of visual elements are involved in a document, such as pictures, tables, and statistical curves. Unreadable document images are often derived and distorted from such noises like ink, wrinkles, distortion, and illumination. The completed pipeline of visual information extraction can be segmented into four steps: first, a pre-processing algorithm should be applied to remove the problem of interference and noise in a manner of correction and denoising. Second, document image-derived text strings and their locations contexts may be extracted in terms of text detection and recognition methods. Subsequently, multimodal feature extraction is required to perform high-level calculation and fusion of text, layout and visual features contained in visually rich documents. Finally, entity category parsing is applied to determine the category of each entity. Existed methods are mainly focused on the latter of two steps, while some take text detection and recognition into account. Early works are concerned of querying key information manually via rule-based methods. The effectiveness of these algorithms is quite lower, and they have poor generalization performance as well. The emerging deep learning technique-based feature extractors like convolutional neural networks and Transformers are linked with depth features for the optimization of performance and efficiency. In recent years, deep learning based methods have been widely applied in real scenarios. To sum up, we review deep-learning-based VIE methods and public datasets proposed in recent years, and these algorithms can be classified by their main characteristics. Recent deep-learning-based VIE methods proposed can be roughly categorized into six types of methods relevant to such contexts of grid-based, graph-neural-network-based (GNN-based), Transformer-based, end-to-end, few-shot, and the related others. Grid-based methods are focused on taking the document image as a two-dimensional matrix, pixels-inner text bounding box are filled with text embedding, and the grid representation can be formed for deep processing. Grid-based methods are often simple and have less computational cost. However, its representation ability is not strong enough, and features of text regions in small size may not be fully exploited. GNN-based methods take text segments as graph nodes, relations between segment coordinates are encoded for edge representations. Such graph convolution-related operations are applied for feature extraction further. GNN-based schemes achieve a good balance between cost and performance, but some characteristics of GNN itself like over-smoothing and gradient vanishing are often challenged to train the model. Transformer-based methods achieve outstanding performance through pre-training with a vast amount of data. These methods are preferred to have powerful generalizability, and it can be applied for multiple scenarios extended to other related document understanding tasks. However, these computational models are often costly and computing resources are required to be optimized. A more efficient architecture and pre-training strategy is still as a challenging problem to be resolved. The VIE is a mutual-benefited process, and text detection and recognition optical character recognition (OCR) are needed as prerequisites. The OCR-attainable problems like coordinate mismatches and text recognition errors will affect the following steps as well. Such end-to-end paradigms can be traced to optimize the OCR error accumulation to some extent. Few-shot methods-related structures can be used to enhance the generalization ability of models efficiently, and intrinsic features can be exploited to some extend in term of a small number of samples only.First, the growth of this research domain is reviewed and its challenging contexts can be predicted as well. Then, recent deep learning based visual information extraction methods and their contexts are summarized and analyzed. Furthermore, multiple categories-relevant methods are predictable, while the algorithm flow and technical development route of the representative models are further discussed and analyzed. Additionally, features of some public datasets are illustrated in comparison with the performance of representative models on these benchmarks. Finally, research highlights and limitations of each sort of model are laid out, and future research direction is forecasted as well.关键词:visual information extraction (VIE);document image analysis and understanding;computer vision;natural language processing;optical character recognition (OCR);deep learning;survey490|770|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:A huge amount of big data-driven documents are required to be digitalized, stored and distributed in relation to images contexts. Such of application scenarios are concerned of document images-oriented key information, such as receipt understanding, card recognition, automatic paper scoring and document matching. Such process is called visual information extraction (VIE), which is focused on information mining, analysis, and extraction from visually rich documents. Documents-related text objects are diverse and varied, multi-language documents can be also commonly-used incorporated with single language scenario. Furthermore, text corpus differs from field to field. For example, a difference in the text content is required to be handled between legal files and medical documents. A complex layout may exist when a variety of visual elements are involved in a document, such as pictures, tables, and statistical curves. Unreadable document images are often derived and distorted from such noises like ink, wrinkles, distortion, and illumination. The completed pipeline of visual information extraction can be segmented into four steps: first, a pre-processing algorithm should be applied to remove the problem of interference and noise in a manner of correction and denoising. Second, document image-derived text strings and their locations contexts may be extracted in terms of text detection and recognition methods. Subsequently, multimodal feature extraction is required to perform high-level calculation and fusion of text, layout and visual features contained in visually rich documents. Finally, entity category parsing is applied to determine the category of each entity. Existed methods are mainly focused on the latter of two steps, while some take text detection and recognition into account. Early works are concerned of querying key information manually via rule-based methods. The effectiveness of these algorithms is quite lower, and they have poor generalization performance as well. The emerging deep learning technique-based feature extractors like convolutional neural networks and Transformers are linked with depth features for the optimization of performance and efficiency. In recent years, deep learning based methods have been widely applied in real scenarios. To sum up, we review deep-learning-based VIE methods and public datasets proposed in recent years, and these algorithms can be classified by their main characteristics. Recent deep-learning-based VIE methods proposed can be roughly categorized into six types of methods relevant to such contexts of grid-based, graph-neural-network-based (GNN-based), Transformer-based, end-to-end, few-shot, and the related others. Grid-based methods are focused on taking the document image as a two-dimensional matrix, pixels-inner text bounding box are filled with text embedding, and the grid representation can be formed for deep processing. Grid-based methods are often simple and have less computational cost. However, its representation ability is not strong enough, and features of text regions in small size may not be fully exploited. GNN-based methods take text segments as graph nodes, relations between segment coordinates are encoded for edge representations. Such graph convolution-related operations are applied for feature extraction further. GNN-based schemes achieve a good balance between cost and performance, but some characteristics of GNN itself like over-smoothing and gradient vanishing are often challenged to train the model. Transformer-based methods achieve outstanding performance through pre-training with a vast amount of data. These methods are preferred to have powerful generalizability, and it can be applied for multiple scenarios extended to other related document understanding tasks. However, these computational models are often costly and computing resources are required to be optimized. A more efficient architecture and pre-training strategy is still as a challenging problem to be resolved. The VIE is a mutual-benefited process, and text detection and recognition optical character recognition (OCR) are needed as prerequisites. The OCR-attainable problems like coordinate mismatches and text recognition errors will affect the following steps as well. Such end-to-end paradigms can be traced to optimize the OCR error accumulation to some extent. Few-shot methods-related structures can be used to enhance the generalization ability of models efficiently, and intrinsic features can be exploited to some extend in term of a small number of samples only.First, the growth of this research domain is reviewed and its challenging contexts can be predicted as well. Then, recent deep learning based visual information extraction methods and their contexts are summarized and analyzed. Furthermore, multiple categories-relevant methods are predictable, while the algorithm flow and technical development route of the representative models are further discussed and analyzed. Additionally, features of some public datasets are illustrated in comparison with the performance of representative models on these benchmarks. Finally, research highlights and limitations of each sort of model are laid out, and future research direction is forecasted as well.关键词:visual information extraction (VIE);document image analysis and understanding;computer vision;natural language processing;optical character recognition (OCR);deep learning;survey490|770|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveVisually-rich document information extraction is committed to such key document images-related text information structure. Invoice-contextual data can be as one of the commonly-used data types of documents. For the enterprises-oriented reimbursement process, much more demands are required of key information extraction of invoices. To resolve this problem, such key techniques like optical character recognition(OCR) and information extraction have been developing intensively. However, the number of related publicly available datasets and the number of images involved are relatively challenged to rich in each dataset.MethodWe develop a real financial scanned Chinese invoice dataset, for which it can be used for collection, annotation, and releasing further. This data set consists of 40 716 images of six types of invoices in the context of aircraft itinerary tickets, taxi invoices, general quota invoices, passenger invoices, train tickets, and toll invoices. It can be divided into training/validation/testing sets further in related to 19 999/10 358/10 359 images. The labeling process of this dataset is concerned of such key steps like pseudo-label generation, manual recheck and cleaning, and manual desensitization, which can offer two sort of labels-related for the OCR task and information extraction deliberately. Such of challenges are still to be resolved in the context of print misalignment, blurring, and overlap. We facilitate a baseline scheme to realize end-to-end inference result. The overall solution can be divided into four steps as mentioned below: 1) a OCR module to predict all text instances’ content and location. 2) A text block ordering module to re-arrange all text instances into a more feasible order and serialize the 2D information into 1D. 3) The LayoutLM v2 model is melted into three modalities information (text, visual, and layout) and generate the prediction of sequence labels, which can utilize knowledge generated from the pre-trained language model. 4) The post-processing module transfer the model’s output to the final structural information. The overall solution can simplify the complexity of the overall ticket system via the integration of multiple invoices.ResultThe baseline experimental results are verified using OCR engine reasoning, OCR model prediction, and OCR ground-truth value. The F1 value of 0.768 7/0.857 0/0.985 7 can be reached as well. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the overall solution and LayoutLM V2 model can be optimized, and the challenging issue of OCR can be reflected in this scenario. Tesla-V100 GPU-based inference speed of the model can be reached to 1.88 frame/s. The accuracy of 90% can be reached using the raw image only as input. We demonstrate that the optimal solutions can be roughly segmented into two categories: one category is focused on melting the structured task into the text detection straightforward (i.e., multi-category detection), and the requirement of recognition model is to identify the text only with the corresponding category of concern. The other one is to implement the general information strategy, and an independent information extraction model can be used to extract key information. These solutions can integrate the potentials of the OCR and information extraction technologies farther.ConclusionThe scanned invoice dataset SCID (scanned Chinese invoice dataset) proposed demonstrates the application scenarios of the OCR technology can provide data support for the research and development of visually-rich document information extraction-related technology and technical implementation. The dataset can be linked and downloaded from https://davar-lab.github.io/dataset/scid.html.关键词:dataset;financial invoices;visually-rich documents;information extraction;optical character recognition (OCR);multi-modal information296|1025|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveVisually-rich document information extraction is committed to such key document images-related text information structure. Invoice-contextual data can be as one of the commonly-used data types of documents. For the enterprises-oriented reimbursement process, much more demands are required of key information extraction of invoices. To resolve this problem, such key techniques like optical character recognition(OCR) and information extraction have been developing intensively. However, the number of related publicly available datasets and the number of images involved are relatively challenged to rich in each dataset.MethodWe develop a real financial scanned Chinese invoice dataset, for which it can be used for collection, annotation, and releasing further. This data set consists of 40 716 images of six types of invoices in the context of aircraft itinerary tickets, taxi invoices, general quota invoices, passenger invoices, train tickets, and toll invoices. It can be divided into training/validation/testing sets further in related to 19 999/10 358/10 359 images. The labeling process of this dataset is concerned of such key steps like pseudo-label generation, manual recheck and cleaning, and manual desensitization, which can offer two sort of labels-related for the OCR task and information extraction deliberately. Such of challenges are still to be resolved in the context of print misalignment, blurring, and overlap. We facilitate a baseline scheme to realize end-to-end inference result. The overall solution can be divided into four steps as mentioned below: 1) a OCR module to predict all text instances’ content and location. 2) A text block ordering module to re-arrange all text instances into a more feasible order and serialize the 2D information into 1D. 3) The LayoutLM v2 model is melted into three modalities information (text, visual, and layout) and generate the prediction of sequence labels, which can utilize knowledge generated from the pre-trained language model. 4) The post-processing module transfer the model’s output to the final structural information. The overall solution can simplify the complexity of the overall ticket system via the integration of multiple invoices.ResultThe baseline experimental results are verified using OCR engine reasoning, OCR model prediction, and OCR ground-truth value. The F1 value of 0.768 7/0.857 0/0.985 7 can be reached as well. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the overall solution and LayoutLM V2 model can be optimized, and the challenging issue of OCR can be reflected in this scenario. Tesla-V100 GPU-based inference speed of the model can be reached to 1.88 frame/s. The accuracy of 90% can be reached using the raw image only as input. We demonstrate that the optimal solutions can be roughly segmented into two categories: one category is focused on melting the structured task into the text detection straightforward (i.e., multi-category detection), and the requirement of recognition model is to identify the text only with the corresponding category of concern. The other one is to implement the general information strategy, and an independent information extraction model can be used to extract key information. These solutions can integrate the potentials of the OCR and information extraction technologies farther.ConclusionThe scanned invoice dataset SCID (scanned Chinese invoice dataset) proposed demonstrates the application scenarios of the OCR technology can provide data support for the research and development of visually-rich document information extraction-related technology and technical implementation. The dataset can be linked and downloaded from https://davar-lab.github.io/dataset/scid.html.关键词:dataset;financial invoices;visually-rich documents;information extraction;optical character recognition (OCR);multi-modal information296|1025|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveElectronic entry of paper documents is normally based on optical character recognition (OCR) technology. A commonly-used OCR system consists of four sequential steps: image acquisition, image preprocessing, character recognition, and typesetting output. The acquired digital image will have a certain degree of geometric distortion because paper document may not be parallel to the plane where the image acquisition device is located. The lens of the image acquisition device may have its own problem of distortion, or its paper document may challenge for deformation. Image acquisition problems of interferences and distortions will be more severe when handheld image capture devices are used (e.g., mobile phone cameras). Computer vision-oriented highly robust correction algorithms are focused on removing geometric distortions derived from imaging process of paper documents. Currrent researches are concerned about neural networks-based geometric correction of document images. Compared to traditional geometric correction algorithms, neural network-based document image correction algorithms have its potential ability in terms of both hardware requirements and algorithm implementation. However, it is still challenged for optimizing processing performance, especially for the contexts of offline and light weight.To improve the visual effect and OCR recognition accuracy of the original image, geometric correction of document graphics can be used to handle distortion, aberration, skew, and other related image-capturing geometric perturbations. Conventional image processing methods are required for such auxiliary hardware like laser scanners or multiple views-captured documents, and the algorithms can not be robusted. The emerging deep learning methods can be used to optimize traditional algorithms via modeling, but these models still have certain limitations. So, we develop a lightweight geometric correction network (AsymcNet), for which an integrated document region localisation and correction method can be oriented to implement geometric correction of document images end-to-end.MethodAsymcNet is designed and dealt with possible geometric interference in image acquisition. It consists of document regions-located segmentation network and a grid regression-rectifying regression network, as well as two sub-networks in a cascade form. Segmentation network-based AsymcNet can achieve good correction results for document images in various fields of view. In the regression part of the network, the resolution of the output regression grid is down to shrink the memory consumption and duration of training and inference. The methodologies are illustrated as follows: 1)Segmentation of the network: a simplified Unet-basd skip connection is set up between the encoder and decoder, in which lower layers-derived features can flow into higher layers directly and melt them into small resolution inputs and outputs. Considering the simplicity of the segmentation task, the segmentation network uses a small resolution (128 × 128 pixels) document image as input and outputs a small resolution segmentation result for the sake of lightweight and possible subsequent localization and mobile porting. 2) Regression network: compared to the segmentation task, the regression task of correcting the grid output is more complex. To capture more details from the image to be corrected for the final corrected grid regression, the regression network can be used to adapt a large resolution (512 × 512 pixels) document image as input with the segmentation result of the segmentation network output as a dot product, and outputs a small resolution (128 × 128 pixels) corrected grid.ResultAsymcNet-relevant comparative analysis is carried out in relevance to 4 popular methods. The multi-scale structural similarity (MS-SSIM) of raw images can be improved from 0.318 to 0.467; The local distortion (LD) is improved from 33.608 to 11.615; and the character error rate (CER) is optimized from 0.570 to 0.273. Compared to displacement flow estimation with fully convolutional network (DFE-FC), AsymcNet’s MS-SSIM is improved by 0.036, LD is lower by 2.193, CER is shrinked by 0.033, and AsymcNet’s average processing time for a single image is required for 8.85% of DFE-FC’s only. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed AsymcNet has certain advantages in comparison with other related correction algorithms. In particular, when the relative area occupied by document regions in the image to be processed is small, the advantage of AsymcNet is more significant due to the integration of sub-networks for document region segmentation in the structure of AsymcNet.ConclusionOur AsymcNet proposed has been validated for its effectiveness and generalization. Compared to existing methods, AsymcNet has its priorities in terms of correction accuracy, computational efficiency, and generalization. Furthermore, the design of AsymcNet is focused on “small resolution grid” as the regression target of the network, which can alleviate the convergence difficulty of the network and the memory consumption during training and inference. The generalizability of the network can be improved further.关键词:image preprocessing;geometric correction;full convolutional network(FCN);grid sampling;end-to-end106|417|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveElectronic entry of paper documents is normally based on optical character recognition (OCR) technology. A commonly-used OCR system consists of four sequential steps: image acquisition, image preprocessing, character recognition, and typesetting output. The acquired digital image will have a certain degree of geometric distortion because paper document may not be parallel to the plane where the image acquisition device is located. The lens of the image acquisition device may have its own problem of distortion, or its paper document may challenge for deformation. Image acquisition problems of interferences and distortions will be more severe when handheld image capture devices are used (e.g., mobile phone cameras). Computer vision-oriented highly robust correction algorithms are focused on removing geometric distortions derived from imaging process of paper documents. Currrent researches are concerned about neural networks-based geometric correction of document images. Compared to traditional geometric correction algorithms, neural network-based document image correction algorithms have its potential ability in terms of both hardware requirements and algorithm implementation. However, it is still challenged for optimizing processing performance, especially for the contexts of offline and light weight.To improve the visual effect and OCR recognition accuracy of the original image, geometric correction of document graphics can be used to handle distortion, aberration, skew, and other related image-capturing geometric perturbations. Conventional image processing methods are required for such auxiliary hardware like laser scanners or multiple views-captured documents, and the algorithms can not be robusted. The emerging deep learning methods can be used to optimize traditional algorithms via modeling, but these models still have certain limitations. So, we develop a lightweight geometric correction network (AsymcNet), for which an integrated document region localisation and correction method can be oriented to implement geometric correction of document images end-to-end.MethodAsymcNet is designed and dealt with possible geometric interference in image acquisition. It consists of document regions-located segmentation network and a grid regression-rectifying regression network, as well as two sub-networks in a cascade form. Segmentation network-based AsymcNet can achieve good correction results for document images in various fields of view. In the regression part of the network, the resolution of the output regression grid is down to shrink the memory consumption and duration of training and inference. The methodologies are illustrated as follows: 1)Segmentation of the network: a simplified Unet-basd skip connection is set up between the encoder and decoder, in which lower layers-derived features can flow into higher layers directly and melt them into small resolution inputs and outputs. Considering the simplicity of the segmentation task, the segmentation network uses a small resolution (128 × 128 pixels) document image as input and outputs a small resolution segmentation result for the sake of lightweight and possible subsequent localization and mobile porting. 2) Regression network: compared to the segmentation task, the regression task of correcting the grid output is more complex. To capture more details from the image to be corrected for the final corrected grid regression, the regression network can be used to adapt a large resolution (512 × 512 pixels) document image as input with the segmentation result of the segmentation network output as a dot product, and outputs a small resolution (128 × 128 pixels) corrected grid.ResultAsymcNet-relevant comparative analysis is carried out in relevance to 4 popular methods. The multi-scale structural similarity (MS-SSIM) of raw images can be improved from 0.318 to 0.467; The local distortion (LD) is improved from 33.608 to 11.615; and the character error rate (CER) is optimized from 0.570 to 0.273. Compared to displacement flow estimation with fully convolutional network (DFE-FC), AsymcNet’s MS-SSIM is improved by 0.036, LD is lower by 2.193, CER is shrinked by 0.033, and AsymcNet’s average processing time for a single image is required for 8.85% of DFE-FC’s only. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed AsymcNet has certain advantages in comparison with other related correction algorithms. In particular, when the relative area occupied by document regions in the image to be processed is small, the advantage of AsymcNet is more significant due to the integration of sub-networks for document region segmentation in the structure of AsymcNet.ConclusionOur AsymcNet proposed has been validated for its effectiveness and generalization. Compared to existing methods, AsymcNet has its priorities in terms of correction accuracy, computational efficiency, and generalization. Furthermore, the design of AsymcNet is focused on “small resolution grid” as the regression target of the network, which can alleviate the convergence difficulty of the network and the memory consumption during training and inference. The generalizability of the network can be improved further.关键词:image preprocessing;geometric correction;full convolutional network(FCN);grid sampling;end-to-end106|417|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveThe Dunhuang manuscripts are evident for cultural heritage researches of China. Most of preserved manuscripts are restricted of its age-derived fragments and remnants and challenged for their collation and contexts. However, artificial reconstruction is time consuming and difficult to be developed. The emerging computer graphics-derived computer-aided virtual recovery technology has been facilitating in the context of high speed, easy to use and accuracy.MethodWe develop a model-hierarchical digital image reconstruction method. First, a dataset of ancient Dunhuang manuscript fragments is constructed. Second, expertise-relevant digital images of the fragments are pre-processed to assist in the rationalization of fragment features and establishment of a plane for the reconstructing process. Moreover, a three layers model is composed of physical, structural and semantic features via fusing multiple collocation cues. For the physical layer, grey-scale feature similarity measures are based on Jaccard correlation coefficients. For the structural layer, geometric contour matching is based on Freeman coding. For the semantic layer, character column spacing consistency features are based on grey-scale fluctuations. The whole reconstruction process is combined with two matching aspects of local and global contexts. The key to the local matching is to determine whether the two pieces match or not, while the vector similarity calculations are performed on the feature descriptors. The local matching results are evaluated and scored by reasonable thresholds between low and the high level. To realize the whole automation process, global matching strategy is implemented in terms of the Hannotta model, and the two aspect of fully automated reconstruction is performed.ResultTo verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are carried out on a 256-fragments dataset, which consists of 31 splinterable fragments (which can be reconstructed in 11 groups) and 225 orphaned fragments. The results analysis illustrates that 8 groups of fragments are fully matched, 2 groups are partially matched, and 218 orphaned fragments are identified as well. The accuracy of completed matching is 95.76% while incomplete matching is 95.70%. Both of their accuracies can be optimized and reached to 95%. To be more specific, each of partial accuracy are reached to 20.62%, 63.44% and 23.43%, and the improvement in complete accuracy of each are 39.85%, 68.09% and 23.33%.ConclusionThe layered model combined with high-speed computing performance of the computer can incorporate multiple features and complete the reconstruction of ancient manuscript fragments effectively. The potential virtual reconstruction is beneficial for secondary damage to the fragile fragments, as well as some irreversible operations. Furthermore, the reconstructed results can provide an important basis for subsequent physical splicing, which can greatly enhance the efficiency of the artificial reconstruction.关键词:ancient manuscript fragments;Dunhuang manuscripts;automatic reconstruction;curve feature;hierarchical model222|297|2更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveThe Dunhuang manuscripts are evident for cultural heritage researches of China. Most of preserved manuscripts are restricted of its age-derived fragments and remnants and challenged for their collation and contexts. However, artificial reconstruction is time consuming and difficult to be developed. The emerging computer graphics-derived computer-aided virtual recovery technology has been facilitating in the context of high speed, easy to use and accuracy.MethodWe develop a model-hierarchical digital image reconstruction method. First, a dataset of ancient Dunhuang manuscript fragments is constructed. Second, expertise-relevant digital images of the fragments are pre-processed to assist in the rationalization of fragment features and establishment of a plane for the reconstructing process. Moreover, a three layers model is composed of physical, structural and semantic features via fusing multiple collocation cues. For the physical layer, grey-scale feature similarity measures are based on Jaccard correlation coefficients. For the structural layer, geometric contour matching is based on Freeman coding. For the semantic layer, character column spacing consistency features are based on grey-scale fluctuations. The whole reconstruction process is combined with two matching aspects of local and global contexts. The key to the local matching is to determine whether the two pieces match or not, while the vector similarity calculations are performed on the feature descriptors. The local matching results are evaluated and scored by reasonable thresholds between low and the high level. To realize the whole automation process, global matching strategy is implemented in terms of the Hannotta model, and the two aspect of fully automated reconstruction is performed.ResultTo verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are carried out on a 256-fragments dataset, which consists of 31 splinterable fragments (which can be reconstructed in 11 groups) and 225 orphaned fragments. The results analysis illustrates that 8 groups of fragments are fully matched, 2 groups are partially matched, and 218 orphaned fragments are identified as well. The accuracy of completed matching is 95.76% while incomplete matching is 95.70%. Both of their accuracies can be optimized and reached to 95%. To be more specific, each of partial accuracy are reached to 20.62%, 63.44% and 23.43%, and the improvement in complete accuracy of each are 39.85%, 68.09% and 23.33%.ConclusionThe layered model combined with high-speed computing performance of the computer can incorporate multiple features and complete the reconstruction of ancient manuscript fragments effectively. The potential virtual reconstruction is beneficial for secondary damage to the fragile fragments, as well as some irreversible operations. Furthermore, the reconstructed results can provide an important basis for subsequent physical splicing, which can greatly enhance the efficiency of the artificial reconstruction.关键词:ancient manuscript fragments;Dunhuang manuscripts;automatic reconstruction;curve feature;hierarchical model222|297|2更新时间:2024-05-07 -
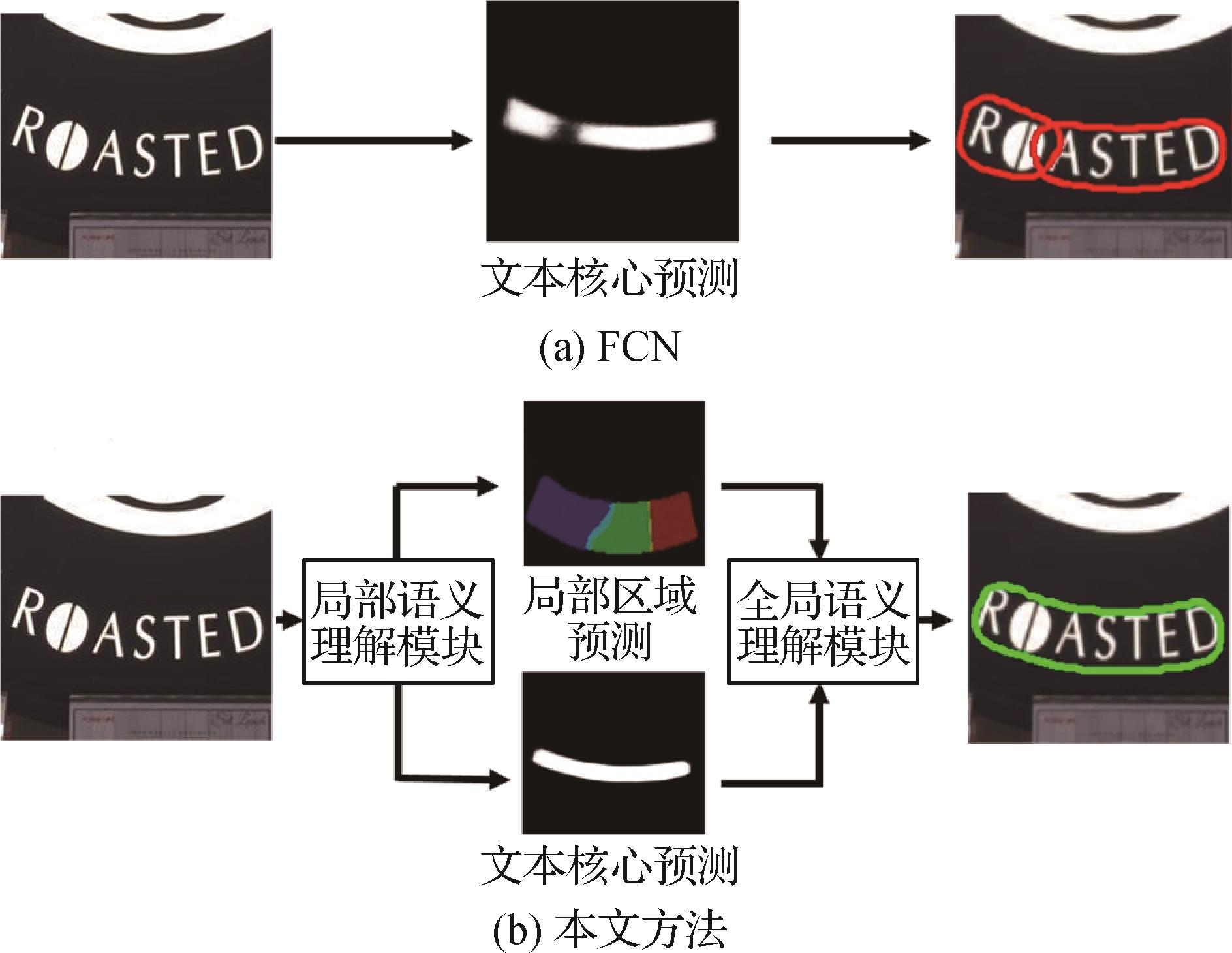 摘要:ObjectiveScene-related text detection is essential for computer vision, which aims to localize text instances for targeted image. It is beneficial for such domain of text recognition applications like scene understanding, translation and text visual question answering. The emerging deep learning based convolution neural network (CNN) has been widely developing in relevance to text detection nowadays. Current researches are focused on texts location in terms of the regression of the quadrangular bounding box. However, since regression based methods unfit texts with arbitrary shapes (e.g., curved texts), many approaches focus on segmentation based methods. Fully convolutional networks (FCN) are commonly used to obtain high-resolution feature maps, and the pixel-level mask is predicted to locate the text instances as well. Due to the extreme aspect ratios and the various sizes of text instances, existing models are challenged for one feature map-related integration of local-level and global-level semantics. More feature maps are introduced from multiple levels of the network, and hierarchical semantics can be generated from the corresponding feature map. But, these modules are required to yield the network to optimize the hierarchical features simultaneously, which may distract the network to a certain extent. Hence, existing networks are required to capture accurate hierarchical semantics further.MethodTo resolve this problem, the segmentation based text detection method is developed and a hierarchical semantic fusion network is demonstrated as well. We decouple the local and global feature extraction process and learn corresponding semantics. Specially, two mutual-benefited components are introduced for enhancing effective local and global feature, sub-region based local semantic understanding module (SLM) and instance based global semantic understanding module (IGM). First, SLM is used to segment the text instance into a kernel and multiple sub-regions in terms of their text-inner position. And, SLM can be used to learn their segmentation, which is an auxiliary task for the model. As a small part of the text, segmenting sub-region requires more local-level information and less long-range context, for which the model can be yielded to learning more accurate local features. Furthermore, ground truth-supervised position information can harness the network to separate the adjacent text instances. Second, IGM is designed for global-contextual feature extraction through capturing text instances-amongst long-range dependency. Thanks to SLM-derived segmentation maps, IGM can be used to filter the noisy background easily, and the instance-level features of each text instance can be obtained as well. Those features are then fed into a Transformer to fuse the semantics from different instances, in which global receptive field-related text features can be generated. And, the similarity is calculated relevant to the original pixel-level feature map. Finally, the global-level feature is aggregated via similarity map-related text features. The integrated SLM and IGM are beneficial for its learning to segment the text from pixel to local region and to text instances further. During this procedure, the hierarchical semantics are collected in the corresponding module, which can shrink the distraction for the other related level manually. In addition, vague semantics-involved ambiguous boundary in segmentation results are be sorted out, which may distort the semantic extraction. To alleviate this problem, we illustrate location aware loss (LAL) to increase the aggression of the misclassification around the border region. The LAL is calculated in terms of a weighted loss, and a higher weight is assigned for the pixels closer to the boundary. This loss function can be used to get a confident and accurate prediction of the boundary-relevant model, which has more accurate and discriminative feature.ResultComparative analysis is carried out on the basis of 12 popular methods. Three sort of challenging datasets are used for a comprehensive evaluation as well, called Total-Text, MSRA-TD500, and ICDAR2015 for each. The quantitative evaluation metrics consists of F-measure, recall, and precision. We achieve over 1% improvement on these two datasets with the F-measure of 87.0% and 88.2%. Especially, the recall and precision on MSRA-TD500 can be reached to 92.1% and 84.5%. For the ICDAR2015 dataset, the precision is improved to 92.3%. And, the F-measure on this dataset is optimized and reached to 87.0%. Additionally, a series of comparative experiments on the Total-Text dataset are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of each module proposed. Such analyses show that the proposed SLM, IGM, and LAL can be used to improve each F-measure of 1.0%, 0.6%, and 0.5%. The qualitative visualization demonstrates that the baseline model can be optimized to a certain extent.ConclusionHierarchical semantic understanding network is developed and a novel loss function is optimized for hierarchical semantics enhancement as well. Decoupling the local and global feature extraction process can be as an essential tool to get more accurate and reliable hierarchical semantics progressively.关键词:scene text;text detection;fully convolutional network (FCN);convolutional neural network (CNN);feature fusion;attention mechanism129|348|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveScene-related text detection is essential for computer vision, which aims to localize text instances for targeted image. It is beneficial for such domain of text recognition applications like scene understanding, translation and text visual question answering. The emerging deep learning based convolution neural network (CNN) has been widely developing in relevance to text detection nowadays. Current researches are focused on texts location in terms of the regression of the quadrangular bounding box. However, since regression based methods unfit texts with arbitrary shapes (e.g., curved texts), many approaches focus on segmentation based methods. Fully convolutional networks (FCN) are commonly used to obtain high-resolution feature maps, and the pixel-level mask is predicted to locate the text instances as well. Due to the extreme aspect ratios and the various sizes of text instances, existing models are challenged for one feature map-related integration of local-level and global-level semantics. More feature maps are introduced from multiple levels of the network, and hierarchical semantics can be generated from the corresponding feature map. But, these modules are required to yield the network to optimize the hierarchical features simultaneously, which may distract the network to a certain extent. Hence, existing networks are required to capture accurate hierarchical semantics further.MethodTo resolve this problem, the segmentation based text detection method is developed and a hierarchical semantic fusion network is demonstrated as well. We decouple the local and global feature extraction process and learn corresponding semantics. Specially, two mutual-benefited components are introduced for enhancing effective local and global feature, sub-region based local semantic understanding module (SLM) and instance based global semantic understanding module (IGM). First, SLM is used to segment the text instance into a kernel and multiple sub-regions in terms of their text-inner position. And, SLM can be used to learn their segmentation, which is an auxiliary task for the model. As a small part of the text, segmenting sub-region requires more local-level information and less long-range context, for which the model can be yielded to learning more accurate local features. Furthermore, ground truth-supervised position information can harness the network to separate the adjacent text instances. Second, IGM is designed for global-contextual feature extraction through capturing text instances-amongst long-range dependency. Thanks to SLM-derived segmentation maps, IGM can be used to filter the noisy background easily, and the instance-level features of each text instance can be obtained as well. Those features are then fed into a Transformer to fuse the semantics from different instances, in which global receptive field-related text features can be generated. And, the similarity is calculated relevant to the original pixel-level feature map. Finally, the global-level feature is aggregated via similarity map-related text features. The integrated SLM and IGM are beneficial for its learning to segment the text from pixel to local region and to text instances further. During this procedure, the hierarchical semantics are collected in the corresponding module, which can shrink the distraction for the other related level manually. In addition, vague semantics-involved ambiguous boundary in segmentation results are be sorted out, which may distort the semantic extraction. To alleviate this problem, we illustrate location aware loss (LAL) to increase the aggression of the misclassification around the border region. The LAL is calculated in terms of a weighted loss, and a higher weight is assigned for the pixels closer to the boundary. This loss function can be used to get a confident and accurate prediction of the boundary-relevant model, which has more accurate and discriminative feature.ResultComparative analysis is carried out on the basis of 12 popular methods. Three sort of challenging datasets are used for a comprehensive evaluation as well, called Total-Text, MSRA-TD500, and ICDAR2015 for each. The quantitative evaluation metrics consists of F-measure, recall, and precision. We achieve over 1% improvement on these two datasets with the F-measure of 87.0% and 88.2%. Especially, the recall and precision on MSRA-TD500 can be reached to 92.1% and 84.5%. For the ICDAR2015 dataset, the precision is improved to 92.3%. And, the F-measure on this dataset is optimized and reached to 87.0%. Additionally, a series of comparative experiments on the Total-Text dataset are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of each module proposed. Such analyses show that the proposed SLM, IGM, and LAL can be used to improve each F-measure of 1.0%, 0.6%, and 0.5%. The qualitative visualization demonstrates that the baseline model can be optimized to a certain extent.ConclusionHierarchical semantic understanding network is developed and a novel loss function is optimized for hierarchical semantics enhancement as well. Decoupling the local and global feature extraction process can be as an essential tool to get more accurate and reliable hierarchical semantics progressively.关键词:scene text;text detection;fully convolutional network (FCN);convolutional neural network (CNN);feature fusion;attention mechanism129|348|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveThe emerging digitization and intelligence techniques have facilitated the path to accept and recognize text content originated from paper documents, photos, or contexts nowadasys. Recent online mathematical expression recognition is widely used for such domain of portable devices like mobile phones and tablet PCs. The devices are required for converting the online handwritten trajectory into mathematical expression text and indicate symbols-between logical relationship in relevance to such of power, subscript and matrix. Online math calculator can be used to receive handwritten mathematical expressions in terms of online mathematical expression recognition, which makes input easier beyond LaTeX mathematical expressions with symbols of complex mathematical relation. At the same time, instant electric recording in complex scenarios becomes feasible for such scenarios like classes and academic meetings. Current encoder-decoder based mathematical expression recognition methods have been developing intensively. The quality and quantity of training data have a great impact on the performance of deep neural network. The lack of data has threatened the optimization of generalization and robustness of the model in consistency. The input form of the mathematical expression in the online scene is recognized as the track point sequence, which needs to be collected on the annotation-before real time handwriting device further. Therefore, cost of online data collection is higher than offline data. The model still has poor performance due to insufficient data.MethodTo resolve the problems mentioned above, we develop an encoder-decoder based generation model for online handwritten mathematical expressions. The model can generate the corresponding online trajectory point sequence in terms of the given mathematical expression text. We also can synthesize different-writing-style mathematical expressions by different style symbols input. A large amount of near real handwriting data is obtained at a very low cost, which expands the scale of training data flexibly and avoids lacked data fitting or over fitting of the model. For generation tasks, the ability of representation and discrimination of the encoder often affect the performance directly. The encoder aims to model the input text effectively. In detail, sufficient difference is needed between the representations of different inputs, and certain similarity is required between the ones of similar inputs as well. Intuitively, the representation of tree structure can well reflect expressions-between similarities and differences to some extent. Therefore, we design a tree representation-based text feature extraction module for the generation model in the encoder, which makes full use of the two-dimensional structure information. In addition, there is no corresponding relationship between each character of input text and the output track points. Therefore, to align the input text sequence with the output track points, we introduce a location-based attention model into the decoder. Simutaneously, to generate multiple handwriting style samples, we also integrate different handwriting style features into the decoder. The decoder can be used to synthesize the skeleton of the track through the input text, and writing style feature-related can be rendered into different styles.ResultThe method proposed is evaluated from two aspects: visual effect of generated results and the improvement of recognition tasks. First, we illustrate generation results of different difficulty, including simple sequence, complex fraction, multi-line expression and long text. Second, we select and display the generated data with similar and different writing styles. Next, we generate a large number of mathematical expression texts and synthesize online data randomly based on the generation model. Finally, we use these synthetic data as data augmentation to train the Transformer-TAP (track, attend, and parse), TAP and Densetap-TD (DenseNet TAP with tree decoder) as well. The performance of these three models is significantly improved beneficial from synthetic data. The additional data enriches the training set and the model is mutual-benefited for more symbol combinations with different writing styles. The results show that each of the absolute recognition rates is increased by 0.98%, 1.55% and 1.06%, as well as each of the relative recognition rates is increased by 9.9%, 12.37% and 9.81%.ConclusionAn online mathematical expression generation method is introduced based on encoder-decoder model. The method can be used to realize the generation of on-line trajectory point sequence from given expression text. It can expand the original data set more flexibly to a certain extent. Experimental result demonstrates that the synthetic data can improve the accuracy of online handwriting mathematical expression recognition effectively. It improves the generalization and robustness of the recognition model further.关键词:deep learning;handwritten expression recognition;end-to-end network;encoder-decoder; data augmentation131|308|2更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveThe emerging digitization and intelligence techniques have facilitated the path to accept and recognize text content originated from paper documents, photos, or contexts nowadasys. Recent online mathematical expression recognition is widely used for such domain of portable devices like mobile phones and tablet PCs. The devices are required for converting the online handwritten trajectory into mathematical expression text and indicate symbols-between logical relationship in relevance to such of power, subscript and matrix. Online math calculator can be used to receive handwritten mathematical expressions in terms of online mathematical expression recognition, which makes input easier beyond LaTeX mathematical expressions with symbols of complex mathematical relation. At the same time, instant electric recording in complex scenarios becomes feasible for such scenarios like classes and academic meetings. Current encoder-decoder based mathematical expression recognition methods have been developing intensively. The quality and quantity of training data have a great impact on the performance of deep neural network. The lack of data has threatened the optimization of generalization and robustness of the model in consistency. The input form of the mathematical expression in the online scene is recognized as the track point sequence, which needs to be collected on the annotation-before real time handwriting device further. Therefore, cost of online data collection is higher than offline data. The model still has poor performance due to insufficient data.MethodTo resolve the problems mentioned above, we develop an encoder-decoder based generation model for online handwritten mathematical expressions. The model can generate the corresponding online trajectory point sequence in terms of the given mathematical expression text. We also can synthesize different-writing-style mathematical expressions by different style symbols input. A large amount of near real handwriting data is obtained at a very low cost, which expands the scale of training data flexibly and avoids lacked data fitting or over fitting of the model. For generation tasks, the ability of representation and discrimination of the encoder often affect the performance directly. The encoder aims to model the input text effectively. In detail, sufficient difference is needed between the representations of different inputs, and certain similarity is required between the ones of similar inputs as well. Intuitively, the representation of tree structure can well reflect expressions-between similarities and differences to some extent. Therefore, we design a tree representation-based text feature extraction module for the generation model in the encoder, which makes full use of the two-dimensional structure information. In addition, there is no corresponding relationship between each character of input text and the output track points. Therefore, to align the input text sequence with the output track points, we introduce a location-based attention model into the decoder. Simutaneously, to generate multiple handwriting style samples, we also integrate different handwriting style features into the decoder. The decoder can be used to synthesize the skeleton of the track through the input text, and writing style feature-related can be rendered into different styles.ResultThe method proposed is evaluated from two aspects: visual effect of generated results and the improvement of recognition tasks. First, we illustrate generation results of different difficulty, including simple sequence, complex fraction, multi-line expression and long text. Second, we select and display the generated data with similar and different writing styles. Next, we generate a large number of mathematical expression texts and synthesize online data randomly based on the generation model. Finally, we use these synthetic data as data augmentation to train the Transformer-TAP (track, attend, and parse), TAP and Densetap-TD (DenseNet TAP with tree decoder) as well. The performance of these three models is significantly improved beneficial from synthetic data. The additional data enriches the training set and the model is mutual-benefited for more symbol combinations with different writing styles. The results show that each of the absolute recognition rates is increased by 0.98%, 1.55% and 1.06%, as well as each of the relative recognition rates is increased by 9.9%, 12.37% and 9.81%.ConclusionAn online mathematical expression generation method is introduced based on encoder-decoder model. The method can be used to realize the generation of on-line trajectory point sequence from given expression text. It can expand the original data set more flexibly to a certain extent. Experimental result demonstrates that the synthetic data can improve the accuracy of online handwriting mathematical expression recognition effectively. It improves the generalization and robustness of the recognition model further.关键词:deep learning;handwritten expression recognition;end-to-end network;encoder-decoder; data augmentation131|308|2更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveChinese calligraphy can be seen as one of the symbolized icons in Chinese culture. Nowadays, Machine learning and pattern recognition techniques-derived calligraphy artworks are required for digitalization and preservation intensively. Our research is mainly focused on Chinese calligraphy classification in related to such font and style classification. However, the difference between calligraphy font and calligraphy style is often distorted. To resolve the problem of style classification, first, we distinguish the difference between font and style. Then, we illustrate a novel multi-loss siamese convolutional neural network to cope with the two mentioned problems simultaneously.MethodThe difference can be summarized between calligraphy font and style as follows: Calligraphy font refers to a broad taxonomy of scripts. For example, the popular Chinese calligraphy fonts are composed of standard, seal, clerical, cursive and semi-cursive fonts. Calligraphy style is closely related to the calligraphers to a certain extent. Each calligrapher has its own unique style. Compared to calligraphy font classification, calligraphy style classification is more challenging due to the subtle difference among different styles. Current researches are dedicated to Chinese calligraphy font classification. Yet, there are only a few literatures are concerned with Chinese style classification. Our network is proposed and composed of two weights-shared streams. Each stream of the network can be used to extract features from the input image using convolutional neural network (CNN). In detail, the CNN has involved of five convolutional layers, while each layer is followed via a max pooling layer. Batch normalization is used to speed up training as well. The ReLU is used as the activation function. Afterwards, the global average pooling is used to aggregate the feature maps into a compactable feature vector. To get a multi-resolution representation of the image, the Haar wavelet decomposition is embedded into each stream. To optimize traditional siamese network, each stream of the proposed siamese network is extended as a classification network. In this way, image-related features extraction is then fed to a fully-connected layer for classification. The cross-entropy loss is employed for each stream. So, the supervised information of each individual image can be fully exploited. The contrastive loss can be used for feature constraints: 1) features-between distance of the two input images from the same category will be reduced; 2) features-between distance of the two input images from different categories will be enlarged. Overall, the proposed network is trained to optimize the two types of loss jointly: contrastive loss and cross-entropy loss. A weight parameter is used to balance the contribution of the two parts as well.ResultWe carried out extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of the proposed network. Since there are no public datasets for Chinese calligraphy font and style classification, we have collected four sort of datasets in related to viz. CNCalliFont, CNCalliNoisyFont, CNCalliStyle and CNCalliNoisyStyle. The CNCalliFont dataset is composed of 30 000 images and melted into five different fonts, called clerical, cursive, seal, semi-cursive and standard fonts for each. Each font has final 6 000 images. The CNCalliNoisyFont dataset can be used to extend CNCalliFont dataset in terms of the added Gaussian noise. The CNCalliStyle dataset consists of 12 000 images, which represent four styles from four popular Chinese ancient calligraphers in related to viz., Ouyang Xun, Yan Zhenqing, Zhao Mengfu and Liu Gongquan. Therefore, each style of that has 3 000 images more. All the images are related to grayscale and kept in JPEG format. Likewise, the CNCalliNoisyStyle dataset can be focused on CNCalliStyle dataset extension via adding Gaussian noise. Each dataset is split into training set, validation set and test set further with a ratio of 6∶2∶2. The training set is used to learn the parameters in the proposed network. Different configuration of the hyper-parameters is compared on the validation set with the best configuration selected, and it is applied to the test set. Ten sort of random splits and the average classification accuracy are melted into as the evaluation metric. The four datasets-related experiments demonstrate that the performance is increased by embedding the Haar wavelet decomposition in each stream of the network. It is mutual-benefited on CNCalliStyle and CNCalliNoisyStyle datasets, indicating that the subtle difference among different styles can be captured better in terms of the Haar wavelet decomposition. The performance of the proposed network is compared with them when the cross-entropy loss is employed only. The result shows that the performance is decreased when the cross-entropy loss is employed only. So, the two types of loss can be mutual-benefited as well. Moreover, we compare the proposed network with such popular methods in the context of manual feature-based, CNN-based and vision transformer-based. For the handcrafted feature-based methods, features like local binary pattern (LBP), Gabor and histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) are first employed, and the suppert vector machine (SVM) classifier is then used. For CNN-based methods, recent four sorts of methods for Chinese calligraphy font and style classification are listed. Additionally, we compare our proposed network with four sort of popular CNNs, which involves AlexNet, Visual Geometry Group (VGG-16), residual neural network (ResNet-50) and Xception. The performances of all the methods are still decreased on the CNCalliStyle dataset. Specifically, a very sharp decrease is observed for the feature-handcrafted methods, the four popular CNNs, as well as the vision transformer-based methods. It indicates that these methods cannot capture the subtle difference among different styles. Each of the accuracy can be reached to 99.90%, 94.09%, 99.38% and 93.28% on the four datasets.ConclusionThe proposed multi-loss siamese CNN can be dealt with the two tasks in relevance to viz. Chinese calligraphy font and calligraphy style classification simultaneously. Two sorts of task can be jointly optimized based on two types of loss as well.关键词:Chinese calligraphy;style classification;font classification;multi-loss siamese convolutional neural network;contrastive loss;cross-entropy loss149|754|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveChinese calligraphy can be seen as one of the symbolized icons in Chinese culture. Nowadays, Machine learning and pattern recognition techniques-derived calligraphy artworks are required for digitalization and preservation intensively. Our research is mainly focused on Chinese calligraphy classification in related to such font and style classification. However, the difference between calligraphy font and calligraphy style is often distorted. To resolve the problem of style classification, first, we distinguish the difference between font and style. Then, we illustrate a novel multi-loss siamese convolutional neural network to cope with the two mentioned problems simultaneously.MethodThe difference can be summarized between calligraphy font and style as follows: Calligraphy font refers to a broad taxonomy of scripts. For example, the popular Chinese calligraphy fonts are composed of standard, seal, clerical, cursive and semi-cursive fonts. Calligraphy style is closely related to the calligraphers to a certain extent. Each calligrapher has its own unique style. Compared to calligraphy font classification, calligraphy style classification is more challenging due to the subtle difference among different styles. Current researches are dedicated to Chinese calligraphy font classification. Yet, there are only a few literatures are concerned with Chinese style classification. Our network is proposed and composed of two weights-shared streams. Each stream of the network can be used to extract features from the input image using convolutional neural network (CNN). In detail, the CNN has involved of five convolutional layers, while each layer is followed via a max pooling layer. Batch normalization is used to speed up training as well. The ReLU is used as the activation function. Afterwards, the global average pooling is used to aggregate the feature maps into a compactable feature vector. To get a multi-resolution representation of the image, the Haar wavelet decomposition is embedded into each stream. To optimize traditional siamese network, each stream of the proposed siamese network is extended as a classification network. In this way, image-related features extraction is then fed to a fully-connected layer for classification. The cross-entropy loss is employed for each stream. So, the supervised information of each individual image can be fully exploited. The contrastive loss can be used for feature constraints: 1) features-between distance of the two input images from the same category will be reduced; 2) features-between distance of the two input images from different categories will be enlarged. Overall, the proposed network is trained to optimize the two types of loss jointly: contrastive loss and cross-entropy loss. A weight parameter is used to balance the contribution of the two parts as well.ResultWe carried out extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of the proposed network. Since there are no public datasets for Chinese calligraphy font and style classification, we have collected four sort of datasets in related to viz. CNCalliFont, CNCalliNoisyFont, CNCalliStyle and CNCalliNoisyStyle. The CNCalliFont dataset is composed of 30 000 images and melted into five different fonts, called clerical, cursive, seal, semi-cursive and standard fonts for each. Each font has final 6 000 images. The CNCalliNoisyFont dataset can be used to extend CNCalliFont dataset in terms of the added Gaussian noise. The CNCalliStyle dataset consists of 12 000 images, which represent four styles from four popular Chinese ancient calligraphers in related to viz., Ouyang Xun, Yan Zhenqing, Zhao Mengfu and Liu Gongquan. Therefore, each style of that has 3 000 images more. All the images are related to grayscale and kept in JPEG format. Likewise, the CNCalliNoisyStyle dataset can be focused on CNCalliStyle dataset extension via adding Gaussian noise. Each dataset is split into training set, validation set and test set further with a ratio of 6∶2∶2. The training set is used to learn the parameters in the proposed network. Different configuration of the hyper-parameters is compared on the validation set with the best configuration selected, and it is applied to the test set. Ten sort of random splits and the average classification accuracy are melted into as the evaluation metric. The four datasets-related experiments demonstrate that the performance is increased by embedding the Haar wavelet decomposition in each stream of the network. It is mutual-benefited on CNCalliStyle and CNCalliNoisyStyle datasets, indicating that the subtle difference among different styles can be captured better in terms of the Haar wavelet decomposition. The performance of the proposed network is compared with them when the cross-entropy loss is employed only. The result shows that the performance is decreased when the cross-entropy loss is employed only. So, the two types of loss can be mutual-benefited as well. Moreover, we compare the proposed network with such popular methods in the context of manual feature-based, CNN-based and vision transformer-based. For the handcrafted feature-based methods, features like local binary pattern (LBP), Gabor and histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) are first employed, and the suppert vector machine (SVM) classifier is then used. For CNN-based methods, recent four sorts of methods for Chinese calligraphy font and style classification are listed. Additionally, we compare our proposed network with four sort of popular CNNs, which involves AlexNet, Visual Geometry Group (VGG-16), residual neural network (ResNet-50) and Xception. The performances of all the methods are still decreased on the CNCalliStyle dataset. Specifically, a very sharp decrease is observed for the feature-handcrafted methods, the four popular CNNs, as well as the vision transformer-based methods. It indicates that these methods cannot capture the subtle difference among different styles. Each of the accuracy can be reached to 99.90%, 94.09%, 99.38% and 93.28% on the four datasets.ConclusionThe proposed multi-loss siamese CNN can be dealt with the two tasks in relevance to viz. Chinese calligraphy font and calligraphy style classification simultaneously. Two sorts of task can be jointly optimized based on two types of loss as well.关键词:Chinese calligraphy;style classification;font classification;multi-loss siamese convolutional neural network;contrastive loss;cross-entropy loss149|754|0更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveHandwritten Chinese character error correction (HCCEC) is developed to handle the complex hierarchical structure, multiple writing styles, and large-scale character vocabulary of Chinese characters recently. The HCCEC is focused on two aspects for assessment and correction. The assessment can be used to determine whether a given handwritten isolated character is correct or not. The correction can be used to locate and correct specific character-misspelled errors. However, HCCEC has its unique chateristics beyond handwritten Chinese character recognition (HCCR) on three aspects as mentioned below: first, such categories of misspelled characters are endless to deal with more inquality Chinese characters, which puts a high demand on the generalization ability of the model. We assume that the training samples are right characters, in which both right characters and misspelled ones are involved in test set. The transfer learning ability of the model is still challenged to handle unclear misspelled characters. Therefore, HCCEC is melted into a generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL) problem further. Compared to zero-shot learning, GZSL-related test set contains seen and unseen classes, which makes it more realistic and challenging. Simutaneously, characters-misspelled misclassification is to be optimized as the right ones when testing. Second, misspelled characters could be quite similar to the right ones. It requires the ability of the model to capture fine-grained features. Third, to optimize HCCR, HCCEC-relevant verification is oriented to link corresponding right characters with misspelled characters.MethodRadical-between similarities is developed in terms of radical shape and structure, and a hierarchical radical network (HRN) is melted into. For the analysis of Chinese characters, the key issue is to extract radical and structural information. For similar radicals, their distance in the representation space should be close. The completed radical information is beneficial for similar characters-between clarification, which is crucial for resolving the HCCEC task to some extent. Structure refers to the two-dimensional spatial contexts of the entire character. The hierarchical decomposition modeling of Chinese characters is also required for dealing with the problem of hierarchical structure of Chinese characters. The attention mechanism is implemented to capture fine-grained image features for similar character-between clarification. Specifically, the HRN is proposed in relevance to a convolutional neural network-based encoder and two attention modules. To obtain the representation of radicals, all radicals in the dictionary are fed into the embedding layer in the input stage. Through the first attention module, attention weights are calculated, which is used to obtain scores on the existence of radicals. After that, the radical attention module is used to balance the weight of each radical in different Chinese characters. Finally, the hierarchical-related embedding can be used to get the probability of each character.ResultExperiments are carried out on the basis of the in-house handwritten Chinese character dataset. It contains 401 400 handwritten samples for 7 000 common characters and 570 misspelled characters. It also consists of corresponding character-level and radical-level labels. Three sorts of metrics are introduced to evaluate the quality of models. The first one is the F1 score, a measure of pre-judgement ability. The second one is accuracy, a fine measure of classification ability. The last one is correction rate, which aims to measure the error correction ability of models. Each HRN is optimized by 0.5% and 9.8% for the right character test set and the misspelled character test set. And, the correction rate is improved by 15.3% on the misspelled character test set. For ablation experiments, we verify the effectiveness of the attention modules and hierarchical embedding for each. At the same time, we also conduct experiments on the dataset Chinese text in the wild (CTW), which has occupied 1 million street view images approximately. The accuracy is improved by 0.5% as well. Due to the diversity and complexity of CTW, it has potential robustness and feasibility of the HRN. Qualitative results show that the attention module can capture the corresponding positions of each radical to a certain extent.Conclusionwe develop a radical shape based hierarchical radical network. It can be used to learn the representation of each radical through the attention mechanism, and fine-grained features can be captured more precisely. Similar radicals can be better sorted out, and handwritten characters-related errors can be detected more easily. Our proposed model is still challenged for sufficient and effective training samples. Future research direction can be probably focused on the extension to text lines beyond isolated characters.关键词:handwritten Chinese character error correction (HCCEC);Chinese character recognition;radical analysis;generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL);attention mechanism;convolutional neural network (CNN)151|528|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveHandwritten Chinese character error correction (HCCEC) is developed to handle the complex hierarchical structure, multiple writing styles, and large-scale character vocabulary of Chinese characters recently. The HCCEC is focused on two aspects for assessment and correction. The assessment can be used to determine whether a given handwritten isolated character is correct or not. The correction can be used to locate and correct specific character-misspelled errors. However, HCCEC has its unique chateristics beyond handwritten Chinese character recognition (HCCR) on three aspects as mentioned below: first, such categories of misspelled characters are endless to deal with more inquality Chinese characters, which puts a high demand on the generalization ability of the model. We assume that the training samples are right characters, in which both right characters and misspelled ones are involved in test set. The transfer learning ability of the model is still challenged to handle unclear misspelled characters. Therefore, HCCEC is melted into a generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL) problem further. Compared to zero-shot learning, GZSL-related test set contains seen and unseen classes, which makes it more realistic and challenging. Simutaneously, characters-misspelled misclassification is to be optimized as the right ones when testing. Second, misspelled characters could be quite similar to the right ones. It requires the ability of the model to capture fine-grained features. Third, to optimize HCCR, HCCEC-relevant verification is oriented to link corresponding right characters with misspelled characters.MethodRadical-between similarities is developed in terms of radical shape and structure, and a hierarchical radical network (HRN) is melted into. For the analysis of Chinese characters, the key issue is to extract radical and structural information. For similar radicals, their distance in the representation space should be close. The completed radical information is beneficial for similar characters-between clarification, which is crucial for resolving the HCCEC task to some extent. Structure refers to the two-dimensional spatial contexts of the entire character. The hierarchical decomposition modeling of Chinese characters is also required for dealing with the problem of hierarchical structure of Chinese characters. The attention mechanism is implemented to capture fine-grained image features for similar character-between clarification. Specifically, the HRN is proposed in relevance to a convolutional neural network-based encoder and two attention modules. To obtain the representation of radicals, all radicals in the dictionary are fed into the embedding layer in the input stage. Through the first attention module, attention weights are calculated, which is used to obtain scores on the existence of radicals. After that, the radical attention module is used to balance the weight of each radical in different Chinese characters. Finally, the hierarchical-related embedding can be used to get the probability of each character.ResultExperiments are carried out on the basis of the in-house handwritten Chinese character dataset. It contains 401 400 handwritten samples for 7 000 common characters and 570 misspelled characters. It also consists of corresponding character-level and radical-level labels. Three sorts of metrics are introduced to evaluate the quality of models. The first one is the F1 score, a measure of pre-judgement ability. The second one is accuracy, a fine measure of classification ability. The last one is correction rate, which aims to measure the error correction ability of models. Each HRN is optimized by 0.5% and 9.8% for the right character test set and the misspelled character test set. And, the correction rate is improved by 15.3% on the misspelled character test set. For ablation experiments, we verify the effectiveness of the attention modules and hierarchical embedding for each. At the same time, we also conduct experiments on the dataset Chinese text in the wild (CTW), which has occupied 1 million street view images approximately. The accuracy is improved by 0.5% as well. Due to the diversity and complexity of CTW, it has potential robustness and feasibility of the HRN. Qualitative results show that the attention module can capture the corresponding positions of each radical to a certain extent.Conclusionwe develop a radical shape based hierarchical radical network. It can be used to learn the representation of each radical through the attention mechanism, and fine-grained features can be captured more precisely. Similar radicals can be better sorted out, and handwritten characters-related errors can be detected more easily. Our proposed model is still challenged for sufficient and effective training samples. Future research direction can be probably focused on the extension to text lines beyond isolated characters.关键词:handwritten Chinese character error correction (HCCEC);Chinese character recognition;radical analysis;generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL);attention mechanism;convolutional neural network (CNN)151|528|1更新时间:2024-05-07
Intelligent Processing and Recognition of Document Images
-
 摘要:Image-related three dimensional reconstruction techniques refer to the process of reconstructing the three dimensional model derived of a single image or multi-view images. It can illustrate a three dimensional model relevant to any view-derived color texture.Traditional three dimensional reconstruction methods are often required for a large number of images in relevance to such multiple contexts like sparse point cloud reconstruction, camera parameter estimation, dense point cloud reconstruction, surface reconstruction and texture mapping. In recent years, deep learning-driven image-related three dimensional reconstruction techniques have been concerned about, and current literatures are focused on introducing the traditional methods of image or special objects-based three dimensional reconstruction. The critical summary of image-based three dimensional reconstructions is called for further in terms of deep learning contexts. We summarize recent situation for deep learning based three dimensional reconstructions in terms of image analysis. First, three dimensional reconstructions are mainly introduced from two aspects: traditional-based and deep learning-based. Three sorts of three dimensional models are listed below: voxel model, point cloud model and mesh model. Voxel is similar to a cube in three-dimensional space, which is equivalent to pixels in three-dimensional space; Mesh is a polyhedral structure composed of the triangles, which is used to simulate the surface of complex objects; Point cloud is a collection of points in the coordinated system, which consists of the information of three-dimensional coordinates, colors and classification. For voxel model, the two-dimensional convolution used in image analysis can be easily extended to three-dimensional space, but the reconstruction of voxel model usually requires large of computing memory. The memory and calculation requirements of the method based on voxel model are cubic proportional to the resolution of voxel model. The point cloud-based shape reconstruction is smoother and takes less memory than voxel model based method. Compared to voxel model and point cloud model, mesh model can be used to analyze the object surface more completely. Then, we faciliate the classification of image-based three dimensional reconstructions, which can be classified from two aspects: the representation of three dimensional models and the type of input images. For the types of three dimensional reconstruction targets, we segment the existing three dimensional reconstruction methods into two categories: single image-related and multi-view images-related. For single image-related three dimensional reconstructions, we divide the method into three categories according to the representation of single image-related three dimensional reconstructions: voxel-based, point cloud based and mesh based. For three dimensional reconstructions in related to multi-view images, we divide the method into two categories as well: voxel-based and mesh-based. Then, existing image-based three dimensional reconstruction methods are introduced in detail, the methods are summarized critically in relevance to the input of three dimensional reconstruction method, three dimensional model representation, model texture color, ground truth and property of reconstruction network. The experiments of three dimensional reconstructions are analyzed from three aspects: evaluation method, dataset and comparison method. For the experimental aspect, current three dimensional reconstruction-related datasets are introduced, e.g., repository of shapes represented by 3D CAD models (ShapeNet) dataset, pattern analysis, statistical modeling and computational learning (PASCAL) 3D+ dataset, 3D CAD model dataset (ModelNet) dataset, database for 3D object recognition (ObjectNet3D) dataset, benchmark of diverse image-shape pairs with pixel-level 2D-3D alignment (Pix3D) dataset, Danmarks Tekniske Universitet (DTU) dataset, New York University (NYU) depth dataset, and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago (KITTI) dataset. For the experiment of three dimensional reconstructions, the ShapeNet dataset is selected and benched for comparison, the pros and cons of the existing methods are analyzed further. Finally, future research direction of image-based three dimensional reconstruction is predicted and its challenging problems and future potentials are summarized from five aspects further as following: the generalization ability of three dimensional reconstruction methods; the fineness of three dimensional reconstruction; the combination of three dimensional reconstruction and the methods of segmentation and recognition; the texture mapping of three dimensional model; and the evaluation system of three dimensional reconstruction.关键词:three dimensional reconstruction;deep learning;voxel model;point cloud model;mesh model602|1072|5更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:Image-related three dimensional reconstruction techniques refer to the process of reconstructing the three dimensional model derived of a single image or multi-view images. It can illustrate a three dimensional model relevant to any view-derived color texture.Traditional three dimensional reconstruction methods are often required for a large number of images in relevance to such multiple contexts like sparse point cloud reconstruction, camera parameter estimation, dense point cloud reconstruction, surface reconstruction and texture mapping. In recent years, deep learning-driven image-related three dimensional reconstruction techniques have been concerned about, and current literatures are focused on introducing the traditional methods of image or special objects-based three dimensional reconstruction. The critical summary of image-based three dimensional reconstructions is called for further in terms of deep learning contexts. We summarize recent situation for deep learning based three dimensional reconstructions in terms of image analysis. First, three dimensional reconstructions are mainly introduced from two aspects: traditional-based and deep learning-based. Three sorts of three dimensional models are listed below: voxel model, point cloud model and mesh model. Voxel is similar to a cube in three-dimensional space, which is equivalent to pixels in three-dimensional space; Mesh is a polyhedral structure composed of the triangles, which is used to simulate the surface of complex objects; Point cloud is a collection of points in the coordinated system, which consists of the information of three-dimensional coordinates, colors and classification. For voxel model, the two-dimensional convolution used in image analysis can be easily extended to three-dimensional space, but the reconstruction of voxel model usually requires large of computing memory. The memory and calculation requirements of the method based on voxel model are cubic proportional to the resolution of voxel model. The point cloud-based shape reconstruction is smoother and takes less memory than voxel model based method. Compared to voxel model and point cloud model, mesh model can be used to analyze the object surface more completely. Then, we faciliate the classification of image-based three dimensional reconstructions, which can be classified from two aspects: the representation of three dimensional models and the type of input images. For the types of three dimensional reconstruction targets, we segment the existing three dimensional reconstruction methods into two categories: single image-related and multi-view images-related. For single image-related three dimensional reconstructions, we divide the method into three categories according to the representation of single image-related three dimensional reconstructions: voxel-based, point cloud based and mesh based. For three dimensional reconstructions in related to multi-view images, we divide the method into two categories as well: voxel-based and mesh-based. Then, existing image-based three dimensional reconstruction methods are introduced in detail, the methods are summarized critically in relevance to the input of three dimensional reconstruction method, three dimensional model representation, model texture color, ground truth and property of reconstruction network. The experiments of three dimensional reconstructions are analyzed from three aspects: evaluation method, dataset and comparison method. For the experimental aspect, current three dimensional reconstruction-related datasets are introduced, e.g., repository of shapes represented by 3D CAD models (ShapeNet) dataset, pattern analysis, statistical modeling and computational learning (PASCAL) 3D+ dataset, 3D CAD model dataset (ModelNet) dataset, database for 3D object recognition (ObjectNet3D) dataset, benchmark of diverse image-shape pairs with pixel-level 2D-3D alignment (Pix3D) dataset, Danmarks Tekniske Universitet (DTU) dataset, New York University (NYU) depth dataset, and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago (KITTI) dataset. For the experiment of three dimensional reconstructions, the ShapeNet dataset is selected and benched for comparison, the pros and cons of the existing methods are analyzed further. Finally, future research direction of image-based three dimensional reconstruction is predicted and its challenging problems and future potentials are summarized from five aspects further as following: the generalization ability of three dimensional reconstruction methods; the fineness of three dimensional reconstruction; the combination of three dimensional reconstruction and the methods of segmentation and recognition; the texture mapping of three dimensional model; and the evaluation system of three dimensional reconstruction.关键词:three dimensional reconstruction;deep learning;voxel model;point cloud model;mesh model602|1072|5更新时间:2024-05-07
Review
-
 摘要:ObjectivePanoptic segmentation can be as a challenging task in computer vision and image segmentation nowadays. It is focused on all objects-related segmentation in an image relevant to such categories of foreground “thing” and background “stuff”. Panoptic segmentation can optimize semantic segmentation and instance segmentation to a certain extent in relevance to such domain of vision applications like autonomous driving, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), multi-object tracking and segmentation (MOTS). Most of panoptic segmentation methods can be used to follow the top-down path and the principle of detection before segmentation. Such method is based on instance segmentation or object detection, and a semantic branch is added to rich semantic segmentation. The segmentation performance of these models is feasible, but it needs a complex post-processing stage to deal with branches-between and within conflicts, which can make the inference be slower. Another category of these methods can follow the idea of bottom-up, for which semantic segmentation can be regarded as the basis, and the image can be recognized as a whole at the pixel level. It can be used to optimize tedious post-processing. Recently, a bottom-up panoptic segmentation (Panoptic-DeepLab) is used to divide the panoptic segmentation task into two branches. Each branch has a specific decoder network and segmentation head network. The semantic segmentation head outputs the semantic segmentation results. The same structure-related two instance heads can be used to predict the center instance and offset simutaneously. It can get better segmentation accuracy and speed. However, the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module is still used in the decoder network to increase the receptive field. For ASPP, to obtain a large enough receptive field, it needs sufficient dilation rate. When the dilation rate is larger, the effect of atrous convolution is worse. On the other hand, residual neural network (ResNet) is used as a shared encoder, which may be sub-optimal for fine-grained image segmentation. To resolve the problems mentioned above, we develop a new panoptic segmentation model for better segmentation performance.MethodA bottom-up panoptic segmentation method is developed in terms of improved ASPP and polarized self-attention. First, for ASPP, we redesigned it, called improved atrous spatial pyramid pooling (IASPP). Specifically, 1) dilation rate of rate1-related output of 3 × 3 convolutions is concatenated with the original input, and it is input into 3 × 3 convolution with the dilation rate2; 2) dilation rate1 and rate2-related output of 3 × 3 convolutions is concatenated with the original input, and it is input into 3 × 3 convolution with the dilation rate of rate3. Then, different dilation rates-related output of convolution is concatenated as well. Finally, the results are obtained and concatenated with other ASPP-related modules. Through a series of atrous convolutions and feature concatenations, final output of the IASPP can obtain a larger receptive field without ASPP-related kernel degradation. Furthermore, the IASPP are not used to increase the size of the model significantly, and the speed of the model is not increased dramatically as well. In addition, polarization self-attention (PSA) can be used to enhance the feature extraction ability of the shared backbone further. After the fourth layer of ResNet-50 is concerned about, improved polarization self-attention (IPSA) module is introduced to extract pixel-level features. This process can enhance the ability of ResNet to extract cost-efficient pixel-level information. The output features can be used preserve pixel-level information, and it can be applied to typical fine-grained image segmentation tasks to estimate the highly nonlinear pixel-wise semantics straightfoward.ResultThe method is tested on the cityscapes dataset. The cityscapes dataset is composed of 19 categories, including 11 background and 8 foreground contexts. It consists of images samples of 2 975 training, 500 validation, and 1 525 test contexts. Each image has a size of 1 024 × 2 048 pixels approximately. The training set can be used to train the network and the validation set is used to test the network. Compared to the baseline, experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model’s panoptic quality (PQ) is improved from 58.26% to 58.61%, and the runtime is optimized from 103 ms to 124 ms when the improved atrous spatial pyramid pooling (IASPP) module is melted into. Additionally, after the addition of the polarized self-attention (PSA), the PQ of the model is improved from 58.61% to 58.86% at the cost of the runtime from 124 ms to 187 ms. After improving the polarized self-attention (IPSA), the PQ of the model is improved from 58.86% to 59.36% while the runtime is reached to 192 ms. We carried out visual experiments, including the visualization of the image, performance comparison of different categories, and comparison with other related methods further.ConclusionTo optimize the bottom-up panoptic segmentation method, a panoptic segmentation method is developed based on improved ASPP (IASPP) and polarized self-attention (IPSA). This redesigned ASPP method can resolve the problem of atrous convolution failure effectively derived of the increase of dilation rate in ASPP, and the introduction of IPSA can improve the ability of ResNet-50 to extract pixel-level fine-grained features, and rich pixel-level feature information can be preserved in the process of feature extraction to estimate the highly nonlinear pixel-wise semantics. To improve the comprehensive performance of panoptic segmentation, it cannot only achieve better segmentation accuracy, but also maintain a better speed further.关键词:panoptic segmentation;semantic segmentation;instance segmentation;polarized self-attention;atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP)73|139|2更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectivePanoptic segmentation can be as a challenging task in computer vision and image segmentation nowadays. It is focused on all objects-related segmentation in an image relevant to such categories of foreground “thing” and background “stuff”. Panoptic segmentation can optimize semantic segmentation and instance segmentation to a certain extent in relevance to such domain of vision applications like autonomous driving, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), multi-object tracking and segmentation (MOTS). Most of panoptic segmentation methods can be used to follow the top-down path and the principle of detection before segmentation. Such method is based on instance segmentation or object detection, and a semantic branch is added to rich semantic segmentation. The segmentation performance of these models is feasible, but it needs a complex post-processing stage to deal with branches-between and within conflicts, which can make the inference be slower. Another category of these methods can follow the idea of bottom-up, for which semantic segmentation can be regarded as the basis, and the image can be recognized as a whole at the pixel level. It can be used to optimize tedious post-processing. Recently, a bottom-up panoptic segmentation (Panoptic-DeepLab) is used to divide the panoptic segmentation task into two branches. Each branch has a specific decoder network and segmentation head network. The semantic segmentation head outputs the semantic segmentation results. The same structure-related two instance heads can be used to predict the center instance and offset simutaneously. It can get better segmentation accuracy and speed. However, the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module is still used in the decoder network to increase the receptive field. For ASPP, to obtain a large enough receptive field, it needs sufficient dilation rate. When the dilation rate is larger, the effect of atrous convolution is worse. On the other hand, residual neural network (ResNet) is used as a shared encoder, which may be sub-optimal for fine-grained image segmentation. To resolve the problems mentioned above, we develop a new panoptic segmentation model for better segmentation performance.MethodA bottom-up panoptic segmentation method is developed in terms of improved ASPP and polarized self-attention. First, for ASPP, we redesigned it, called improved atrous spatial pyramid pooling (IASPP). Specifically, 1) dilation rate of rate1-related output of 3 × 3 convolutions is concatenated with the original input, and it is input into 3 × 3 convolution with the dilation rate2; 2) dilation rate1 and rate2-related output of 3 × 3 convolutions is concatenated with the original input, and it is input into 3 × 3 convolution with the dilation rate of rate3. Then, different dilation rates-related output of convolution is concatenated as well. Finally, the results are obtained and concatenated with other ASPP-related modules. Through a series of atrous convolutions and feature concatenations, final output of the IASPP can obtain a larger receptive field without ASPP-related kernel degradation. Furthermore, the IASPP are not used to increase the size of the model significantly, and the speed of the model is not increased dramatically as well. In addition, polarization self-attention (PSA) can be used to enhance the feature extraction ability of the shared backbone further. After the fourth layer of ResNet-50 is concerned about, improved polarization self-attention (IPSA) module is introduced to extract pixel-level features. This process can enhance the ability of ResNet to extract cost-efficient pixel-level information. The output features can be used preserve pixel-level information, and it can be applied to typical fine-grained image segmentation tasks to estimate the highly nonlinear pixel-wise semantics straightfoward.ResultThe method is tested on the cityscapes dataset. The cityscapes dataset is composed of 19 categories, including 11 background and 8 foreground contexts. It consists of images samples of 2 975 training, 500 validation, and 1 525 test contexts. Each image has a size of 1 024 × 2 048 pixels approximately. The training set can be used to train the network and the validation set is used to test the network. Compared to the baseline, experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model’s panoptic quality (PQ) is improved from 58.26% to 58.61%, and the runtime is optimized from 103 ms to 124 ms when the improved atrous spatial pyramid pooling (IASPP) module is melted into. Additionally, after the addition of the polarized self-attention (PSA), the PQ of the model is improved from 58.61% to 58.86% at the cost of the runtime from 124 ms to 187 ms. After improving the polarized self-attention (IPSA), the PQ of the model is improved from 58.86% to 59.36% while the runtime is reached to 192 ms. We carried out visual experiments, including the visualization of the image, performance comparison of different categories, and comparison with other related methods further.ConclusionTo optimize the bottom-up panoptic segmentation method, a panoptic segmentation method is developed based on improved ASPP (IASPP) and polarized self-attention (IPSA). This redesigned ASPP method can resolve the problem of atrous convolution failure effectively derived of the increase of dilation rate in ASPP, and the introduction of IPSA can improve the ability of ResNet-50 to extract pixel-level fine-grained features, and rich pixel-level feature information can be preserved in the process of feature extraction to estimate the highly nonlinear pixel-wise semantics. To improve the comprehensive performance of panoptic segmentation, it cannot only achieve better segmentation accuracy, but also maintain a better speed further.关键词:panoptic segmentation;semantic segmentation;instance segmentation;polarized self-attention;atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP)73|139|2更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveFine-grained requirement is focused on images segmentation for such domain like multiple wild birds or vehicles-between features extraction in related to transferring benched category into more detailed subcategories. Due to the subtle inter-category differences and large intra-category is existed, it is challenging to capture specific regions-targeted subtle differences for classification. The attention mechanism are still used to pay attention to the salient features in the picture only although Transformer architecture-based network has its potentials for image classification, and most of the latent features are ignored and self-attention mechanism-based Transformer are required to be involved as well. To get more effective information, discriminative latent features-derived feature representations are required to be learnt for fine-grained classification. To get more effective feature, we develop a complementary attention diversity feature fusion (CADF) network, which can extract multi-scale features and models from the channel and spatial feature interactions of images.MethodA mutual attention diversity feature fusion network is facilitated and it consists of two modules: 1) potential feature module (PFM): it can be focused on the features of different parts, and the salient features can be enhanced with the preservation of latent features. 2) Diversity feature fusion module (DFFM): multiple features-between channel and spatial information interaction modeling is used to enhance rich feature, and information of specific parts of features can be enhanced in terms of feature fusion module. The scalable features can realize mutual-benefited information, and robustness of the features can be enhanced and the features can be more discriminative. Our network proposed is configured in PyTorch on an NVIDIA 2080Ti GPU. The weight parameters of the model are initialized using ImageNet classification dataset-related Swin-Transformer parameters pre-trained. The optimization is performed on the AdamW optimizer with a momentum of 0.9 and a cosine annealing scheduler. The batch size is set to 6, the learning rate of the backbone layer is set to 0.000 1, the newly layer is added and set to 0.000 01, and a weight decay of 0.05 is used as well. For training, the input images are resized to 550 × 550 pixels and cropped to 448 × 448 pixels randomly, and random horizontal flips are used for data augmentation further. For testing, the input images are resized to 550 × 550 pixels and cropped to 448 × 448 pixels from the center. The hyper-parameters of λ = 1, β = 0.5 is set as well.ResultTo verify the effectiveness, the experiments are carried out on four fine-grained datasets: CUB-Birds, Stanford Dogs, Stanford Cars, and FGVC-Aircraft. Each of the classification accuracy can be reached to the following percentages: 92.6%, 94.5%, 95.3% and 93.5%. For the ablation experiments, the effectiveness of the PFM module and the DFFM module are verified further. Compared to the benched framework, it can improve the accuracy greatly via adding the PFM module only. Swin-B + PFM can be used to improve the accuracy by 1.4%, 1.4% and 0.8% on multiple datasets of CUB-Birds, Stanford Dogs and Stanford Cars datasets. Compared to PFM module-added network only, the accuracy of each feature exchange fusion module (Swin-B + PFM + DFFM) is also improved by 0.4%, 0.5% and 0.3% as well. It shows that the CADF model has strong feature extraction ability to a certain extent, and the effectiveness of each structure in the network is verified on the dataset potentially. The feature visualization is conducted to get the regional features of attention mechanism intuitively. In the ablation study, the effectiveness of each module in this model is verified further.ConclusionTo resolve the problem of insufficient attention mechanism-based feature extraction, we develop a latent feature extraction method for fine-grained image classification further.关键词:fine grained classification;diversity characteristics;potential characteristics;feature fusion;end to end learning115|249|3更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveFine-grained requirement is focused on images segmentation for such domain like multiple wild birds or vehicles-between features extraction in related to transferring benched category into more detailed subcategories. Due to the subtle inter-category differences and large intra-category is existed, it is challenging to capture specific regions-targeted subtle differences for classification. The attention mechanism are still used to pay attention to the salient features in the picture only although Transformer architecture-based network has its potentials for image classification, and most of the latent features are ignored and self-attention mechanism-based Transformer are required to be involved as well. To get more effective information, discriminative latent features-derived feature representations are required to be learnt for fine-grained classification. To get more effective feature, we develop a complementary attention diversity feature fusion (CADF) network, which can extract multi-scale features and models from the channel and spatial feature interactions of images.MethodA mutual attention diversity feature fusion network is facilitated and it consists of two modules: 1) potential feature module (PFM): it can be focused on the features of different parts, and the salient features can be enhanced with the preservation of latent features. 2) Diversity feature fusion module (DFFM): multiple features-between channel and spatial information interaction modeling is used to enhance rich feature, and information of specific parts of features can be enhanced in terms of feature fusion module. The scalable features can realize mutual-benefited information, and robustness of the features can be enhanced and the features can be more discriminative. Our network proposed is configured in PyTorch on an NVIDIA 2080Ti GPU. The weight parameters of the model are initialized using ImageNet classification dataset-related Swin-Transformer parameters pre-trained. The optimization is performed on the AdamW optimizer with a momentum of 0.9 and a cosine annealing scheduler. The batch size is set to 6, the learning rate of the backbone layer is set to 0.000 1, the newly layer is added and set to 0.000 01, and a weight decay of 0.05 is used as well. For training, the input images are resized to 550 × 550 pixels and cropped to 448 × 448 pixels randomly, and random horizontal flips are used for data augmentation further. For testing, the input images are resized to 550 × 550 pixels and cropped to 448 × 448 pixels from the center. The hyper-parameters of λ = 1, β = 0.5 is set as well.ResultTo verify the effectiveness, the experiments are carried out on four fine-grained datasets: CUB-Birds, Stanford Dogs, Stanford Cars, and FGVC-Aircraft. Each of the classification accuracy can be reached to the following percentages: 92.6%, 94.5%, 95.3% and 93.5%. For the ablation experiments, the effectiveness of the PFM module and the DFFM module are verified further. Compared to the benched framework, it can improve the accuracy greatly via adding the PFM module only. Swin-B + PFM can be used to improve the accuracy by 1.4%, 1.4% and 0.8% on multiple datasets of CUB-Birds, Stanford Dogs and Stanford Cars datasets. Compared to PFM module-added network only, the accuracy of each feature exchange fusion module (Swin-B + PFM + DFFM) is also improved by 0.4%, 0.5% and 0.3% as well. It shows that the CADF model has strong feature extraction ability to a certain extent, and the effectiveness of each structure in the network is verified on the dataset potentially. The feature visualization is conducted to get the regional features of attention mechanism intuitively. In the ablation study, the effectiveness of each module in this model is verified further.ConclusionTo resolve the problem of insufficient attention mechanism-based feature extraction, we develop a latent feature extraction method for fine-grained image classification further.关键词:fine grained classification;diversity characteristics;potential characteristics;feature fusion;end to end learning115|249|3更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveWith the continuous in-depth development of computer technology and artificial intelligence, the intelligent robot contexts have been developing intensively. The simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) can be as an effective robot-related technique to recognize scene information. Simultaneous localization and mapping is focused on robot motion location starting from the unknown position of the unknown environment while its own position can be identified and located through the observed map features, and a complete map of the scene is then constructed based on its own posture and trajectory. The environment map constructed by traditional SLAM lacks semantic information, and the robot cannot recognize the scene environment to a certain extent. To achieve the ability to perceive increasingly complex scenes, some scholars have been focused on introducing deep learning methods into SLAM systems to achieve the recognition of scenario objects. However, there are still some challenging problems to be resolved for insufficient scene recognition and map building. SLAM tasks-related robots are required to explore unknown environments and use effective scene information of complex environments. Aiming at the problems that the existing SLAM algorithms understanding insufficiently of scene details and lack of information of map building details, as well as the existing semantic segmentation algorithms do not perform well in the segmentation of multi-scale objects, have slow segmentation speed and indistinct segmentation pictures, We develop main research objectives of improving the recognition ability of the semantic segmentation algorithm for multi-scale objects and improving the accuracy and precision of map construction by semantic SLAM technology. A method of unknown environment-related map construction is constructed linked with SLAM point cloud localization technology and semantic segmentation network, which can identify objects of different sizes in the scene effectively and realize high-precision 3D map reconstruction.MethodWe design a spatial multi-scale sparse and dense features-fused deep learning semantic segmentation network, which is called hierarchical semantic network (HieSemNet). A spatial pyramid module is opted with different dilation rates of dilated convolution, and to capture global contextual information, such features can be extracted using multi-scale structure. To extract features deliberately, the network consists of two branches of the feature extraction base network and the spatial pyramid module. Besides, to supervise the training and calculate the loss function, the semantic labels can be used solely at different scales of the two branches. The final feature map can be generated in terms of weighted fusion method of the feature maps of the two branches. The built semantic segmentation network is then applied to the SLAM system, and the map construction is completed by three modules: tracking, local mapping and LoopClosing. The tracking module extracts ORB (oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF) features from the image sequences acquired by the RGB-D camera, determines key frames based on the ORB feature point pairs between frames and performs camera pose estimation. The local mapping module further filters the inserted key frames, then calculates and filters the map points associated with the key frames. The LoopClosing module performs optimization and updates the generated maps. The steps of the algorithm are as follows: First, it uses the real-time color information of the scene captured by RGB-D camera for camera’s positional estimation and trajectory calculation. And then, to achieve semantic segmentation of unknown scene information and obtain real-time 2D semantic information of the scene, it constructs HieSemNet in the context of a deep learning network fusing spatial multiscale sparse and dense features. Second, spatial point cloud estimation using depth information and camera poses to construct an octree of spatial relations of point clouds. Finally, to build a high-precision point cloud map with semantic information and realizing 3D map reconstruction, the semantic segmentation 2D information is fused with 3D point cloud information, and the result of semantic segmentation can correspond the corresponding spatial position of the octree.ResultTo verify the effectiveness of the method proposed, validation experiments are conducted for the constructed HieSemNet and the semantic SLAM system. The HieSemNet analysis is compared to other related frontier networks full connected network (FCN), segmentation network (SegNet), PSPNet (pyramid scene parsing network), DeepLabv3 and SETR (segmentation transformer) in terms of segmentation accuracy on the classical semantic segmentation dataset ADE20k. The experimental results show that the network proposed has its potentials for mean pixel accuracy and mean intersection over union. Since the HieSemNet can obtain a large perceptual field using dilated convolution without losing too much detail information, it can have much more accurate segmentation results for both of large-size targets and small-size objects. Compared to the above network, the mean pixel accuracy value of the networks can be improved by 17.47%, 11.67%, 4.86%, 2.90% and 0.44%, respectively, and the mean intersection over union value can be improved by 13.94%, 1.10%, 6.28%, 2.28% and 0.62%, respectively as well. The proposed SLAM algorithm is tested in related to such contexts of office scenes, warehouse scenes of TUM RGB-D dataset and natural environment. This paper shows the map building process, the trajectory accuracy and absolute trajectory error for three of different scenes by the SLAM algorithm. The comparative results show that our constructed maps can obtain more information for map building, fewer blank or wrong parts in the maps, the contour and position information of objects in the maps constructed is more accurate, and the adverse effects caused by small and chaotic objects are less. It is able to show the actual scene more accurately.ConclusionThe segmentation effect of objects of different sizes can be fully involved in, and the proposed HieSemNet network can be used to improve the scene semantic segmentation accuracy potentially.关键词:simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM);semantic segmentation;semantic three-dimensional map;spatial multiscale features99|228|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveWith the continuous in-depth development of computer technology and artificial intelligence, the intelligent robot contexts have been developing intensively. The simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) can be as an effective robot-related technique to recognize scene information. Simultaneous localization and mapping is focused on robot motion location starting from the unknown position of the unknown environment while its own position can be identified and located through the observed map features, and a complete map of the scene is then constructed based on its own posture and trajectory. The environment map constructed by traditional SLAM lacks semantic information, and the robot cannot recognize the scene environment to a certain extent. To achieve the ability to perceive increasingly complex scenes, some scholars have been focused on introducing deep learning methods into SLAM systems to achieve the recognition of scenario objects. However, there are still some challenging problems to be resolved for insufficient scene recognition and map building. SLAM tasks-related robots are required to explore unknown environments and use effective scene information of complex environments. Aiming at the problems that the existing SLAM algorithms understanding insufficiently of scene details and lack of information of map building details, as well as the existing semantic segmentation algorithms do not perform well in the segmentation of multi-scale objects, have slow segmentation speed and indistinct segmentation pictures, We develop main research objectives of improving the recognition ability of the semantic segmentation algorithm for multi-scale objects and improving the accuracy and precision of map construction by semantic SLAM technology. A method of unknown environment-related map construction is constructed linked with SLAM point cloud localization technology and semantic segmentation network, which can identify objects of different sizes in the scene effectively and realize high-precision 3D map reconstruction.MethodWe design a spatial multi-scale sparse and dense features-fused deep learning semantic segmentation network, which is called hierarchical semantic network (HieSemNet). A spatial pyramid module is opted with different dilation rates of dilated convolution, and to capture global contextual information, such features can be extracted using multi-scale structure. To extract features deliberately, the network consists of two branches of the feature extraction base network and the spatial pyramid module. Besides, to supervise the training and calculate the loss function, the semantic labels can be used solely at different scales of the two branches. The final feature map can be generated in terms of weighted fusion method of the feature maps of the two branches. The built semantic segmentation network is then applied to the SLAM system, and the map construction is completed by three modules: tracking, local mapping and LoopClosing. The tracking module extracts ORB (oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF) features from the image sequences acquired by the RGB-D camera, determines key frames based on the ORB feature point pairs between frames and performs camera pose estimation. The local mapping module further filters the inserted key frames, then calculates and filters the map points associated with the key frames. The LoopClosing module performs optimization and updates the generated maps. The steps of the algorithm are as follows: First, it uses the real-time color information of the scene captured by RGB-D camera for camera’s positional estimation and trajectory calculation. And then, to achieve semantic segmentation of unknown scene information and obtain real-time 2D semantic information of the scene, it constructs HieSemNet in the context of a deep learning network fusing spatial multiscale sparse and dense features. Second, spatial point cloud estimation using depth information and camera poses to construct an octree of spatial relations of point clouds. Finally, to build a high-precision point cloud map with semantic information and realizing 3D map reconstruction, the semantic segmentation 2D information is fused with 3D point cloud information, and the result of semantic segmentation can correspond the corresponding spatial position of the octree.ResultTo verify the effectiveness of the method proposed, validation experiments are conducted for the constructed HieSemNet and the semantic SLAM system. The HieSemNet analysis is compared to other related frontier networks full connected network (FCN), segmentation network (SegNet), PSPNet (pyramid scene parsing network), DeepLabv3 and SETR (segmentation transformer) in terms of segmentation accuracy on the classical semantic segmentation dataset ADE20k. The experimental results show that the network proposed has its potentials for mean pixel accuracy and mean intersection over union. Since the HieSemNet can obtain a large perceptual field using dilated convolution without losing too much detail information, it can have much more accurate segmentation results for both of large-size targets and small-size objects. Compared to the above network, the mean pixel accuracy value of the networks can be improved by 17.47%, 11.67%, 4.86%, 2.90% and 0.44%, respectively, and the mean intersection over union value can be improved by 13.94%, 1.10%, 6.28%, 2.28% and 0.62%, respectively as well. The proposed SLAM algorithm is tested in related to such contexts of office scenes, warehouse scenes of TUM RGB-D dataset and natural environment. This paper shows the map building process, the trajectory accuracy and absolute trajectory error for three of different scenes by the SLAM algorithm. The comparative results show that our constructed maps can obtain more information for map building, fewer blank or wrong parts in the maps, the contour and position information of objects in the maps constructed is more accurate, and the adverse effects caused by small and chaotic objects are less. It is able to show the actual scene more accurately.ConclusionThe segmentation effect of objects of different sizes can be fully involved in, and the proposed HieSemNet network can be used to improve the scene semantic segmentation accuracy potentially.关键词:simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM);semantic segmentation;semantic three-dimensional map;spatial multiscale features99|228|1更新时间:2024-05-07
Image Understanding and Computer Vision
-
 摘要:ObjectiveComputer graphics-oriented realistic simulation of solid-fluid interaction can be as a branch of physical animation simulation technology in relevance to such domains like film and television special effects, video games, and disaster rehearsal. The fluid impact-derived fracture of solids is a common phenomenon in solid-fluid interaction. For solid simulation, current researches are mainly focused on solids-between interactions, for which it can pay much attention for solid-fluid interacted simulation of dynamics, deformation and other related phenomena. Solid fracture-related researches are required to be richer. The smoothed particle hydrodynamics(SPH) solid-fluid interaction solver is coupled and relatively poor and a large amount of coupling overhead can yield the performance of the simulation system to be decreased. For solid-fluid interacted simulation of the solid fracture phenomenon, physical models of fluid-relevant solid-fluid interaction and solid behavior are so complicated. It is required to combine the characteristics of the solid solver and the solid-fluid for real-time simulation. The characteristics of the interactive simulation system can facilitate the coupling of multiple solvers. If the solid fracture method is directly introduced, it will often prefer to a complex simulation system, a large amount of calculation, and poor coupling. To simulate solid-fluid interacted phenomenon derived from fluid impact, we develop a SPH unified particle framework-based real-time solid fracture simulation method in terms of the mixture of physics and geometry, for which it is challenged for the lack of related research, the difficulty of realism and real-time performance, and the poor coupling with the solid-fluid interaction simulation system.MethodThe construction of the theoretical model is based on the mechanism of fracture mechanics. First, due to the particle form of the solid and the neighborhood characteristics of the SPH method, energy limit conditions are obtained through real-time analysis of the energy transfer between the fluid particles and the solid boundary particles and the energy conversion of the solid itself. Then, the heuristic point set is used as the seed point, and the Voronoi diagram is employed as well, which can be constructed in parallel as the solid fragment generation method to quickly divide the solid volume space into subspaces for the generated solid fragmentation. To preserve its real-time performance of the simulation, the proposed method is optimized in parallel and loaded into graphics processing unit(GPU) for massive parallel acceleration.ResultMultifaceted and particle scale-derived simulation results demonstrate that the fluid-affected method can simulate the fracture phenomenon of solids in terms of different fracture resistances, and the fracture details have well realism more. Real-time simulation is possible in scenes with 650 k particle count. Interactive simulation is implemented in scenes with 3 360 k particle counts. Such methods can be optimized in parallel and accelerated on the GPU, and the benefit of parallel acceleration is significant. In addition, the accelerated ratio can optimize the scale of the scene.ConclusionOur method is proposed and compared to current researches, which can fully melt the physical method into the geometric method. It has higher time efficiency while the realism can be preserved to meet the needs of real-time simulation. A better coupling can be reached between the method and the SPH unified particle framework. The simulation system can be used to simulate fluid impact-derived solid fracture. For simulation, details of fracture are cohesive to the laws of physics in the real world in related to realistic lighting rendering. Its potentials are beneficial for such simulation domains of natural disasters or video games.关键词:physical animation;fluid simulation;smooth particle hydrodynamics;solid-fluid interaction;solid fracture119|355|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveComputer graphics-oriented realistic simulation of solid-fluid interaction can be as a branch of physical animation simulation technology in relevance to such domains like film and television special effects, video games, and disaster rehearsal. The fluid impact-derived fracture of solids is a common phenomenon in solid-fluid interaction. For solid simulation, current researches are mainly focused on solids-between interactions, for which it can pay much attention for solid-fluid interacted simulation of dynamics, deformation and other related phenomena. Solid fracture-related researches are required to be richer. The smoothed particle hydrodynamics(SPH) solid-fluid interaction solver is coupled and relatively poor and a large amount of coupling overhead can yield the performance of the simulation system to be decreased. For solid-fluid interacted simulation of the solid fracture phenomenon, physical models of fluid-relevant solid-fluid interaction and solid behavior are so complicated. It is required to combine the characteristics of the solid solver and the solid-fluid for real-time simulation. The characteristics of the interactive simulation system can facilitate the coupling of multiple solvers. If the solid fracture method is directly introduced, it will often prefer to a complex simulation system, a large amount of calculation, and poor coupling. To simulate solid-fluid interacted phenomenon derived from fluid impact, we develop a SPH unified particle framework-based real-time solid fracture simulation method in terms of the mixture of physics and geometry, for which it is challenged for the lack of related research, the difficulty of realism and real-time performance, and the poor coupling with the solid-fluid interaction simulation system.MethodThe construction of the theoretical model is based on the mechanism of fracture mechanics. First, due to the particle form of the solid and the neighborhood characteristics of the SPH method, energy limit conditions are obtained through real-time analysis of the energy transfer between the fluid particles and the solid boundary particles and the energy conversion of the solid itself. Then, the heuristic point set is used as the seed point, and the Voronoi diagram is employed as well, which can be constructed in parallel as the solid fragment generation method to quickly divide the solid volume space into subspaces for the generated solid fragmentation. To preserve its real-time performance of the simulation, the proposed method is optimized in parallel and loaded into graphics processing unit(GPU) for massive parallel acceleration.ResultMultifaceted and particle scale-derived simulation results demonstrate that the fluid-affected method can simulate the fracture phenomenon of solids in terms of different fracture resistances, and the fracture details have well realism more. Real-time simulation is possible in scenes with 650 k particle count. Interactive simulation is implemented in scenes with 3 360 k particle counts. Such methods can be optimized in parallel and accelerated on the GPU, and the benefit of parallel acceleration is significant. In addition, the accelerated ratio can optimize the scale of the scene.ConclusionOur method is proposed and compared to current researches, which can fully melt the physical method into the geometric method. It has higher time efficiency while the realism can be preserved to meet the needs of real-time simulation. A better coupling can be reached between the method and the SPH unified particle framework. The simulation system can be used to simulate fluid impact-derived solid fracture. For simulation, details of fracture are cohesive to the laws of physics in the real world in related to realistic lighting rendering. Its potentials are beneficial for such simulation domains of natural disasters or video games.关键词:physical animation;fluid simulation;smooth particle hydrodynamics;solid-fluid interaction;solid fracture119|355|0更新时间:2024-05-07
Computer Graphics
-
 摘要:ObjectiveEarly renal cancer can be identified and treated effectively via enucleation of renal tumor. To optimize surgery and its surgical complications, it is necessary to evaluate the surgical feasibility efficiently and effectively. To quantify the difficulty index of surgical contexts, Mayo adhesive probability (MAP) score and R.E.N.A.L score can be involved in for its applications. computed tomography(CT) images-based manual analysis is roughly estimated in terms of these two scoring standards-related corresponding difficulty score. To optimize the accuracy and reliability of evaluation, this sort of qualitative manual evaluation method is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Thanks to deep learning technique based medical radiomics and image analysis, we develop an automatic evaluation method of CT images-based surgical optimization in relevance to enucleation of renal tumors.MethodFirst, a three-layer cascade end-to-end segmentation model is illustrated to segment the kidney, renal tumor and abdominal wall simutanesoualy. Each layer is linked with an extended U-Net for segmentation. The abdominal wall segmentation is at the top of them, followed by the kidney segmentation, and the renal tumor is at the bottom. This stratification is derived of a learning process of spatial constraints. For the extended U-Net, the dense connection is reflected in the convolution block of the coding layer or coding and decoding layer-between same layer, as well as upper and lower-between layers. This kind of dense connection at the three levels can be used to obtain more semantic connections and transmit more information in the training, and overall gradient flow can be effectively enhanced, and the global optimal solution can be sorted out smoothly. To alleviate the loss of redundant texture detail in the up-sampling process, the sub-pixel convolution mode is used further. This method proposed can generate higher resolution images through the pixel order-related intervention of multiple low resolution feature images. At the same time, image mode-medical attention mechanism is used to preserve the accuracy of small volume tumor segmentation. Then, the misjudged renal tumors are removed in terms of radiomics features, which are high-dimensional non-invasive image biomarkers and beneficial to mine, quantify and analyze the deep-seated features of naked eye-related unrecognized malignant tumors. In this study, seven groups of radiomics features are calculated, including such features in relevance to gray level coocurrence matrix (GLCM), square-statistical contexts, gradient, moment, run length (RL), boundary, and wavelet features. Finally, segmentation analysis-based international standard MAP score and R.E.N.A.L score are used to evaluate and calculate the kidney and renal tumor automatically, and the surgical dilemma of enucleation of renal tumor is located further.ResultThe synchronized results of segmentation of kidney, renal tumor and abdominal wall are evaluated. The performance indicators like dice coefficient (DC), positive predicted value (PPV) and sensitivity are illustrated. The sensitivity, PPV and Dice are 0.1, 0.08 and 0.09 higher than the worst U-Net++, 0.04, 0.04 and 0.05 higher than the better BlendMask. The highest values of sensitivity, PPV and Dice can be reached to 0.97, 0.98 and 0.98. To remove false-positive tumor areas effectively, the binary classification model is adopted as well. The random forest (RF) machine learning method is used, because the average performance of RF in various test samples can be optimal to a certain extent. The five-fold cross validation accuracy of RF is 0.95 (±0.03), and the area under curve (AUC) value is 0.99, which is much higher than other related classification methods. For the MAP and R.E.N.A.L scoring experiments, the results of all 5 times can keep consistent with the evaluation results of two experts-least for P, L and R values; For N and E values, four of the five results are in consistency in related to the evaluation results of least two experts. It can be seen that the scoring ability of automatic individual items has been very close to the focused experts. The final operation difficulty evaluation results are compared with the three medical experts in the urology department of class A tertiary hospital. The average results-predictable automation method can demonstrate its potential consistency in relevance to the expert evaluation level as a whole.ConclusionWe facilitate an accurate and reliable decision for accurate preoperative diagnosis, individualized planning of surgical scheme and surgical approach selection. Furthermore, our method proposed can be integrated into the medical-relevant image cloud platform to provide intelligent and optimal medical solutions.关键词:enucleation of renal tumor;medical image segmentation;radiomics;deep learning;surgical evaluation136|298|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveEarly renal cancer can be identified and treated effectively via enucleation of renal tumor. To optimize surgery and its surgical complications, it is necessary to evaluate the surgical feasibility efficiently and effectively. To quantify the difficulty index of surgical contexts, Mayo adhesive probability (MAP) score and R.E.N.A.L score can be involved in for its applications. computed tomography(CT) images-based manual analysis is roughly estimated in terms of these two scoring standards-related corresponding difficulty score. To optimize the accuracy and reliability of evaluation, this sort of qualitative manual evaluation method is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Thanks to deep learning technique based medical radiomics and image analysis, we develop an automatic evaluation method of CT images-based surgical optimization in relevance to enucleation of renal tumors.MethodFirst, a three-layer cascade end-to-end segmentation model is illustrated to segment the kidney, renal tumor and abdominal wall simutanesoualy. Each layer is linked with an extended U-Net for segmentation. The abdominal wall segmentation is at the top of them, followed by the kidney segmentation, and the renal tumor is at the bottom. This stratification is derived of a learning process of spatial constraints. For the extended U-Net, the dense connection is reflected in the convolution block of the coding layer or coding and decoding layer-between same layer, as well as upper and lower-between layers. This kind of dense connection at the three levels can be used to obtain more semantic connections and transmit more information in the training, and overall gradient flow can be effectively enhanced, and the global optimal solution can be sorted out smoothly. To alleviate the loss of redundant texture detail in the up-sampling process, the sub-pixel convolution mode is used further. This method proposed can generate higher resolution images through the pixel order-related intervention of multiple low resolution feature images. At the same time, image mode-medical attention mechanism is used to preserve the accuracy of small volume tumor segmentation. Then, the misjudged renal tumors are removed in terms of radiomics features, which are high-dimensional non-invasive image biomarkers and beneficial to mine, quantify and analyze the deep-seated features of naked eye-related unrecognized malignant tumors. In this study, seven groups of radiomics features are calculated, including such features in relevance to gray level coocurrence matrix (GLCM), square-statistical contexts, gradient, moment, run length (RL), boundary, and wavelet features. Finally, segmentation analysis-based international standard MAP score and R.E.N.A.L score are used to evaluate and calculate the kidney and renal tumor automatically, and the surgical dilemma of enucleation of renal tumor is located further.ResultThe synchronized results of segmentation of kidney, renal tumor and abdominal wall are evaluated. The performance indicators like dice coefficient (DC), positive predicted value (PPV) and sensitivity are illustrated. The sensitivity, PPV and Dice are 0.1, 0.08 and 0.09 higher than the worst U-Net++, 0.04, 0.04 and 0.05 higher than the better BlendMask. The highest values of sensitivity, PPV and Dice can be reached to 0.97, 0.98 and 0.98. To remove false-positive tumor areas effectively, the binary classification model is adopted as well. The random forest (RF) machine learning method is used, because the average performance of RF in various test samples can be optimal to a certain extent. The five-fold cross validation accuracy of RF is 0.95 (±0.03), and the area under curve (AUC) value is 0.99, which is much higher than other related classification methods. For the MAP and R.E.N.A.L scoring experiments, the results of all 5 times can keep consistent with the evaluation results of two experts-least for P, L and R values; For N and E values, four of the five results are in consistency in related to the evaluation results of least two experts. It can be seen that the scoring ability of automatic individual items has been very close to the focused experts. The final operation difficulty evaluation results are compared with the three medical experts in the urology department of class A tertiary hospital. The average results-predictable automation method can demonstrate its potential consistency in relevance to the expert evaluation level as a whole.ConclusionWe facilitate an accurate and reliable decision for accurate preoperative diagnosis, individualized planning of surgical scheme and surgical approach selection. Furthermore, our method proposed can be integrated into the medical-relevant image cloud platform to provide intelligent and optimal medical solutions.关键词:enucleation of renal tumor;medical image segmentation;radiomics;deep learning;surgical evaluation136|298|0更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveTo diagnose the fetal congenital heart disease (CHD) during screening, clinical-related ultrasound technique is adopted and focused on the captured images in terms of different critical cardiac scanning planes. Ultrasound scanning image quality assessment (QA) is indispensable for its efficiency and effectiveness. Four-chamber (4C) view-related multiple fetal cardiac ultrasound scan planes are commonly-used for CHD. The emerging artificial intelligence (AI) technique is beneficial for automatic fetal 4C view QA algorithm research further. In recent years, deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) based AI technique has been widely developing in the context of medical image processing and analysis. However, duo to the lack of relevant data-sets and the 4C region only occupying a small part in the whole fetal 4C view, the confidence of detection bounding-box from general purpose object detection network is challenged to reflect the visibility and clarity of four chambers of the heart and its related crux area well, which includes mitral valve, tricuspid valve, interatrial septum and interventricular septum in cardiac region. In addition, current fetal 4C view QA methods are still challenged for reasonable explainability based on pure deep learning (DL) techniques. To resolve this problem, we proposed a novel fetal 4C view QA algorithm through the integration of object detection and two-stage segmentation operations, which is mutual-benefited for both of DL and traditional image processing techniques to get better accuracy and interpretability.MethodA self-built medical data-set of 1 696 images is used for fetal 4C view QA research. The data-set offers common objects in context (COCO) format labels for 4C and thorax regions, semantic segmentation labels for 4C inner regions, and also contains QA labels annotated manually. First, object detection network of you only look once v5x (YOLOv5x) is trained to realize effective 4C region detection and extraction. It illustrates that the 4C region’s location is normal and can be treated as the region of interest (ROI) when the detected 4C region locates inner the thorax region. And the ROI will be fed into the semantic segmentation network U2-Net which is well trained based the 4C inner region data-set which is a sub-set of the self-built data-set. The U2-Net considers four chambers of the heart and crux areas as foreground and implements the initial segmentation. And, the U2-Net output is a gray-scale image, in which values of background pixels are restrained effectively and foreground pixels are highlighted as well. Then, the maximum inter-class variance method (OTSU’s method) is adopted to binarize the U2-Net output. The morphological erosion operation is employed to optimize the binary segmentation result further, and a binary mask is produced to isolate the gray-scale 4C region. Next, OTSU-integrated histogram adjustment is used to separate the crux area leveraged from the isolated 4C region. And, the rest part of it can be considered as the four chambers of the heart area. After that, three QA indices are designed, and they can be used to represent area ration of the crux and four chambers of the heart, average gray scale of the crux and four chambers of the heart. Finally, to achieve effective fetal 4C view QA, evaluation formulations and standards are developed based on the three QA indices above.ResultThe experimental results show that the well trained YOLOv5x model based on the self-built data-set can achieve 99.5% mAP@0.5 and 84.6% mAP@0.5-0.95 in the object detection task for thorax and 4C regions respectively, and the recall rate is as high as 99.9%; and the well trained U2-Net model can achieve 95.0% sensitivity, 95.1% specificity and 94.9% accuracy in the segmentation task for 4C inner region. The proposed fetal 4C view QA method can get 93.7%, 90.3% and 99.1% accuracy on each evaluation data-set of class A, B and C.ConclusionTo solve the problem that DL based image classification network cannot consider the location relationships of anatomy parts, and the object detection network cannot reflect their visibility and clarity, which leads to unreliable evaluation results, a fetal 4C view QA algorithm is proposed based on an object detection incorporated with two-stage segmentation. Evaluation results show that the trained object detection network has its potentials for 4C and thorax region detection, and the trained semantic segmentation network is optimized for 4C inner region extraction as well. The adopted two-stage segmentation strategy which combines DL and traditional image processing can not only shrink the costs of data annotation and network training greatly, but also strengthen optimal explainable results as well. The designed QA standards can be developed farther in terms of the three key indices.关键词:deep learning(DL);convolutional neural network (CNN);ultrasound image quality assessment;object detection;two-stage image segmentation71|224|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveTo diagnose the fetal congenital heart disease (CHD) during screening, clinical-related ultrasound technique is adopted and focused on the captured images in terms of different critical cardiac scanning planes. Ultrasound scanning image quality assessment (QA) is indispensable for its efficiency and effectiveness. Four-chamber (4C) view-related multiple fetal cardiac ultrasound scan planes are commonly-used for CHD. The emerging artificial intelligence (AI) technique is beneficial for automatic fetal 4C view QA algorithm research further. In recent years, deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) based AI technique has been widely developing in the context of medical image processing and analysis. However, duo to the lack of relevant data-sets and the 4C region only occupying a small part in the whole fetal 4C view, the confidence of detection bounding-box from general purpose object detection network is challenged to reflect the visibility and clarity of four chambers of the heart and its related crux area well, which includes mitral valve, tricuspid valve, interatrial septum and interventricular septum in cardiac region. In addition, current fetal 4C view QA methods are still challenged for reasonable explainability based on pure deep learning (DL) techniques. To resolve this problem, we proposed a novel fetal 4C view QA algorithm through the integration of object detection and two-stage segmentation operations, which is mutual-benefited for both of DL and traditional image processing techniques to get better accuracy and interpretability.MethodA self-built medical data-set of 1 696 images is used for fetal 4C view QA research. The data-set offers common objects in context (COCO) format labels for 4C and thorax regions, semantic segmentation labels for 4C inner regions, and also contains QA labels annotated manually. First, object detection network of you only look once v5x (YOLOv5x) is trained to realize effective 4C region detection and extraction. It illustrates that the 4C region’s location is normal and can be treated as the region of interest (ROI) when the detected 4C region locates inner the thorax region. And the ROI will be fed into the semantic segmentation network U2-Net which is well trained based the 4C inner region data-set which is a sub-set of the self-built data-set. The U2-Net considers four chambers of the heart and crux areas as foreground and implements the initial segmentation. And, the U2-Net output is a gray-scale image, in which values of background pixels are restrained effectively and foreground pixels are highlighted as well. Then, the maximum inter-class variance method (OTSU’s method) is adopted to binarize the U2-Net output. The morphological erosion operation is employed to optimize the binary segmentation result further, and a binary mask is produced to isolate the gray-scale 4C region. Next, OTSU-integrated histogram adjustment is used to separate the crux area leveraged from the isolated 4C region. And, the rest part of it can be considered as the four chambers of the heart area. After that, three QA indices are designed, and they can be used to represent area ration of the crux and four chambers of the heart, average gray scale of the crux and four chambers of the heart. Finally, to achieve effective fetal 4C view QA, evaluation formulations and standards are developed based on the three QA indices above.ResultThe experimental results show that the well trained YOLOv5x model based on the self-built data-set can achieve 99.5% mAP@0.5 and 84.6% mAP@0.5-0.95 in the object detection task for thorax and 4C regions respectively, and the recall rate is as high as 99.9%; and the well trained U2-Net model can achieve 95.0% sensitivity, 95.1% specificity and 94.9% accuracy in the segmentation task for 4C inner region. The proposed fetal 4C view QA method can get 93.7%, 90.3% and 99.1% accuracy on each evaluation data-set of class A, B and C.ConclusionTo solve the problem that DL based image classification network cannot consider the location relationships of anatomy parts, and the object detection network cannot reflect their visibility and clarity, which leads to unreliable evaluation results, a fetal 4C view QA algorithm is proposed based on an object detection incorporated with two-stage segmentation. Evaluation results show that the trained object detection network has its potentials for 4C and thorax region detection, and the trained semantic segmentation network is optimized for 4C inner region extraction as well. The adopted two-stage segmentation strategy which combines DL and traditional image processing can not only shrink the costs of data annotation and network training greatly, but also strengthen optimal explainable results as well. The designed QA standards can be developed farther in terms of the three key indices.关键词:deep learning(DL);convolutional neural network (CNN);ultrasound image quality assessment;object detection;two-stage image segmentation71|224|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveThe human dentition-related third molar can be developed and erupted as an impacted tooth. The stomatologists are often required to clarify the current status and potential complications of the disease in terms of panoramic image analyzed impaction level and angle of the mandibular third molar. The panorama is a two-dimensional view, and the artifacts, image overlap and deformation-derived interpretation are vulnerable. The diagnosis and evaluation of diseases are often challenged for manual interpretation of medical images. To get optimal artificial intelligence medical aided diagnosis, we attempt to melt deep learning-based target detection algorithm into panoramic film data. Consensus object image analysis is restricted by complex background, and the obvious texture difference of categories is challenged for vulnerable perception of convolutional neural network in the panoramic image, texture-consistent teeth are closely pre-arranged in related to the integration of fixed front background relationship and certain spatial structure characteristics. Stomatologist is still required to judge the abnormal condition of wisdom teeth in terms of mutual relationship between the spatial position and tooth interaction, and discrimination process of this relationship can be concerned and modeled in terms of visual task-relevant spatial attention mechanism. Specifically, the attention mechanism is beneficial to suppress redundant channels or pixels to a certain extent. It can be melted into the trunk neural network as a plug-in module, or attached to the top of the trunk to extract high-level semantic relations, for which the bottom layer of convolution features can be preserved.MethodThe convolution property of neural network is analyzed, and the attention-specific inner convolution operator to the spatial element information can be used optimally. It is melted into you only look once (YOLO) target detection model to improve the performance and reduce the parameters on the premise of ensuring the advantages of YOLO itself. A YOLO-based panoramic wisdom tooth detection scheme is proposed as well. The main contributions are listed as follows: 1) an improved cross stage partial (CSP) structure (invoCSP) is proposed, which can optimize the integration of CSP structure and revolution operator, and the YOLO model is introduced derived from its stacking and the related revolution operator. The contextual information can be summarized in a wider spatial range, and different area-oriented weight can be adaptively balanced and allocated in the feature map as well. Finally, spatial modeling ability is improved to fully extract the spatial structure information on the data set; 2) we analyze the defect of task coupling in the YOLO model, excavate the potential properties of the involution operator, and summarize the external conditions. To fully decompose and decouple the three specific tasks of the two properties of target detection, a three-branch decoupling structure is constructed in the detection head structure. The applicability of the YOLO model can be improved further. This scheme can be used to alleviate its training process and non-convergence problem of the involution method; 3) three branch detection head can avoid sharing weight parameters further for independent optimization. The modified loss function can be used to optimize the tasks on different branches, introduce focal-loss to the confidence loss, and a newly intersection of union (IoU)-loss is applied to the boundary regression of the prediction frame and an advanced classification loss.ResultTo realize the classification and labeling of mandibular wisdom teeth, a newly panoramic film data set is developed for the winter classification method, which is commonly-used in the diagnosis and treatment of wisdom teeth in oral clinic. It can be randomly disturbed after histogram equalization. Three stomatologists focus on labeling the mandibular wisdom teeth independently for many times under the circumstances of unified diagnostic criteria and labeling rules, and a total of 973 consistent data can be reached. Finally, the panoramic wisdom tooth data set-constructed experimental results demonstrate its potentials for single-stage target detection model in terms of the detection performance and model parameters. Compared to the benched model of YOLOX-tiny, the parameter is lower by 42.5% and the mAP_50 index is higher by 6.3 percentage points. In addition, comparative analysis is carried out with nine sort of popular single-stage target detection models as well. The performance of the yooid model is beneficial for same parameter quantity-related optimization. It can not only identify wisdom tooth types accurately, but also return to the prediction frame stably with high IoU and closer to the real label. It is comparable to the detection performance of large model in terms of constraints of smaller parameters, and the highest mAP_50 index can be even achieved.ConclusionTo deal with the problem of panorama-based wisdom tooth detection, the convolution property is analyzed in the neural network. The involution operator is adopted, in which specific attention is added to the spatial element information of additional network structure excluded, and it is introduced into the YOLO target detection model feasibly. The performance is improved and the parameters can be reduced on the premise of ensuring the advantages of YOLO. A panoramic wisdom tooth detection network model is facilitated based on involution decoupling. Through the comparison of qualitative and quantitative experiments, it is verified that the proposed model can effectively detect the constructed target object, and the rationality of the design idea of the model can be improved as well. Furthermore, it demonstrates that the decoupled structure can fit the design of involution. We sort the relationship between involution and coupling out, and a multiple-branch decoupled structure can be used to improve the YOLO model-oriented adaptability of involution operator further. The parameters of this model are reduced greatly beyond high efficiency of performance, which is suitable for the application environment of real-time detection. It is predicted that this method proposed is beneficial to realize lightweight application level deployment in preliminary screening and objective reference for Stomatology further.关键词:panoramic radiograph;wisdom tooth;target detection;you only look once (YOLO);decoupling;involution92|297|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveThe human dentition-related third molar can be developed and erupted as an impacted tooth. The stomatologists are often required to clarify the current status and potential complications of the disease in terms of panoramic image analyzed impaction level and angle of the mandibular third molar. The panorama is a two-dimensional view, and the artifacts, image overlap and deformation-derived interpretation are vulnerable. The diagnosis and evaluation of diseases are often challenged for manual interpretation of medical images. To get optimal artificial intelligence medical aided diagnosis, we attempt to melt deep learning-based target detection algorithm into panoramic film data. Consensus object image analysis is restricted by complex background, and the obvious texture difference of categories is challenged for vulnerable perception of convolutional neural network in the panoramic image, texture-consistent teeth are closely pre-arranged in related to the integration of fixed front background relationship and certain spatial structure characteristics. Stomatologist is still required to judge the abnormal condition of wisdom teeth in terms of mutual relationship between the spatial position and tooth interaction, and discrimination process of this relationship can be concerned and modeled in terms of visual task-relevant spatial attention mechanism. Specifically, the attention mechanism is beneficial to suppress redundant channels or pixels to a certain extent. It can be melted into the trunk neural network as a plug-in module, or attached to the top of the trunk to extract high-level semantic relations, for which the bottom layer of convolution features can be preserved.MethodThe convolution property of neural network is analyzed, and the attention-specific inner convolution operator to the spatial element information can be used optimally. It is melted into you only look once (YOLO) target detection model to improve the performance and reduce the parameters on the premise of ensuring the advantages of YOLO itself. A YOLO-based panoramic wisdom tooth detection scheme is proposed as well. The main contributions are listed as follows: 1) an improved cross stage partial (CSP) structure (invoCSP) is proposed, which can optimize the integration of CSP structure and revolution operator, and the YOLO model is introduced derived from its stacking and the related revolution operator. The contextual information can be summarized in a wider spatial range, and different area-oriented weight can be adaptively balanced and allocated in the feature map as well. Finally, spatial modeling ability is improved to fully extract the spatial structure information on the data set; 2) we analyze the defect of task coupling in the YOLO model, excavate the potential properties of the involution operator, and summarize the external conditions. To fully decompose and decouple the three specific tasks of the two properties of target detection, a three-branch decoupling structure is constructed in the detection head structure. The applicability of the YOLO model can be improved further. This scheme can be used to alleviate its training process and non-convergence problem of the involution method; 3) three branch detection head can avoid sharing weight parameters further for independent optimization. The modified loss function can be used to optimize the tasks on different branches, introduce focal-loss to the confidence loss, and a newly intersection of union (IoU)-loss is applied to the boundary regression of the prediction frame and an advanced classification loss.ResultTo realize the classification and labeling of mandibular wisdom teeth, a newly panoramic film data set is developed for the winter classification method, which is commonly-used in the diagnosis and treatment of wisdom teeth in oral clinic. It can be randomly disturbed after histogram equalization. Three stomatologists focus on labeling the mandibular wisdom teeth independently for many times under the circumstances of unified diagnostic criteria and labeling rules, and a total of 973 consistent data can be reached. Finally, the panoramic wisdom tooth data set-constructed experimental results demonstrate its potentials for single-stage target detection model in terms of the detection performance and model parameters. Compared to the benched model of YOLOX-tiny, the parameter is lower by 42.5% and the mAP_50 index is higher by 6.3 percentage points. In addition, comparative analysis is carried out with nine sort of popular single-stage target detection models as well. The performance of the yooid model is beneficial for same parameter quantity-related optimization. It can not only identify wisdom tooth types accurately, but also return to the prediction frame stably with high IoU and closer to the real label. It is comparable to the detection performance of large model in terms of constraints of smaller parameters, and the highest mAP_50 index can be even achieved.ConclusionTo deal with the problem of panorama-based wisdom tooth detection, the convolution property is analyzed in the neural network. The involution operator is adopted, in which specific attention is added to the spatial element information of additional network structure excluded, and it is introduced into the YOLO target detection model feasibly. The performance is improved and the parameters can be reduced on the premise of ensuring the advantages of YOLO. A panoramic wisdom tooth detection network model is facilitated based on involution decoupling. Through the comparison of qualitative and quantitative experiments, it is verified that the proposed model can effectively detect the constructed target object, and the rationality of the design idea of the model can be improved as well. Furthermore, it demonstrates that the decoupled structure can fit the design of involution. We sort the relationship between involution and coupling out, and a multiple-branch decoupled structure can be used to improve the YOLO model-oriented adaptability of involution operator further. The parameters of this model are reduced greatly beyond high efficiency of performance, which is suitable for the application environment of real-time detection. It is predicted that this method proposed is beneficial to realize lightweight application level deployment in preliminary screening and objective reference for Stomatology further.关键词:panoramic radiograph;wisdom tooth;target detection;you only look once (YOLO);decoupling;involution92|297|0更新时间:2024-05-07
Medical Image Processing
-
 摘要:ObjectiveSpectrometers-based hyperspectral imaging technique is focused on multi-spectral bands data collection in the same region, e.g., ranging from 400 nm to 2 500 nm. Targets information is beneficial from both spectral and spatial information in terms of spectral bands-derived multiple and consistent features. Compared to such standardized RGB image, hyperspectral image (HSI) is capable for some image-contexual applications like remote sensing, food safety and medical diagnosis. However, due to thermal electronics, dark current, and random error of light count are challenged to be resolved for image processing, the obtained HSI is inevitably affected by such severe noise, including Gaussian noise, impulse noise, dead lines and stripes. It will definitely degrade image quality and hinder its subsequent applications. As a result, HSI-derived noise removal has emerged and developed to deal with that. Currrent HSI denoising algorithms can be segmented into two categories: one category is concerned about data-driven contexts and the other one is focused on model-driven contexts. Data-driven deep learning technique is beneficial for HSI denoising. For model-based aspect, low-rank approximation performs well without training. Low-rank based denoising methods can be divided into matrix- and tensor-based contexts. The matrix-based denoising methods can be used to unfold the three-dimensional tensor into a matrix or treat each band solely. These two-dimensional denoising algorithms are challenged to achieve optimal results since the joint spatial-spectral information of HSI is distorted partially. To resolve this problem, the low-rank tensor recovery uses both the spectral and spatial information of the HSI, and it can achieve better results than the low rank matrix recovery methods to some extent. However, existing tensor-based methods like CP-based or Tucker-based ones are used to treat HSI as a 3rd-order image only, and image-prior information is required to be taken into account for processing. Actually, the HSI has its own prior information beyond image attributes. For example, spectral vectors are linked to a low-dimensional linear subspace in this manner and its corresponding coefficient matrix has a low rank structure.MethodWe develop an orthogonal vectors-based structural low rank matrix-vector tensor factorization (MVTF). It decouples an HSI into a sum of outer matrix-vector products, where the vectors are orthogonal bases and matrices are the corresponding coefficients, called eigen-images. Due to the low-rank structure of eigen-images is existed, nuclear norm minimization operators are penertrated into the matrices straighforward, and the global spatial-spectral information of HSI can be well extracted. Additionally, the anisotropic total variation is used for spatial piecewise smoothness farther. Furthermore, sparse noise is composed of impulse noise, dead lines and stripes, and it is detected by the
摘要:ObjectiveSpectrometers-based hyperspectral imaging technique is focused on multi-spectral bands data collection in the same region, e.g., ranging from 400 nm to 2 500 nm. Targets information is beneficial from both spectral and spatial information in terms of spectral bands-derived multiple and consistent features. Compared to such standardized RGB image, hyperspectral image (HSI) is capable for some image-contexual applications like remote sensing, food safety and medical diagnosis. However, due to thermal electronics, dark current, and random error of light count are challenged to be resolved for image processing, the obtained HSI is inevitably affected by such severe noise, including Gaussian noise, impulse noise, dead lines and stripes. It will definitely degrade image quality and hinder its subsequent applications. As a result, HSI-derived noise removal has emerged and developed to deal with that. Currrent HSI denoising algorithms can be segmented into two categories: one category is concerned about data-driven contexts and the other one is focused on model-driven contexts. Data-driven deep learning technique is beneficial for HSI denoising. For model-based aspect, low-rank approximation performs well without training. Low-rank based denoising methods can be divided into matrix- and tensor-based contexts. The matrix-based denoising methods can be used to unfold the three-dimensional tensor into a matrix or treat each band solely. These two-dimensional denoising algorithms are challenged to achieve optimal results since the joint spatial-spectral information of HSI is distorted partially. To resolve this problem, the low-rank tensor recovery uses both the spectral and spatial information of the HSI, and it can achieve better results than the low rank matrix recovery methods to some extent. However, existing tensor-based methods like CP-based or Tucker-based ones are used to treat HSI as a 3rd-order image only, and image-prior information is required to be taken into account for processing. Actually, the HSI has its own prior information beyond image attributes. For example, spectral vectors are linked to a low-dimensional linear subspace in this manner and its corresponding coefficient matrix has a low rank structure.MethodWe develop an orthogonal vectors-based structural low rank matrix-vector tensor factorization (MVTF). It decouples an HSI into a sum of outer matrix-vector products, where the vectors are orthogonal bases and matrices are the corresponding coefficients, called eigen-images. Due to the low-rank structure of eigen-images is existed, nuclear norm minimization operators are penertrated into the matrices straighforward, and the global spatial-spectral information of HSI can be well extracted. Additionally, the anisotropic total variation is used for spatial piecewise smoothness farther. Furthermore, sparse noise is composed of impulse noise, dead lines and stripes, and it is detected by the -
 摘要:ObjectiveA tropical cyclone can generate such severe weather condition like strong winds or heavy precipitation, as well as such secondary disasters derived of floods, landslides, and mudslides. Tropical cyclones may often threaten survival contexts in related to coastal community. The intensity of tropical cyclones (TC) can be estimated accurately and it is beneficial for weather forecasting and warning. Deep learning techniques-based convolutional neural networks (CNNs) methods have its optimal ability for estimation task of tropical cyclone intensity apparently. However, CNN-based methods are still challenging for such problem of insufficient use of multi-channel satellite images, and the input images are preferred to be centered on the location of tropical cyclones. To resolve large estimation errors and real-time estimation results. we develop a network called intensity-estimation-fusing-location (IEFL) to improve accuracy of intensity estimation further.MethodThe training data is captured from Himawari-8 satellite images from 2015 to 2018 in comparason with such data contexts from 2019 to 2020. The dataset contains 42 028 training images and 5 229 testing images. First, the data are preprocessed to remove non-TC cloud systems via clipping satellite images. Then, the implementation of data augmentation strategy is oriented to optimize the over-fitting problem and enhance the model robustness. Moreover, multiple channel images analysis is required to reveal varied features of TCs. Thus, a better combination for intensity estimation can be developed through fusing multi-channel images. The network is set up via a two-branch structure, which can be used to fuse different channel images effectively. Two sort of tasks can be optimized simultaneously and learnt mutually. In addition, the network can feed location task-extracted features into intensity estimation task. Specifically, their feature maps can be concatenated and intensity estimation results are generated as following. The experiment is segmented into two categories as mentioned below: for the first category, it is focused on intensity estimation model only, and different channels-related location information fusion results can be used to analyze the location information-fused impact in relevance to intensity estimation. For the second one, multi-channel integration is selected for the model with location information to analyze the integrated effect of different channel for intensity estimation. The IEFL network is configurable on the Pytorch toolbox. The input images are resized to 512 × 512 pixels for training, the momentum parameter is set to 0.9, the learning rate is set to 0.001, the batch size is set to 5, and the weight decay is 10-4. The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) learning procedure is optimized using an NVIDIA GTX TITAN XP device. The loss function of intensity estimation regression is root mean square error (RMSE). The RMSE can be used to measure the difference between the ground truth and predictable values of tropical cyclone intensity. The smaller the RMSE, the better the performance of the model. Furthermore, the loss function of location regression is recognized as the RMSE as well. Therefore, the total loss function of the model can be set as the sum of the intensity loss and location loss. The main contributions are listed below: 1) develop a location information-fused model to estimate tropical cyclone intensity and location, called intensity-estimation-fusing-location(IEFL); 2) validate the intensities of tropical cyclones using different channel images captured from the Himawari-8 satellite, and 3) analyze the intensity estimation performance of each channel and the integrated effect of different channel.ResultThe non-location information-relevant intensity of root mean square error (RMSE) is 5.08 m/s, in which the location information-relevant intensity of RMSE is 4.74 m/s. Compared to the network without the location task, the RMSE values are reduced by 7%. The error-related comparative analyses are carried out between the IEFL model and other six related methods. Compared to the traditional method deviation angle variance technique (DAVT), it is increased by about 27%. Compared to the CNN-based methods, it is 11% higher than convolutional neural network-tropical cyclone (CNN-TC), 8% higher than tropical cyclone intensity estimation net (TCIENet), as well as 4% higher than tropical cyclone intensity classification and estimation net (TCICENet).Conclusionwe develop the IEFL model to estimate intensity in terms of location information fusion. This IEFL is focused on improving the accuracy of intensity estimation beyond location accuracy. The experiment result shows that location information-fused model has its optimal potentials farther.关键词:intensity estimation;tropical cyclone (TC);convolutional neural network (CNN);center location;Himawari-892|226|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveA tropical cyclone can generate such severe weather condition like strong winds or heavy precipitation, as well as such secondary disasters derived of floods, landslides, and mudslides. Tropical cyclones may often threaten survival contexts in related to coastal community. The intensity of tropical cyclones (TC) can be estimated accurately and it is beneficial for weather forecasting and warning. Deep learning techniques-based convolutional neural networks (CNNs) methods have its optimal ability for estimation task of tropical cyclone intensity apparently. However, CNN-based methods are still challenging for such problem of insufficient use of multi-channel satellite images, and the input images are preferred to be centered on the location of tropical cyclones. To resolve large estimation errors and real-time estimation results. we develop a network called intensity-estimation-fusing-location (IEFL) to improve accuracy of intensity estimation further.MethodThe training data is captured from Himawari-8 satellite images from 2015 to 2018 in comparason with such data contexts from 2019 to 2020. The dataset contains 42 028 training images and 5 229 testing images. First, the data are preprocessed to remove non-TC cloud systems via clipping satellite images. Then, the implementation of data augmentation strategy is oriented to optimize the over-fitting problem and enhance the model robustness. Moreover, multiple channel images analysis is required to reveal varied features of TCs. Thus, a better combination for intensity estimation can be developed through fusing multi-channel images. The network is set up via a two-branch structure, which can be used to fuse different channel images effectively. Two sort of tasks can be optimized simultaneously and learnt mutually. In addition, the network can feed location task-extracted features into intensity estimation task. Specifically, their feature maps can be concatenated and intensity estimation results are generated as following. The experiment is segmented into two categories as mentioned below: for the first category, it is focused on intensity estimation model only, and different channels-related location information fusion results can be used to analyze the location information-fused impact in relevance to intensity estimation. For the second one, multi-channel integration is selected for the model with location information to analyze the integrated effect of different channel for intensity estimation. The IEFL network is configurable on the Pytorch toolbox. The input images are resized to 512 × 512 pixels for training, the momentum parameter is set to 0.9, the learning rate is set to 0.001, the batch size is set to 5, and the weight decay is 10-4. The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) learning procedure is optimized using an NVIDIA GTX TITAN XP device. The loss function of intensity estimation regression is root mean square error (RMSE). The RMSE can be used to measure the difference between the ground truth and predictable values of tropical cyclone intensity. The smaller the RMSE, the better the performance of the model. Furthermore, the loss function of location regression is recognized as the RMSE as well. Therefore, the total loss function of the model can be set as the sum of the intensity loss and location loss. The main contributions are listed below: 1) develop a location information-fused model to estimate tropical cyclone intensity and location, called intensity-estimation-fusing-location(IEFL); 2) validate the intensities of tropical cyclones using different channel images captured from the Himawari-8 satellite, and 3) analyze the intensity estimation performance of each channel and the integrated effect of different channel.ResultThe non-location information-relevant intensity of root mean square error (RMSE) is 5.08 m/s, in which the location information-relevant intensity of RMSE is 4.74 m/s. Compared to the network without the location task, the RMSE values are reduced by 7%. The error-related comparative analyses are carried out between the IEFL model and other six related methods. Compared to the traditional method deviation angle variance technique (DAVT), it is increased by about 27%. Compared to the CNN-based methods, it is 11% higher than convolutional neural network-tropical cyclone (CNN-TC), 8% higher than tropical cyclone intensity estimation net (TCIENet), as well as 4% higher than tropical cyclone intensity classification and estimation net (TCICENet).Conclusionwe develop the IEFL model to estimate intensity in terms of location information fusion. This IEFL is focused on improving the accuracy of intensity estimation beyond location accuracy. The experiment result shows that location information-fused model has its optimal potentials farther.关键词:intensity estimation;tropical cyclone (TC);convolutional neural network (CNN);center location;Himawari-892|226|0更新时间:2024-05-07
Remote Sensing Image Processing
-
 摘要:ObjectiveThe artificial intelligence (AI) technology based intelligent unmanned equipments like unmanned surface vehicles have been developing for such domains of marine technology-derived military operation and counter-terrorism, resource exploration, seabed topography mapping, water quality testing, and marine search and rescue. In recent years, such issues of unmanned surface vehicles-related path planning have been concerned about. However, existing tasks are still focused on the path planning of single unmanned surface vehicle. The methods and simulations are only based on narrowed water areas like lakes and ports, and the problem of energy constraint is required to be melted into as well. For large-scale sea patrol scenarios, multi-unmanned surface vehicles can be incorporated into coverage path planning tasks in terms of quick response-relevant fast speed, high efficiency and low risk. However, small unmanned surface vessels for sea patrol are mainly driven electrically. Their navigating range and operating time are limited. It is necessary to divide the large-scale sea patrol task into multiple tasks and the problem of energy constraint is required to be resolved for unmanned surface ships. Therefore, we develop a solution of area coverage path planning based on multiple unmanned surface vehicles-integrated large-scale sea patrol tasks.MethodFirst, we define and model the problem of sea patrol of multi-unmanned surface vehicles, a task-equal region division strategy and multiple evaluation criteria are proposed and implemented through constructing the sea grid map. The task-equal region division strategy can make all unmanned surface vehicles get similar size of task area and ensure that the full task can be completed to reach the minimum total time. Second, we analyse and compare several traditional traversal algorithms, including round-trip traversal algorithm or spiral traversal algorithm. The breadth-first search algorithm is combined with these traversal algorithms to perform the area coverage path planning task. We demonstrate two sort of traversal algorithms under two different conditions, that is, energy constraint is included or excluded. Especially, two energy constraint-derived charging path planning strategies are taken into account, including the original route or a new route after charging. Intuitively, the advantage of the former is a kind of decoupling path planning in terms of energy supply, while the limition is linked with the duplication of charging path. The redundancy is derived of repetition rate and wastes part of energy. The pros of the latter is concerned that the charging route is not traversed again, while the cons is that complexity of the task map can be increased due to redundant routes. It may cause more energy supply.ResultA Python-related simulation platform is built up based on the sea map of more than 15 000 square kilometers around Sansha city of China. Specifically, such configurable settings are listed: the physics simulation engine is Pymunk, the rendering tool is Pygame, and the numerical calculation tool is Numpy. We carry our three sorts of key experiments and get some following results. 1) The advantages and disadvantages of different traversal algorithms are analysed and compared under the conditions of energy constraints-included or excluded. In detail, we adopt breadth-first search algorithm in related to round-trip traversal algorithm or spiral traversal algorithm. For non-energy constraint, round-trip coverage method is generally better than spiral coverage method. It means that the repetition rate, the total number of steps and the total time of the round-trip traversal algorithm are lower than spiral algorithm under the same circumstances. 2) The effectiveness of the proposed task-equal region division strategy is validated. For example, under the setting of five unmanned ships for operation, the coverage rates of the coveraged areas are 20.8%, 20.4%, 20%, 19.8% and 19.0% in the total area. Similar sized task areas can ensure consistent task time for different ships to minimize total task time. 3) Compared to non-energy constraints, energy constraint-related setting is challenged much more, and the energy constraint-relevant setting can illustrate higher repetition rate, total steps and total time on the basis of the same number of unmanned ships and the same traversal algorithm. Energy constraint can be used to validate the potentials of routes replanning after charging beyond the original path after charging. Furthermore, ablation experiments are carried out in relevance to parameters-based number of ships, coverage rate and battery range of the unmanned ship. Ablation experimental results demonstrate that: 1) Increasing the number of unmanned ships will significantly reduce the total time to complete the task. There is an inverse relationship between the number of unmanned ships and the total task time. In practice, the increasment of the number of unmanned vessels can be as the most effective scheme to improve the efficiency within the range of purchase cost. 2) Appropriate reduction of the coverage requirement can reduce the repetition rate and the total task time. Actually, you can compensate the reduced coverage requirements to perform multiple tasks through changing the starting point. 3) Battery range of unmanned ships can be increased to improve task efficiency dramatically.ConclusionA solution of area coverage path planning is developed based on multiple unmanned surface vehicles cooperation for large-scale sea patrol tasks. The solution can deal with the problems of task division and energy supply of multiple unmanned surface vehicles, and be viewed as a certain reference for the practical application of multi-unmanned surface vehicles performing large-scale sea patrol tasks. Next, we will further study the relationship between charging equipment deployment strategy and algorithm efficiency in real sea environment, consider the problem of sudden collision avoidance during the navigation of unmanned ships, and expand the application scope of the proposed method, such as the seabed three-dimensional detection task.关键词:sea patrol;unmanned surface vehicle;area coverage path planning;energy constraint;simulation188|176|1更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveThe artificial intelligence (AI) technology based intelligent unmanned equipments like unmanned surface vehicles have been developing for such domains of marine technology-derived military operation and counter-terrorism, resource exploration, seabed topography mapping, water quality testing, and marine search and rescue. In recent years, such issues of unmanned surface vehicles-related path planning have been concerned about. However, existing tasks are still focused on the path planning of single unmanned surface vehicle. The methods and simulations are only based on narrowed water areas like lakes and ports, and the problem of energy constraint is required to be melted into as well. For large-scale sea patrol scenarios, multi-unmanned surface vehicles can be incorporated into coverage path planning tasks in terms of quick response-relevant fast speed, high efficiency and low risk. However, small unmanned surface vessels for sea patrol are mainly driven electrically. Their navigating range and operating time are limited. It is necessary to divide the large-scale sea patrol task into multiple tasks and the problem of energy constraint is required to be resolved for unmanned surface ships. Therefore, we develop a solution of area coverage path planning based on multiple unmanned surface vehicles-integrated large-scale sea patrol tasks.MethodFirst, we define and model the problem of sea patrol of multi-unmanned surface vehicles, a task-equal region division strategy and multiple evaluation criteria are proposed and implemented through constructing the sea grid map. The task-equal region division strategy can make all unmanned surface vehicles get similar size of task area and ensure that the full task can be completed to reach the minimum total time. Second, we analyse and compare several traditional traversal algorithms, including round-trip traversal algorithm or spiral traversal algorithm. The breadth-first search algorithm is combined with these traversal algorithms to perform the area coverage path planning task. We demonstrate two sort of traversal algorithms under two different conditions, that is, energy constraint is included or excluded. Especially, two energy constraint-derived charging path planning strategies are taken into account, including the original route or a new route after charging. Intuitively, the advantage of the former is a kind of decoupling path planning in terms of energy supply, while the limition is linked with the duplication of charging path. The redundancy is derived of repetition rate and wastes part of energy. The pros of the latter is concerned that the charging route is not traversed again, while the cons is that complexity of the task map can be increased due to redundant routes. It may cause more energy supply.ResultA Python-related simulation platform is built up based on the sea map of more than 15 000 square kilometers around Sansha city of China. Specifically, such configurable settings are listed: the physics simulation engine is Pymunk, the rendering tool is Pygame, and the numerical calculation tool is Numpy. We carry our three sorts of key experiments and get some following results. 1) The advantages and disadvantages of different traversal algorithms are analysed and compared under the conditions of energy constraints-included or excluded. In detail, we adopt breadth-first search algorithm in related to round-trip traversal algorithm or spiral traversal algorithm. For non-energy constraint, round-trip coverage method is generally better than spiral coverage method. It means that the repetition rate, the total number of steps and the total time of the round-trip traversal algorithm are lower than spiral algorithm under the same circumstances. 2) The effectiveness of the proposed task-equal region division strategy is validated. For example, under the setting of five unmanned ships for operation, the coverage rates of the coveraged areas are 20.8%, 20.4%, 20%, 19.8% and 19.0% in the total area. Similar sized task areas can ensure consistent task time for different ships to minimize total task time. 3) Compared to non-energy constraints, energy constraint-related setting is challenged much more, and the energy constraint-relevant setting can illustrate higher repetition rate, total steps and total time on the basis of the same number of unmanned ships and the same traversal algorithm. Energy constraint can be used to validate the potentials of routes replanning after charging beyond the original path after charging. Furthermore, ablation experiments are carried out in relevance to parameters-based number of ships, coverage rate and battery range of the unmanned ship. Ablation experimental results demonstrate that: 1) Increasing the number of unmanned ships will significantly reduce the total time to complete the task. There is an inverse relationship between the number of unmanned ships and the total task time. In practice, the increasment of the number of unmanned vessels can be as the most effective scheme to improve the efficiency within the range of purchase cost. 2) Appropriate reduction of the coverage requirement can reduce the repetition rate and the total task time. Actually, you can compensate the reduced coverage requirements to perform multiple tasks through changing the starting point. 3) Battery range of unmanned ships can be increased to improve task efficiency dramatically.ConclusionA solution of area coverage path planning is developed based on multiple unmanned surface vehicles cooperation for large-scale sea patrol tasks. The solution can deal with the problems of task division and energy supply of multiple unmanned surface vehicles, and be viewed as a certain reference for the practical application of multi-unmanned surface vehicles performing large-scale sea patrol tasks. Next, we will further study the relationship between charging equipment deployment strategy and algorithm efficiency in real sea environment, consider the problem of sudden collision avoidance during the navigation of unmanned ships, and expand the application scope of the proposed method, such as the seabed three-dimensional detection task.关键词:sea patrol;unmanned surface vehicle;area coverage path planning;energy constraint;simulation188|176|1更新时间:2024-05-07 -
 摘要:ObjectiveThe study of bird satellite tracking data has positive implications for the conservation of both the birds themselves and the ecological environment. To effectively conserve bird species and to better understand their habitat suitability, it is necessary to study the spatial and temporal characteristics of bird populations. It is essential for recognizing the dominants of species distribution and their dynamics and its relevant conservation. The development of satellite tracking technology can be used to improve the ability of ornithologists to remotely collect large amounts of track movement data for birds, and global positioning system(GPS)-based track migration data is one of commonly-used collected types of data today. Analysis of acquired satellite track data can help solve many problems, such as how individual birds interact with each other, the foraging strategies, migration and movement routes of individuals in different time dimensions, and the effects of environmental changes due to climate and human factors. With recent technological advances, the frequency of positioning satellite transmitters and the variety of data collected have increased greatly, and a major challenge that has arisen is how to adequately and effectively analyze these large data. Ornithologists use existing data analysis methods to analyze data using Excel or R libraries, or plotting data points on satellite maps directly. Data visualization and visual analysis techniques, as a way to present large amounts of data, can yield users to gain better understanding and insight into datasets, providing them with an emerging tool, which can uncover complex patterns contained in the data and inspire new hypotheses and analyses.MethodNipponia nippon is a world-endangered species and a national class I key protected animal, mainly distributed in the Hanzhong Nipponia Nippon National Nature Reserve and surrounding counties in Shaanxi. With continuous conservation efforts, the wild population of Nipponia nippon has steadily increased in recent years, and its distribution has spread to the periphery of the reserve further. In order to follow the trend of the spreading activities of the Nipponia nippon and its adaptation to the contextual of the reserve, bird-related expertise has conducted a satellite tracking study of the Nipponia nippon from 2013—2019. The transmitter accounts for about 1.5% of the Nipponia nippon’s body weight and is worn on its back to receive information on its activity loci and status at regular intervals. Based on the satellite tracking data of Nipponia nippon, as a national class I key protected species, we develop an in-depth demand analysis of the visualization and visual analysis of tracking data based on the needs of ornithologists for data analysis and around the concerns of ornithologists for Nipponia nippon. The distribution and changes of foraging and nocturnal sites of Nipponia nippon are as an important basis for analyzing its living environment and living condition; the changes of daily foraging movement and the distance of foraging movement of Nipponia nippon can reflect the ease of access to food and the activity level of individuals of Nipponia nippon on that day, and thus we investigate the visual analysis method in detail. Furthermore, we propose a visual analysis method of movement trajectory through the interactive layout of multi-view collaborative display based on 2D map and visual analysis of the cluster analysis-based movement trajectory of Nipponia nippon. Correlative ornithologists can observe and explore the tracking data of one or more Nipponia nippon, and the influence of individual living states, behavioral characteristics, living environment conditions of Nipponia nippon can be explored, and the differences among individuals to facilitate corresponding conservation measures. In addition, due to the problems of sensing equipment and communication conditions, some of Nipponia nippon-related data collected by the transmitter are missing for satellite tracking data, and the missing data are random in terms of period length and distribution. This affects the analysis and mining of the data inevitably, and it is not conducive to the exploration of the life habits of Nipponia nippon by experts. Therefore, we interpolate the missing data in the Nipponia nippon tracking dataset based on long short-term memory(LSTM) deep learning method.ResultA visual analysis system for the movement of Nipponia nippon is designed and implemented. Based on the visual analysis method proposed, users are able to observe the movement trajectory of Nipponia nippon from multiple dimensions spatiotemporally, and the night-time and foraging sites are analyzed for Nipponia nippon in related to its dimensions with different ecological significance, and daily foraging activity distance indexes of interest is analyzed and revealed their changes over time. Compared with the existing data analysis methods for Nipponia nippon, the visual analysis method proposed can be used to analyze the dynamic data from several different dimensions at the same time, and more in-depth analysis and mining are conducted for the living condition and habits of Nipponia nippon.ConclusionThe case study shows that based on the method proposed, ornithologists can analyze Nipponia nippon movement track data comprehensively from multiple perspectives. The system is oriented to a visual analysis system for comprehensive analysis of Nipponia nippon tracking data, which can meet the requirements for analysis of Nipponia nippon movement trajectories and an effective method is offered for research utilization of tracking data. Its potentials can be implicated for other related flying bird tracking data.关键词:satellite tracking;visual analysis;multi-view collaboration;cluster analysis;time-series data interpolation136|244|0更新时间:2024-05-07
摘要:ObjectiveThe study of bird satellite tracking data has positive implications for the conservation of both the birds themselves and the ecological environment. To effectively conserve bird species and to better understand their habitat suitability, it is necessary to study the spatial and temporal characteristics of bird populations. It is essential for recognizing the dominants of species distribution and their dynamics and its relevant conservation. The development of satellite tracking technology can be used to improve the ability of ornithologists to remotely collect large amounts of track movement data for birds, and global positioning system(GPS)-based track migration data is one of commonly-used collected types of data today. Analysis of acquired satellite track data can help solve many problems, such as how individual birds interact with each other, the foraging strategies, migration and movement routes of individuals in different time dimensions, and the effects of environmental changes due to climate and human factors. With recent technological advances, the frequency of positioning satellite transmitters and the variety of data collected have increased greatly, and a major challenge that has arisen is how to adequately and effectively analyze these large data. Ornithologists use existing data analysis methods to analyze data using Excel or R libraries, or plotting data points on satellite maps directly. Data visualization and visual analysis techniques, as a way to present large amounts of data, can yield users to gain better understanding and insight into datasets, providing them with an emerging tool, which can uncover complex patterns contained in the data and inspire new hypotheses and analyses.MethodNipponia nippon is a world-endangered species and a national class I key protected animal, mainly distributed in the Hanzhong Nipponia Nippon National Nature Reserve and surrounding counties in Shaanxi. With continuous conservation efforts, the wild population of Nipponia nippon has steadily increased in recent years, and its distribution has spread to the periphery of the reserve further. In order to follow the trend of the spreading activities of the Nipponia nippon and its adaptation to the contextual of the reserve, bird-related expertise has conducted a satellite tracking study of the Nipponia nippon from 2013—2019. The transmitter accounts for about 1.5% of the Nipponia nippon’s body weight and is worn on its back to receive information on its activity loci and status at regular intervals. Based on the satellite tracking data of Nipponia nippon, as a national class I key protected species, we develop an in-depth demand analysis of the visualization and visual analysis of tracking data based on the needs of ornithologists for data analysis and around the concerns of ornithologists for Nipponia nippon. The distribution and changes of foraging and nocturnal sites of Nipponia nippon are as an important basis for analyzing its living environment and living condition; the changes of daily foraging movement and the distance of foraging movement of Nipponia nippon can reflect the ease of access to food and the activity level of individuals of Nipponia nippon on that day, and thus we investigate the visual analysis method in detail. Furthermore, we propose a visual analysis method of movement trajectory through the interactive layout of multi-view collaborative display based on 2D map and visual analysis of the cluster analysis-based movement trajectory of Nipponia nippon. Correlative ornithologists can observe and explore the tracking data of one or more Nipponia nippon, and the influence of individual living states, behavioral characteristics, living environment conditions of Nipponia nippon can be explored, and the differences among individuals to facilitate corresponding conservation measures. In addition, due to the problems of sensing equipment and communication conditions, some of Nipponia nippon-related data collected by the transmitter are missing for satellite tracking data, and the missing data are random in terms of period length and distribution. This affects the analysis and mining of the data inevitably, and it is not conducive to the exploration of the life habits of Nipponia nippon by experts. Therefore, we interpolate the missing data in the Nipponia nippon tracking dataset based on long short-term memory(LSTM) deep learning method.ResultA visual analysis system for the movement of Nipponia nippon is designed and implemented. Based on the visual analysis method proposed, users are able to observe the movement trajectory of Nipponia nippon from multiple dimensions spatiotemporally, and the night-time and foraging sites are analyzed for Nipponia nippon in related to its dimensions with different ecological significance, and daily foraging activity distance indexes of interest is analyzed and revealed their changes over time. Compared with the existing data analysis methods for Nipponia nippon, the visual analysis method proposed can be used to analyze the dynamic data from several different dimensions at the same time, and more in-depth analysis and mining are conducted for the living condition and habits of Nipponia nippon.ConclusionThe case study shows that based on the method proposed, ornithologists can analyze Nipponia nippon movement track data comprehensively from multiple perspectives. The system is oriented to a visual analysis system for comprehensive analysis of Nipponia nippon tracking data, which can meet the requirements for analysis of Nipponia nippon movement trajectories and an effective method is offered for research utilization of tracking data. Its potentials can be implicated for other related flying bird tracking data.关键词:satellite tracking;visual analysis;multi-view collaboration;cluster analysis;time-series data interpolation136|244|0更新时间:2024-05-07
Geoinformatics
0

